(i) Electroscope:
Purpose: A device used to detect electric charge.
How It Works: It consists of a jar, a cardboard lid with a hole, a paper clip, and two aluminium foil strips. When a charged object is brought near, the foil strips repel each other, indicating the presence of charge.
Charging and Discharging:
Charging: When a charged object touches the paper clip, it transfers charge to the foil strips, causing them to repel each other.
Discharging: Touching the paper clip with your hand causes the foil strips to collapse because the charge is transferred to the ground through your body.
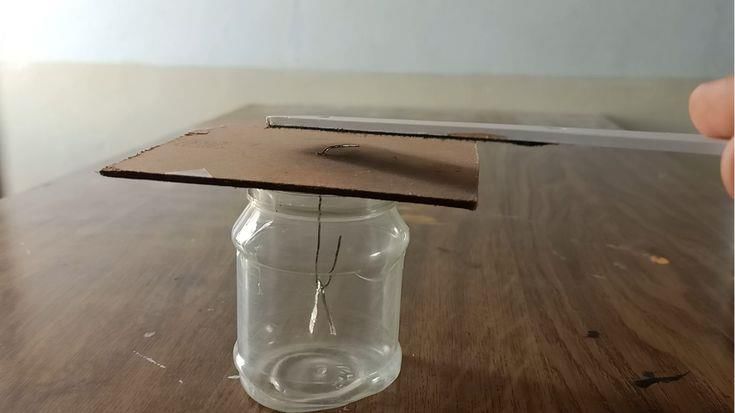 A simple Electroscope(ii) Earthing:The process of transferring excess charge safely to the earth. Earthing in buildings protects against electrical shocks by grounding stray electrical currents.
A simple Electroscope(ii) Earthing:The process of transferring excess charge safely to the earth. Earthing in buildings protects against electrical shocks by grounding stray electrical currents.
The story of lightning
- Air Currents and Water Droplets:
- In a thunderstorm, the air moves upward while the water droplets fall down.
- This movement causes a mix-up of electric charges.
Separation of Charges:
- During these strong movements, positive and negative charges separate.
- Positive Charges: These gather at the top of the clouds.
- Negative Charges: These collect at the bottom of the clouds.
- Additionally, positive charges build up near the ground.
Building Up of Charges:
- As more charges gather, they create a strong electric field.
- Normally, air does not conduct electricity well, but when the charge is very high, the air can no longer stop the flow of electricity.
Electric Discharge:
- When the negative charges from the clouds meet the positive charges from the ground, they create a sudden release of energy.
- This release of energy is what we see as lightning.
- The bright flash of light and the sound we hear (thunder) are both results of this electric discharge.
 Accumulation of charges leading to lightning
Accumulation of charges leading to lightning
Lightning Safety
- During lightning and thunderstorm no open place is safe.
- Hearing thunder is an alert to rush to a safer place.
- After hearing the last thunder, wait for some time before coming out of the safe place.
