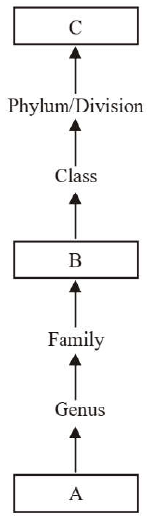
Q1: Consider following diagram and fill the following blank spaces/boxes.
 (a) A-Strain, B-Order, C-Sub kingdom
(a) A-Strain, B-Order, C-Sub kingdom
(b) A-Species, B-Order, C-Kingdom
(c) A-Subspecies, B-Tribe, C-Domain
(d) A-Species, B-Cohort, C-Subdivision
Ans: (b)
There are 7 obligate hierarchial levels of taxonomic categories. These started from species, which is the unit/basis of taxonomical studies. It constitute the group of interbreeding organisms. This is natural unit of taxonomical group. Group of families with more or less similar characteristics called order. The upppermost category in which Divisions/Phylum present called Kingdom. It form the uppermost category of hierarchial system in taxonomical studies.
Q2: Identify the correct sequence of taxonomic categories.
(a) Species → Genus → Order → Class → Family → Phylum/Division → Kingdom
(b) Species → Genus → Family → Class → Phylum/ Division → Order → Kingdom
(c) Species → Family → Genus → Order → Class → Phylum/Division → Kingdom
(d) Species → Genus → Family → Order → Class → Phylum/Division → Kingdom
Ans: (d)
Species is the lowest category in basic taxonomic hierarchy and has the maximum common characterstics with other species under the same genus. The genus is an aggregate or a group of closely related species. Family is the group of closely related genera, and has less common characterstics than species or genus rank. Order is a higher taxon and is the assemblage of families having similar characterstics. Class is a group of related orders.
Phylum: The classes with similar features are grouped into phylum in animals and division in plants. The phyla are grouped into still broader categories, called kingdom.
Q3: Two plants can be conclusively said to belong to the same species if they
(a) Have same number of chromosomes.
(b) Can reproduce freely with each other and form seeds.
(c) Have more than 90 per cent similar genes.
(d) Look similar and possess identical secondary metabolites.
Ans: (b)
Two plants can be conclusively said to belong to the same species if they can reproduce freely with each other and form seeds. The formed seed must be viable. Two animals can be regarded as species when they can interbred each other and form fertile progency.
Q4: ‘Taxa’ differs from ‘taxon’ due to being
(a) A higher taxonomic category than taxon.
(b) Lower taxonomic category than taxon.
(c) The plural of taxon.
(d) The singular of taxon.
Ans: (c)
Taxa is a plural form of taxon. Taxon is a grouping of organisms of any level in hierarchial classification which is based on some common characteristics. It represents real biological objects placed in any category while category itself is an abstract term.
Q5: Taxonomic hierarchy refers to
(a) Step-wise arrangement of all categories for classification of plants and animals.
(b) A group of senior taxonomists who decide the nomenclature of plants and animals.
(c) A list of botanists or zoologists who have worked on taxonomy of a species or group.
(d) Classification of a species based on fossil record.
Ans: (a)
Taxonomical hierarchy (introduced by Linneaus) is arrangement of various taxonomic levels in the descending order, starting from kingdom upto species. The number of similar characters of categories decreases from lowest rank to highest rank i.e., from species to kingdom. There are 7 obligate categories which constitute taxonomical hierarchy. In addition to these obligate categories there are some optional categories are as follows. e.g., Tribe, subclass, superclass, etc.
Q6: Two animals which are the members of the same order must also be the members of the same __________.
(a) Class
(b) Family
(c) Genus
(d) Species
Ans: (a)
Class is a group of related orders.
Q7: Which of the following organisms has self-consciousness?
(a) All organisms
(b) Only Human
(c) All Plants
(d) All animals
Ans: (b)
All organisms therefore, are aware of their surroundings. However, human being is the only organism who is aware of himself, i.e., has selfconsciousness.
Q8: The disadvantage of using common names for species is that
(a) The names may change.
(b) One name does not apply universally.
(c) One species may have several common names and one common name may be applied to two species.
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
The disadvantage of using common name for species is that the names may change, one name does not apply universally, one species may have several common names and one common name may be applied to two species.
Q9: Which one of the following is included in taxonomy?
(a) Nomenclature
(b) Identification
(c) Classification
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
Characterisation, identification, classification and nomenclature are the processes that are basic to taxonomy.
Q10: As we go from species to kingdom in a taxonomic hierarchy, the number of common characteristics
(a) Will decrease
(b) Will increase
(c) Remain same
(d) May increase or decrease
Ans: (a)
All the members of a taxonomic category possess some similar characters which are different from those of others. The placement of individuals or organisms in species, genus, family, order, class and phylum are determined by their specific similar characters and relationships. Maximum similarity occurs in species which is also the lowest category in the hierarchy of categories. Similarity of characters decreases with the ascent in hierarchy.
Q11: Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct for metabolism?
(a) It is the sum total of all physical reactions taking place inside a living system.
(b) All plants, animals, fungi and microbes exhibit metabolism.
