Summary of the Chapter - Crop Production & Management - Class 8 PDF Download
Introduction
Agriculture is the science, which mainly deals with the diverse processes or the methods used for the cultivating different varieties of plants and livestock farming or animal husbandry on the basis of human requirements.
When plants of the same variety are cultivated on a large scale, they are called crops. The crops are divided on the basis of the seasons in which they grow:
The crops are divided on the basis of the seasons in which they grow:
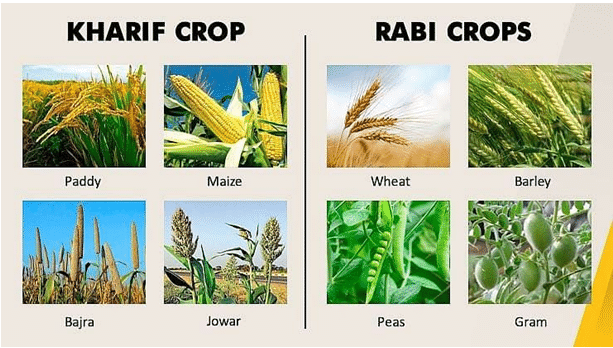
- Kharif Crops: These crops are sown in the early monsoon season, which generally varies by crop and region of cultivation. In India, Kharif crops are sown at the beginning of the rainy season, between the month of June and July. These crops are harvested at the end of monsoon season, between the month of September and October. Paddy is the main Kharif crop.
- Rabi Crops: These crops are sown during winter and after the monsoon, which is between the month of October and November. In India, Rabi crops are harvested during the spring between the month of March and April. Wheat is the main Rabi crop.
Crop Production and Management Methods
About 70% of the Indian population practices agriculture. Hence, the production and management of crops is an important aspect to ensure optimal productivity in the fields.
The major agricultural practices involved in crop production and management are listed below: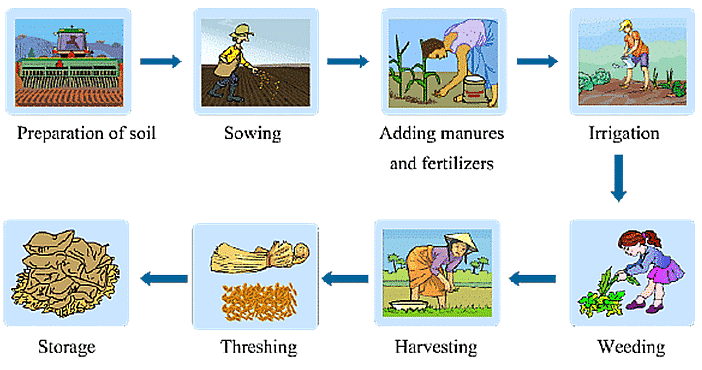
- Preparation of Soil
- Sowing of Seeds
- Addition of Manure and Fertilizers
- Irrigation
- Protection from Weeds
- Harvesting
- Storage
1. Preparation of Soil: The soil is loosened and tilted before the seeds are sown. Ploughs are used for the purpose. If the soil contains big lumps, they are broken with the help of a hoe. This process aerates the soil so that the roots breathe easily. The nutrients and minerals get properly mixed with the soil and come at the top. Thus, the fertility of the soil increases and is fit for plantation.
2. Sowing of Seeds: The good quality, infection-free seeds are collected and sown on the prepared land. The seeds should be sown at proper depths and proper distances.
Following are the various methods used to sow the seeds:
- Traditional techniques
- Broadcasting
- Dibbling
- Drilling
- Seed dropping behind the plough
- Transplanting
- Hill dropping
- Check row planting
3. Addition Of Manures And Fertilizers: The soil may not have the right nutrients to efficiently sustain plant growth. Hence, manures and fertilizers are added to the soil to increase its fertility and help plants grow better. Manure is prepared by using decomposing plant and animal matter in compost pits. Fertilizers, on the other hand, are chemicals prepared in factories which contain nutrients for a specific plant. They give faster results than manures. However, when excessively used, they turn the soil infertile.
4. Irrigation: Crops require water at regular intervals for proper growth. The supply of water to the plants is known as irrigation. Well, rivers, lakes, tube-wells are different sources for irrigation. The traditional methods of agriculture involve the use of humans and animals. The various traditional ways are moats, chain-pump, dhekli, rahat.
The modern techniques of irrigation include the sprinkler system and the drip system. Water is very important for the germination of seeds. It helps in the proper development of flowers, fruits, seeds, and plants. Therefore, it should be present in plants in large quantities.
5. Protection from Weeds: The undesirable plants that grow along with the crops are called weeds. These weeds, feed on the nutrients provided to the crops and thus reduce the supply of nutrients to the crops, thereby, inhibiting their growth. The growth of these weeds needs to be prevented in order to enhance the growth of the plants.
The process of removal of weeds is called weeding. To achieve this, weedicides are employed, which are essentially chemicals specifically made to destroy weeds. They are usually sprayed before seeding and flowering.
6. Harvesting: When the crop matures, it is cut for further processing. This process is known as harvesting. It is usually manual labour, done with the help of sickle. However, mechanical harvesting is used these days – machines such as combine harvesters are used where the crops are harvested and threshed in one go.
- Threshing: Separation of grains from the harvested crops is called threshing. It is done either mechanically or by cattle.
- Winnowing: The separation of grains and chaff is called winnowing. It is done either mechanically or manually.
7. Storage: The grains should be properly stored if they are to be kept for longer periods. They need to be protected from pests and moisture. The freshly harvested seeds should be dried before they are stored. This prevents the attack from microorganisms and pests.
The harvested and separated grains are stored in airtight metallic bins or in the jute bags. Dried neem leaves are added to protect them from damage at home. Large amounts of grains are stored in granaries or silos with specific chemical treatments, to protect them from pests and insects.
Food From Animals
Animals are an important source of food. The rearing of animals for food is known as animal husbandry. Some animals like cows and buffaloes are reared for milk, others for meat like goats and poultry. Some people consume fish as a part of their diet. Honey bees are reared for honey. Thus, animals are an integral source of food and food products.
Key Points Of Crop Production and Management
- The entire world depends on agriculture for its food. Therefore, it is very important to produce and store the harvested crops carefully.
- The soil should be loosened and aerated properly during crop production.
- Manures and fertilizers need to be added carefully. Too much fertilizer damages the soil while too little makes the crop deficient in nutrients.
- The crops should be irrigated periodically.
- The unwanted plants should be removed from the cultivated fields. These plants absorb the nutrients provided to the crop and obstruct their growth and development.
- The matured crops are harvested mechanically or manually.
- The harvested grains are dried and stored to protect them from pests and pathogens.
FAQs on Summary of the Chapter - Crop Production & Management - Class 8
| 1. What is crop production and management? |  |
| 2. Why is soil preparation important in crop production? |  |
| 3. What are the different methods of irrigation used in crop production? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of crops grown in India? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of crop rotation in crop production? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|


