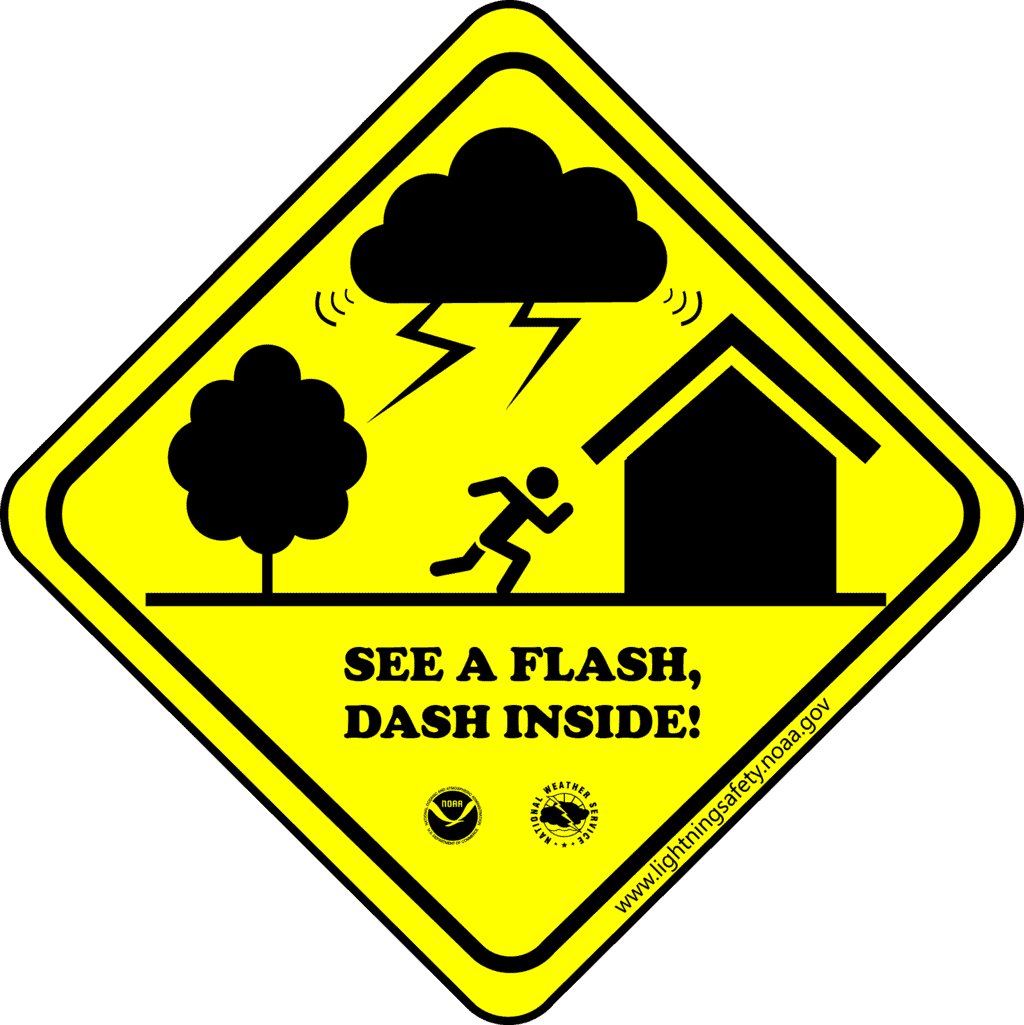
Dos and Don’ts during a Thunderstorm:
Outside:
- Open vehicles, such as motorbikes, tractors, and convertibles, are not safe during storms.
- Open areas, tall trees, and park shelters do not offer protection from lightning strikes.
- Bringing an umbrella is not a wise choice during thunderstorms.
- If you find yourself in a forest, seek shelter under shorter trees. If no cover is available and you're in an open field, stay away from all trees.
- Maintain a distance from poles and other metal objects.
- Do not lie flat on the ground. Instead, squat low on the ground.
 Safe position during Lightning
Safe position during Lightning
Inside the House:
- Lightning can hit telephone wires, electrical cords, and metal pipes. It's best to stay away from these during a thunderstorm.
- Using mobile phones and cordless phones is a safer choice.
- Avoid bathing during thunderstorms to prevent contact with water that is running.
- Unplug electrical appliances like computers and televisions.
- You can keep lights on during a storm.
Lightning Conductors
- Lightning Conductor is a device designed to protect buildings from lightning.
- A metal rod, which is taller than the building, is installed in the walls during construction.
- One end of the rod is exposed to the air, while the other end is buried deep in the ground.
- The rod serves as an easy path for the electric charge to flow into the ground.
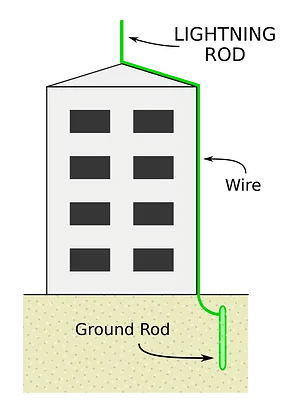 Lightning conductor
Lightning conductor
- The metal columns used in building construction, along with electrical wires and water pipes, provide some level of protection for us. However, it is crucial to avoid touching them during a thunderstorm.