(c) Isolated metabolic reactions in-vitro are nonliving reactions.
(d) All of the above
Ans: (b)
Metabolism is defined as the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in our body. All plants, animals, fungi and microbes exhibit metabolism. Isolated metabolic reactions in vitro are not living things but are living reactions.
Q12: Which one of the following statements is correct about biodiversity?
(a) It is the occurrence of varied types of organisms on earth.
(b) Each different kind of plant, animal or organism represents a species.
(c) The number of species that are known and described range between 1.7–1.8 million.
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
Biodiversity is the term used to describe the variety of life found on Earth and all of the natural processes. This includes ecosystem, genetic and cultural diversity, and the connections between these and all species. The different aspects of biodiversity all have a very strong influence on each other.
Q13: Which of the following statements are not correct?
(i) Lower the taxon, more are the characteristics that the members within the taxon share.
(ii) Order is the assemblage of genera which exhibit a few similar characters.
(iii) Cat and dog are included in the same family Felidae.
(iv) Binomial nomenclature was introduced by Carolus Linnaeus.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Ans: (d)
Order being higher category is the assemblage of families which exhibit a few similar characteristic. Dog (Canis familaris) and Cat (Felis domesticus) belong to two different families—Canidae and Felidae respectively.
Q14: Growth and reproduction are mutually exclusive events in ________.
(a) All organisms
(b) Only in unicellular organisms
(c) Only in multicellular organisms
(d) All animates and inanimates
Ans: (c)
In majority of higher animals and plants, growth and reproduction are mutually exclusive events.
Q15: Which of the following statement(s) is/are not correct?
(i) Reproduction is the production of progeny possessing features dissimilar to their parents.
(ii) The fungi, the filamentous algae, the protonema of mosses, all multiply by budding.
(iii) Many organisms like mules, sterile worker bees do not reproduce.
(iv) Reproduction is not an all-inclusive defining characteristic of living organisms.
(a) Only (i)
(b) Both (i) and (ii)
(c) Both (ii) and (iv)
(d) All of these
Ans: (b)
Reproduction refers to the production of progeny possessing features more or less similar to those of parents. The fungi, the filamentous algae, the protonema of mosses, all easily multiply by fragmentation.
Q16: Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
(i) All living organisms have the ability to respond to environmental stimuli which could be physical, chemical, or biological.
(ii) Plants respond to external factors like light, water, temperature, other organisms, pollutants, etc.
(iii) Photoperiod affects the process of reproduction.
(iv) Human beings are the only organisms who have self-consciousness.
(a) Only (i)
(b) Both (ii) and (iii)
(c) Both (i) and (iv)
(d) All of these
Ans: (d)
All the given statements are correct. All living organisms have the ability to respond the environment stimuli which could be physical, chemical or biological. Plant responds to external factors like light, water, temperature etc.
Photoperiod is defined as the developmental responses of plants to the relative lengths of light and dark periods. It exclusively affects the reproduction in seasonal breeders, both plants and animals. Human being is the only organism who has self - consciousness.
Q17: Which of the following statement(s) is/are not correct?
(i) Genus comprises a group of related species which has more characters in common in comparison to species of other genera.
(ii) Three different genera such as Solanum, Datura, and Petunia are placed in the family Malvaceae.
(iii) In the case of plants, classes with a few similar characters are assigned to a higher category called phylum.
(a) Both (i) and (ii)
(b) Only (iii)
(c) Both (ii) and (iii)
(d) All of these
Ans: (c) Three different genera such as Solanum, Datura and Petunia are placed in the family solanaceae.
In case of plants, classes with a few similar characters are assigned to a higher category called division. Phylum is used in case of animals.
Q18: Which of the following is not true for living organisms?
(a) Cellular organisation
(b) Responding to external stimuli
(c) Absence of metabolism
(d) All of these
Ans: (c)
Some characteristics of living organisms are growth, reproduction, responsiveness to stimuli, and metabolism.
Q19: Which of the following statements regarding growth is incorrect?
(a) In animals, growth is seen up to a certain age.
(b) Increase in body mass is considered as growth.
(c) Growth by cell division occurs continuously throughout their life span in animals.
(d) Increase in mass and number of individuals is the characteristic feature of animal growth.
Ans: (c)
Growth may be defined as a positive change in size, often over a period of time. It can occur as a stage of maturation or a process toward fullness or fulfillment. Growth by cell division occurs continuously throughout their life span in plants.
Q20: Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) The scientific name for humans is Homo sapiens.
(b) Organisms placed in the same genus are least closely related.
(c) Moving from species to kingdom, more different species are included in each higher category.
(d) Species that are in the same genus share very specific characteristics.
Ans: (b)
Genus comprises a group of related species which has more characters in common in comparison to species of other genera.
Q21: Which of the following organisms do not reproduce?
(a) Mules
(b) Worker bees
(c) Infertile human couples
(d) All of these
Ans: (d)
A mule is sterile. Worker bees are sterile females. Infertile human couples cannot produce fertile offspring.
Q22: Statement I: Name of the author appears after the generic name and before the specific epithet and is written in an abbreviated form.
Statement II: In Mangifera indica Linn, Linn indicates that this species was first described by Linnaeus.
(a) Both statements are correct.
(b) Statement I is correct & II is incorrect.
(c) Statement I is incorrect & II is correct.
(d) Both statements are incorrect.
Ans: (c)
(I) Name of the author appears after the specific epithet, and is written in an abbreviated form.
Q23: The number of species that are known and described range between -
(a) 1.7 - 1.8 million
(b) 0.5 - 1.0 million
(c) 2.7 - 2.8 million
(d) 0.7 - 0.8 million
Ans: (a) Species refers to each different kind of plant, animal or organism in our surroundings.
Biodiversity is the total number and types of living organisms present on earth. The number of species range between 1.7 - 1.8 million.
Q24: The number and types of organisms present on earth is known as -
(a) Biodiversity
(b) Biomagnification
(c) Biome
(d) Biosphere
Ans: (a)
The number and types of organisms present on earth is known as biodiversity.
Q25: Assertion: Biology is the story of evolution of living organisms on earth.
Reason: All living organisms – present, past, and future are linked to one another by the sharing of the common genetic material, but to varying degrees.
(a) Assertion and reason both are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is wrong.
(d) Assertion and reason both are wrong.
Ans: (a)
All living organisms—present, past and future are linked to one another by the sharing of the common genetic material, but to varying degrees.
The genetic material of living organisms undergoes mutations and reshuffling of genes. This causes variations in the genetic material. Variations are so abundant that no two individuals of the same race are exactly similar.
Q26: _____ written at the end of the biological name, i.e., after the specific epithet and is written in an abbreviated form -
(a) Name of the place
(b) Name of the country
(c) Name of the author
(d) All of these
Ans: (c)
Name of the author appears after the specific epithet, i.e., at the end of the biological name, and is generally written in an abbreviated form, e.g., Mangifera indica Linn.
Q27: Assertion: Families are characterised on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species.
Reason: Three different genera Solanum, Petunia, and Datura are placed in the family Anacardiaceae.
(a) Assertion and reason both are true and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are true but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is wrong.
(d) Assertion and reason both are wrong.
Ans: (c)
Three different genera Solanum, Petunia and Datura are placed in the family Solanaceae.
Q28: Assertion: Genus Panthera, comprising lion, tiger, leopard, is put along with genus Felis in the family Felidae.
Reason: Families like Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae are included in the genera Solanum mainly based on the floral characters.
(a) Assertion and reason both are true and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are true but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is wrong.
(d) Assertion and reason both are wrong.
Ans: (c)
Plant families like Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae are included in the order Polymoniales mainly based on the floral characters.
Q29: The scientific name of dog is correctly written as -
(a) Canis Familiaris
(b) Canis familiaris
(c) Canis familiaris
(d) Canis Familiaris
Ans: (c)
The scientific name of dog is Canis familiaris.
Q30: In Chlamydomonas and Amoeba -
(a) Reproduction is synonymous with growth i.e., increase in number of cells.
(b) Multicellular organization may be formed.
(c) Growth does not occur by increase in mass.
(d) Growth does not occur by increase in mass but not by increase in number.
Ans: (a)
In unicellular organism like bacteria, algae (unicellular) and amoeba, reproduction involves increase in number of cells and thus, it is synonymous with growth.
Q31: Select the correctly written botanical/zoological name.
(a) Homo Sapiens
(b) Panthera tigris
(c) Pisum sativum
(d) Mangifera Indica
Ans: (b)
The scientific naming of an organism is termed binomial nomenclature. It was first given by Carl Linnaeus. In this system, the first section of the name indicates genus, and the second one indicating the species name. Genus name should always start with a capital letter and the species name should start with a small letter. In the biological name both the words, when handwritten are separately underlined or printed in italics.
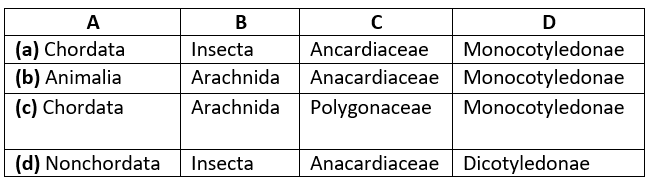
Q.32 Study the following table which shows different organisms with their taxonomic categories.

Select the correct option for A, B, C and D.
 Ans: (a)
Ans: (a)
Q33: Select the incorrect statement out of the following.
(a) All animals belonging to various phyla are assigned to the kingdom Animalia.
(b) As we go higher from species to kingdom, the number of common characteristics goes on increasing.
(c) Different classes comprising fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals together constitute the phylum Chordata.
(d) Plant order Polymoniales includes the families like Solanaceae and Convolvulaceae based on the vegetative and floral characters.
Ans: (b)
As we go higher from species to kingdom, the number of common characteristics goes on decreasing.
Q34: Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
(a) Only living organisms grow.
(b) Plants grow only up to a certain age.
(c) The growth in living organisms is from inside.
(d) All of the above.
Ans: (c)
Growth is the act or process, or a manner of growing; development; gradual increase. It is an exclusive event in majority of the higher animals and plants. In plants, growth occurs continuously throughout their life span and in animal, growth is seen only up to a certain age.
In living organisms, growth is from inside.
Therefore, it cannot be taken as a defining property of living organisms.
Q35: Growth in living organisms occurs by
(a) Division of cells.
(b) Increase in biomass.
(c) Accumulation of material by an external agency.
(d) Both (a) and (b).
Ans: (d)
Accumulation of material by external agency cause extrinsic growth which occurs in non living objects.
Q36: Non-living things -
(a) Show extrinsic growth
(b) Show extrinsic as well as intrinsic growth
(c) Can perform metabolism
(d) Show intrinsic growth
Ans: (a)
Non-living things show extrinsic growth.
Q37: Which two points are known as the twin characteristics of growth?
(i) Increase in mass
(ii) Differentiation
(iii) Increase in number
(iv) Response to stimuli
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Ans: (d)
Increase in mass and increase in number are twin characteristics of growth. Growth is defined as increase in size and mass during the development of an organism over a period of time. It is measured as an increase in biomass and is associated with cell division by mitosis, subsequent increases in cell size, and with the differentiation of cells to perform particular functions.
Q38: Which of the following statements regarding nomenclature is correct?
(a) Generic name always begins with a capital letter whereas specific name with a small letter.
(b) Scientific name should be printed in italics.
(c) Scientific name when typed or handwritten should be underlined.
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
All the statements regarding nomenclature are correct. Nomenclature is giving distinct scientific names to various structures including living organisms for their identification. It is a set of rules used for forming the names or terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. Nomenclature is only possible when the organism is described correctly and we know to what organisms the name is attached to (called identification).
Q39: Which of the following is an incorrect sequence?
(a) Tritium - Poaceae - Poales - Monocotyledonae
(b) Mangifera - Sapindanceae - Sapindales - Dicotyledonae
(c) Musca - Muscidae - Diptera - Insecta
(d) Homo - Hominidae - Primata - Mammalia
Ans: (b)
Q40: Which of the following statements regarding growth is incorrect?
(a) In plants, growth by cell division is seen only up to a certain stage.
(b) Growth exhibited by non-living objects is by accumulation of material on the surface.
(c) A multicellular organism grows by cell division.
(d) Growth in in-vitro culture of unicellular organisms can be observed by counting the number of cells.
Ans: (a)
In plants, growth by cell division occurs continuously throughout their life span.This continuos growth in plant is axial (i.e., takes place on two axes) and unique. Plant growth consists of primary and secondary growth, on the basis of time when it occurs.
Q41: Which of the following is not an advantage of taxonomy?
(a) Avoid confusion in the scientific community
(b) Provides a valid name of an organism
(c) Provides help in studying them
(d) Prevents loss of biodiversity
Ans: (d)
Taxonomy play no role in protection of biodiversity
Q42: If an organism is in the same class but not in the same family, then it may belong to the same
(a) Genus
(b) Species
(c) Variety
(d) Order
Ans: (d)
Order is a higher taxon and is the assemblage of families having similar characteristics. However, the common characteristic will be fewer than at family or genus level. In mammals the common orders are primates (monkey, gorilla and human), carnivora, rodentia and cetacea (whale and dolphin).
Q43: Which of the following characters given below displays the description of the lowest taxonomic category of organisms in the plant and animal kingdom?
(a) It includes one or more than one order.
(b) It is a group containing one or more families.
(c) It is a group of related organisms that resemble one another.
(d) It is a group of organisms that are closely related and share similar characteristics.
Ans: (d)
Species is the lowest category in taxonomic hierarchy. Species is a group of animals, plants or other living things that all share common characteristics and that are all classified as alike in some manner.
Q44: "X" being a higher category is the assemblage of families which exhibit a few "Y" characters. The "Z" characters are less in number as compared to different genera included in a family. Identify "X," "Y," and "Z."
(a) X - Order; Y - Similar; Z - Similar
(b) X - Genus; Y - Similar; Z - Different
(c) X - Species; Y - Different; Z - Similar
(d) X - Class; Y - Different; Z - Different
Ans: (a)
Order being a higher category is the assemblage of families which exhibit a few similar characters. The similar characters are less in number as compared to different genera included in a family.
Q45: Which of the following represents the correct binomial name of wheat?
(a) Triticum aetivum Linn
(b) Triticum aestivum Linn
(c) Triticum aestivum Linn
(d) Triticum aestivum Linn
Ans: (b)
The rules of binomial nomenclature states that
1. All living organisms should have scientific name consisting of two words, the first is the genus and starts with a capital letter and the second is the species, starting with a small letter.
2. All names should be in italics if typed or printed.
3. When handwritten, the two words of the scientific name are separately underlined.
So the correct scientific name of wheat is TriticumaestivumLinn.
Q46: Which of the following is not included in the classification of mango?
(a) Plantae
(b) Anacardiaceae
(c) Monocotyledonae
(d) Dicotyledonae
Ans: (c)
Class of mango is dicotyledone.
Q47: Which of the following is incorrect regarding rules of binomial nomenclature?
(a) Biological names are in Latin language.
(b) Biological names should be italicized when typed.
(c) Biological names consist of a generic name and a subspecific epithet.
(d) Citation with a biological name provides information about the scientist who first gave the valid name.
Ans: (c)
Biological names are consist of generic name and specific epithet
Q48: The living organisms can be unexceptionally distinguished from the non-living things on the basis of their ability for
(a) Interaction with the environment and progressive evolution
(b) Reproduction
(c) Growth and movement
(d) Responsiveness to touch
Ans: (a)
The living beings continuously interact with the environment. Living beings also show continuous progressive evolution to become more advanced. Example, in the continuous exposure to the antibiotics, bacteria develop antibiotic resistance and become more evolved.Non living things do not interact with the environment and they do not evolve.
Q49: The most important feature of all living systems is to
(a) Utilize oxygen to generate energy
(b) Replicate the genetic information
(c) Produce gametes
(d) Utilize solar energy for metabolic activities
Ans: (b)
Replication of the genetic information causes transfer of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Q50: Which of the following is against the rules of ICBN?
(a) Generic and specific names should be written starting with small letters.
(b) Handwritten scientific names should be underlined.
(c) Every species should have a generic name and a specific epithet.
(d) Scientific names are in Latin and should be italicized.
Ans: (a)
The first word denoting the genus starts with a capital letter while the specific epithet starts with a small letter.
Q51: Which of the following are characteristics of living organisms?
(a) Growth and reproduction
(b) Reproduction and ability to sense the environment
(c) Metabolism and interaction
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
All living organisms share certain unified and basic characteristics including energy utilization, regulation or homeostasis, growth, development, reproduction, adaptation metabolism and interaction.
Q52: Cell division occurs _______ in plants and _______ in animals.
(a) Continuously, only up to a certain age
(b) Only up to a certain age, continuously
(c) Continuously, never
(d) Once, twice
Ans: (a)
All cells arise from pre-existing cells by a process of cell division. Cell division is the phenomenon of production of daughter cell from parent cell. It occurs continuously in plants and only up to a certain age in animals.
Q53: In unicellular organisms, with respect to growth and reproduction, the following can be true:
1. Growth and reproduction are inclusive events.
2. Unicellular organisms grow by cell division.
3. Both are exclusive.
(a) Only 1 correct
(b) Only 2 correct
(c) Both 1 and 2 correct
(d) Only 3 correct
Ans: (c)
In unicellular organisms, both growth and reproduction are inclusive events as unicellular organisms simply grow by cell division, in which their population size also increases. Both the features are exclusive in multicellular organisms.
Q54: Reproduction is synonymous with growth ______.
(a) In all organisms
(b) Only in unicellular organisms
(c) Only in multicellular organisms
(d) Non-livings
Ans: (b)
When it comes to unicellular organisms like bacteria, unicellular algae or Amoeba, reproduction is synonymous with growth, i.e., increase in number of cells.
Q55: Non-living objects:
1. Grow from external surface by collecting substances on it.
2. Grow from internal surface like living organisms.
3. Do not grow at all.
Which of the following options is correct?
(a) Only 1 correct
(b) Only 2 correct
(c) Only 3 correct
(d) All 1, 2, 3 correct
Ans: (a)
Non-living objects have characteristic growth called extrinsic growth in which object grows after accumulating substance over its surface. Living organisms show intrinsic growth (i.e., grows from inside).
Q56: In multicellular organisms, _____ refers to the production of progeny possessing features more or less similar to those of parents.
(a) Growth
(b) Reproduction
(c) Metabolism
(d) Consciousness
Ans: (b)
Reproduction ensures the continuity of the species, generation after generation. Genetic variations are created and inherited during reproduction.
Q57: The fungi, the filamentous algae, the protonema of mosses, all easily multiply by _____.
(a) Budding
(b) Fission
(c) Regeneration
(d) Fragmentation
Ans: (d)
Fragmentation is asexual mode of reproduction in which an organism is split into fragments. Each of these fragments develops into mature, fully grown individuals that are clones of the original organism. The fungi, the filamentous algae and the protonema of mosses all easily multiply by fragmentation.
Q58: The sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in our body is known as
(a) Metabolism
(b) Growth
(c) Regeneration
(d) Reproduction
Ans: (a)
Catabolism – Breakdown of substances eg., Respiration
Anabolism – Formation of substances. eg., Photosynthesis.
Catabolism + Anabolism = Metabolism.
These are defining features of all life forms.
Q59: Which of the following terms is used to refer to the number of varieties of plants and animals on earth?
(a) Taxonomy
(b) Identification
(c) Biodiversity
(d) Classification
Ans: (c)
The term biodiversity is used for the variety and variability among all forms of living organisms like plants, animals, and micro-organisms present in a given region under natural conditions.
Biodiversity can be defined as the totality of genes, species and ecosystem of a region. India is very rich in biodiversity.
Q60: ICBN stands for
(a) International Code for Botanical Nomenclature
(b) International Congress of Biological Names
(c) Indian Code of Botanical Nomenclature
(d) Indian Congress of Biological Names
Ans: (a)
ICBN (International Code for Botanical Nomenclature) is one of the code of nomenclature which is independent of zoological and bacteriological nomenclature. The foundations of ICBN was found in Philosophia Botanica, a book written by C. Linnaeus.
Q61: Choose the correct option for the missing words (A, B, C, D).
(1) Petunia, A → Solanaceae
(2) Felis, B → C.
(3) Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae → D.
(a) A- Triticum; B- Panthera; C- Canidae; D- Poales
(b) A- Datura; B- Panthera; C- Felidae; D- Polymoniales
(c) A- Datura; B- Panthera; C- Felidae; D- Polymoniales
(d) A- Solanum; B- Panthera; C- Felidae; D- Polymoniales
Ans: (c)
Panthera and Felis belong to the family Felidae. Plant families like Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae are included in the order Polymoniales mainly based on the floral characters.
Q62: Which of the following pair is correctly matched?
(i) Fungi – Regeneration
(ii) Mosses – Fragmentation
(iii) Planaria – Budding
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) Both (i) and (iii)
(c) Only (ii)
(d) Only (iii)
Ans: (c)
Fungi shows fragmentation, budding, Planaria truely regenerate during its life cycle.
Mossess shows fragmentation for propagation of their progenies. Thallus tip, protonema fragments and even rhizoids can grow into new moss thallus.
Q63: ICZN stands for
(a) International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
(b) International Congress of Zoological Names
(c) Indian Code of Zoological Nomenclature
(d) Indian Congress of Zoological Names
Ans: (a)
ICZN stands for International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
Q64: Match the common name given in Column I with their taxonomic category order given in Column II and choose the correct combination.
 (a) A – I; B – II; C – IV; D – III
(a) A – I; B – II; C – IV; D – III
(b) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(c) A – II; B – IV; C – I; D – III
(d) A – III; B – IV; C – II; D – I
Ans: (b)
A - IV; B - III; C - II; D - I
Q65: Match the common name given in Column I with their taxonomic category family given in Column II and choose the correct combination.
 (a) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(a) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(b) A – IV; B – III; C – I; D – II
(c) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV
(d) A – I; B – III; C – II; D – IV
Ans: (a)
A - IV; B - III; C - II; D - I
Q66: Find the wrong statement.
(a) Classification is the process of grouping of anything into categories based on some easily observable characters.
(b) Dogs, cats, animals represent taxa at the same levels.
(c) Each category commonly represents a taxon.
(d) Rank of taxon represents a unit of classification.
Ans: (b)
Dogs, cats and animals represents taxa at different levels
Q67: Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option.
 (a) A – IV; B – III; C – V; D – II; E – I
(a) A – IV; B – III; C – V; D – II; E – I
(b) A – V; B – IV; C – II; D – I; E – III
(c) A – IV; B – V; C – II; D – I; E – III
(d) A – V; B – III; C – II; D – I; E – IV
Ans: (b)
A - V; B - IV; C - II; D - I; E - III
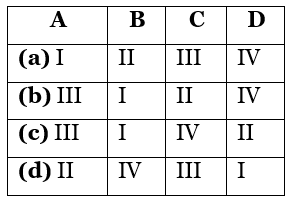
Q68: Match Column I with Column II and select the correct match.

 Ans: (c)
Ans: (c)
A – III, B – I, C – IV, D – II.
Q69: Datura inoxia belongs to the order and family respectively -
(a) Malvales, Moraceae
(b) Passiflorales, Rhamnaceae
(c) Polymoniales, Solanaceae
(d) Sapindales, Anacardiaceae
Ans: (c)
The genus Datura with its nine species are a group of poisonous plants, especially their seeds and flowers. Being herbaceous leafy annuals and short-lived perennials, their fruit are spiny capsule that splits open when mature to release numerous seeds. This plant is placed under the family Solanaceae because it shows the characteristics of a the family with a solitary flower with five fused sepals and petals, superior ovary with two fused carpels and obliquely placed in the flower.
Q70: The term systematics was introduced by -
(a) Mayr
(b) Bentham
(c) Hutchinson
(d) Linnaeus
Ans: (d)
Human beings were, since long, not only interested in knowing more about different kinds of organisms and their diversities, but also the relationships among them. This branch of study was referred to as systematics. The word systematics is derived from the Latin word ‘systema’ which means systematic arrangement of organisms. Linnaeus used Systema Naturae as the title of his publication.
Q71: Binomial nomenclature means
(a) One name given by two scientists.
(b) One scientific name consisting of a generic name and a specific epithet.
(c) Two names, one latinized, other of a person.
(d) Two names of the same plant.
Ans: (b)
Binomial nomenclature means that the scientific name of any organism consist of a generic epithet and a specific epithet. Binomial nomenclature was developed by Linnaeus.
Q72: In printed scientific names, the first letter of only ______ is capitalized.
(a) Class
(b) Species
(c) Genus
(d) Family
Ans: (c)
In printed scientific names, only the first letter of genus is capitalized. Genus is an assembly of related species which evolved from a common ancestor and have certain common characters.
Eg, Solanum tuberosum and Solanum melongena are two species which belongs to the same genus of Solanum.
Q73: Each category of taxonomic hierarchy refers to as a unit of ______.
(a) Systematic
(b) Identification
(c) Nomenclature
(d) Classification
Ans: (d)
Taxonomic hierarchy is the sequence of arrangements of taxonomic categories in a descending order during the classification of organisms. Each category of taxonomic hierarchy refers to as a unit of classification.
Q74: Systematics refers to the
(a) Identification and classification of plants and animals.
(b) Nomenclature and identification of plants and animals.
(c) Diversity of kinds of organisms and their relationship.
(d) Different kinds of organisms and their classification.
Ans: (c)
Systematics, is the study of diversity of organisms, their comparative and evolutionary relationships on the basis of findings from various fields of biology.
Q75: Taxon is a
(a) Unit of classification.
(b) Species.
(c) Highest rank of classification.
(d) All of the above
Ans: (a)
A taxon is a unit of classification. It includes a taxonomic group of any rank, such as a species, family, or class. Species is the lowest level of classification.
A kingdom is the highest level of classification.
Q76: Why is growth not considered as a defining property of living beings?
(a) Because growth occurs in livings only
(b) Because growth also occurs in non-livings
(c) Because growth is irreversible
(d) Because growth is reversible
Ans: (b)
Non-living objects also grow if we take increase in body mass as a criterion for growth. Mountains, boulders and sand mounds do grow. However, this kind of growth exhibited by non-living objects is by accumulation of material on the surface.
Q77: Families are characterized on which of the following features of plant species?
(a) External morphology
(b) Anatomy of parts
(c) Vegetative and reproductive parts
(d) Seasonal similarities and variations
Ans: (c)
A family is a subdivision of an order consisting of a group of related genera which in turn are composed of groups of related species. Families are characterized on the basis of vegetative and reproductive parts of the plants species. Suffix added in families of both plants and animals may be –aceae or –ae.
Q78: The order generally ends with
(a) -ales
(b) -aceae
(c) -eae
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
The order generally ends with ales. Order being a higher category is the assemblage of families which exhibit a few similar characters.
Q79: Find out if one of the following categories is incorrect w.r.t. Mango -
(a) Family - Anacardiaceae
(b) Order - Polymoniales
(c) Class - Dicotyledonae
(d) Division - Angiospermae
Ans: (b)
Q80: Anabolism is
(a) Synthesizing process
(b) Breaking process
(c) Bidirectional process
(d) Destructive process
Ans: (a)
Smaller organic molecules are used for the production of the large complex molecules. The process is an endergonic process in which the energy is supplied which is required for the formation of the new bonds in the larger complexes. The energy is required when the small amino acids are attached for the formation of peptide bonds in proteins.
Q81: Select the correctly written scientific name of Mango which was first described by Carolus Linnaeus.
(a) Mangifera indica Car. Linn.
(b) Mangifera indica Linn.
(c) Mangifera indica
(d) Mangifera Indica
Ans: (b)
According to rules of binomial nomenclature, correctly written scientific name of mango is Mangifera indica Linn.
This system of nomenclature was given by Carlous Linnaeus. The scientific name of mango is given as Mangifera indica Linn. Mangifera indicates the 'genus' while indica represents a particular species or 'specific epithet' and Linn indicates the Biologist Linnaeus who first described the species of mango.
Q82: Nomenclature is governed by certain universal rules. Which one of the following is contrary to the rules of nomenclature?
(a) Biological names can be written in any language.
(b) The first word in a biological name represents the genus name and the second is a specific epithet.
(c) The names are written in Latin and are italicised.
(d) When written by hand the names are to be underlined.
Ans: (a)
Binomial nomenclature is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms.
Q83: The common characteristics between tomato and potato will be maximum at the level of their
(a) Genus
(b) Family
(c) Order
(d) Division
Ans: (b)
Familes are characterised on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) and potato (Solanum tuberosum) belong to the same family Solanaceae.
Q84: Species are considered as
(a) A group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities
(b) A group of individual organisms with fundamental dissimilarities
(c) The highest units of classification
(d) Artificial concept of the human mind which cannot be defined in absolute terms
Ans: (a)
Taxonomic studies consider a group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities as a species.
Q85: What is true for individuals of the same species?
(a) Live in the same niche
(b) Live in the same habitat
(c) Interbreeding
(d) Live in a different habitat
Ans: (c)
Individuals of the same species can interbreed. No two individuals share the same ecological niche.
Q86: Binomial nomenclature was introduced by
(a) De Vries
(b) Carolus Linnaeus
(c) Huxley
(d) John Ray
Ans: (b)
Binomial nomenclature was introduced by Carolus Linnaeus. He is known as 'Father of modern taxonomy'. The binomial nomenclature system combines two names to give all species unique scientific names. The first part of a scientific name is called the genus. The second part is the species name.
Q87: Binomial nomenclature consists of two words
(a) Genus and species
(b) Order and family
(c) Family and genus
(d) Species and variety
Ans: (a) Binomial nomenclature consists of two wordsgenus and species. First word denotes genus name and second word denotes species name.
Q88: The sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in our body is known as
(a) Metabolism
(b) Growth
(c) Regeneration
(d) Reproduction
Ans: (a) The anabolic processes are the reactions in which Metabolism is the sum total of all chemical reactions occuring in our body. It is made up of catabolism and anabolism. The anabolic processes are the reactions in which the smaller organic molecules are used for the production of the large complex molecules. The process is an endergonic process in which the energy is supplied which is required for the formation of the new bonds in the larger complexes. The energy is required when the small amino acids are attached for the formation of peptide bonds in proteins.
Q89: Which of the following taxonomic categories of housefly is incorrectly matched?
(a) Genus – Musca
(b) Family – Muscidae
(c) Order – Primata
(d) Class – Insecta
Ans: (c)
Housefly belongs to the order diptera.
Q90: Term systematics was derived from _____ word "Systema" which means _____.
(a) Greek, evolutionary relationship
(b) Latin, systematic arrangement of organisms
(c) English, taxonomy of organisms
(d) Both (b) & (c)
Ans: (b)
G. Simpson in 1961 defined systematics is the study of the diversity of organisms along with the relationships among them. Derived from the Latin word "systema" this refers to the systematic arrangement of organisms
Q91: Find the odd one (w.r.t. taxonomic categories) -
(a) Muscidae
(b) Primata
(c) Sapindales
(d) Poales
Ans: (a)
Muscidae is a family, rest all belongs to order.
Q92: Solanum, Petunia, and Datura are placed in the same
(a) Species
(b) Family
(c) Genus
(d) All are incorrect
Ans: (b)
Families are characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Among plants for example, three different genera Solanum, Petunia and Datura are placed in the family Solanaceae.
Q93: For plants, scientific names are based on agreed principles and criteria, which are provided in
(a) ICNB
(b) ICBN
(c) ICNCP
(d) ICTV
Ans: (b) Universally accepted Binomial nomenclature of Plants follows the International Code for Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN). It uses various resources like articles, photographs, and recommendations for carrying out the above function.
Q94: The earliest classifications were based on the ________ of various organisms.
(a) Use
(b) Morphology
(c) Anatomy
(d) Habitat
Ans: (a)
Earliest classification were based on the food, clothing, shelter or uses of various organisms.
Q95: Which one of the following animals is correctly matched with its correct taxonomic category?
(a) Tiger – Panthera, the genus
(b) Solanum – China rose, the genus
(c) Humans – Primata, the family
(d) Housefly – Musca, an order
Ans: (a)
Primata is an order of class Mammalia.
The zoological name of the tiger is Pantheratigris; tigris being one of the species classified under the genus Panthera.
Q96: Panthera leo is the scientific name for
(a) Tiger
(b) Leopard
(c) Lion
(d) Cat
Ans: (c)
The scientific name for the lions is Panther Leo.
Q97: The taxonomic unit ‘Phylum’ in the classification of animals is equivalent to which hierarchical level in the classification of plants
(a) Class
(b) Order
(c) Division
(d) Family
Ans: (c)
Phylum = Division, Phylum is used in Zoology & Division in Plants.
Q98: Scientific name for leopard is
(a) Panthera leo
(b) Panthera pardus
(c) Panthera tigris
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b)
Leopard, (Panthera pardus), , also called panther, large cat closely related to the lion.
Q99: Order of housefly is
(a) Muscidae
(b) Diptera
(c) Insecta
(d) Musca
Ans: (b)
The taxonomy classification of a housefly whose scientific name is muscadomestica is as follows: the Animalia kingdom, the Arthropoda phylum, the Insecta class, the Diptera order, the Schizophora section, the Muscidae family, the Musca genus, and the Musca domestica species.
Q100: All living organisms are linked to one another because
(a) They have different genetic material
(b) They share common genetic material but to varying degrees
(c) All have the same size and shape
(d) All of the above
Ans: (b)
In fact, the whole theory of evolution is based on the similarity of genetic materials which indicates common ancestry for living organisms. Variations in the similarity of genetic material give biodiversity which we see all around us.
 (a) A-Strain, B-Order, C-Sub kingdom
(a) A-Strain, B-Order, C-Sub kingdom
 Ans: (a)
Ans: (a)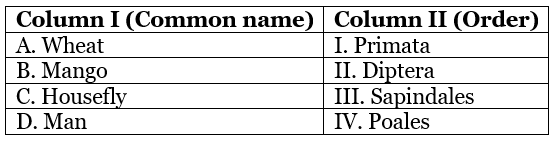 (a) A – I; B – II; C – IV; D – III
(a) A – I; B – II; C – IV; D – III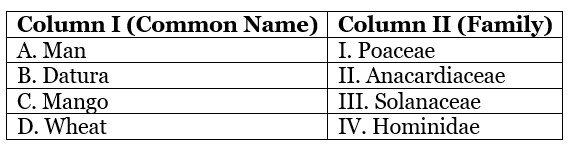 (a) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(a) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I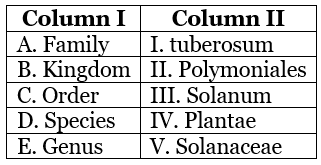 (a) A – IV; B – III; C – V; D – II; E – I
(a) A – IV; B – III; C – V; D – II; E – I
 Ans: (c)
Ans: (c)