- You may see trident-shaped iron rods on the tops of temples, TV towers, and cell phone towers. These rods serve as lightning conductors.
Earthquakes
- Thunderstorms and lightning can cause significant damage but can be somewhat predicted by the weather department.
- Thunderstorms may lead to lightning and cyclones, giving time for protective measures.
- Earthquakes, however, remain unpredictable and can cause widespread destruction.
- Notable earthquakes in India include the 2005 North Kashmir quake and the 2001 Bhuj quake in Gujarat.
What is an Earthquake?
An earthquake is a sudden shaking or trembling of the earth lasting for a very short time.
 Earthquake
Earthquake
- Earthquakes are caused by disruptions deep within the Earth's crust.
- They happen all over the world and often go unnoticed.
- Major earthquakes are much less common than smaller ones.
- These events can lead to serious damage to buildings, bridges, dams, and people.
- There can be significant loss of life and property due to earthquakes.
- Earthquakes may also trigger floods, landslides, and tsunamis.
What Causes an Earthquake
Ancient Beliefs: People did not understand what caused earthquakes.
Modern Understanding: Caused by disturbances in the Earth's crust, the uppermost layer of the Earth (called crust).
Earth's Layers: The Earth's outer layer is not solid; it's broken into pieces and called as plates. These plates are constantly moving.
 Structure of Earth
Structure of Earth
Plate Movements: When plates brush past each other or one plate slides under another, it creates disturbances in the crust. A plate goes under another due to collision. These disturbances result in the shaking we feel during an earthquake.
 Movement of Earth's Plate
Movement of Earth's Plate
Weak Zones: The edges of these tectonic plates are weak zones where earthquakes are more likely to occur. These areas are known as seismic or fault zones.
- Areas in India at Risk: Kashmir, Western and Central Himalayas, North-East India, Rann of Kutch, Rajasthan, Indo-Gangetic Plain, Some parts of South India.
- Richter scale: The power of an earthquake is expressed in terms of a magnitude on a scale called Richter scale. Really destructive earthquakes have magnitudes higher than 7 on the Richter scale. Both Bhuj and Kashmir earthquakes had magnitudes greater than 7.5.

Note: The tremors produce waves on the surface of the earth. These are called seismic waves. The waves are recorded by an instrument called the seismograph.
Protection against Earthquakes
- It is advisable to make the structure simple so that it is ‘Quake Safe’.
- Be prepared for earthquakes in seismic zones.
- Design simple, earthquake-resistant buildings.
- Use lighter materials like mud or timber in highly seismic areas.
- Keep roofs light to reduce damage if the structure collapses.
- Secure cupboards, shelves, and wall decorations to walls.
- Place heavy objects carefully to avoid falling hazards.
- Ensure firefighting equipment is functional in all buildings.

In the event of an earthquake, take the following measures:
1. If you are at home
- Take cover under a table and remain there until the shaking comes to an end.
- Avoid tall and heavy items that could potentially fall on you.
- If you are lying in bed, stay there and protect your head with a pillow.
2. If you are outdoors
- Find a safe location: Look for a clear area that is far from buildings, trees, and power lines.
- Drop to the ground: If you feel shaking, get down to protect yourself.
- If you are in a vehicle: Stay inside the car or bus. Do not exit.
- Ask the driver: Request that the driver slowly move to a safer spot.
- Wait for the shaking to stop: Remain inside the vehicle until the tremors have finished
Ans. Lightning is caused due to the buildup and discharge of static electricity in the Earth's atmosphere. This takes place when there is an electrical imbalance between the clouds and the ground. The lightning bolt is the discharge of this built-up energy.
2. Can lightning strike the same place twice?
Ans. Yes, lightning can strike the same place multiple times. High structures, such as tall buildings or antennas, are more likely to be struck by lightning multiple times due to their height and conductivity.
3. How does a thunderstorm form?
Ans. A thunderstorm forms when warm, moist air rises and cools, forming clouds. These clouds continue to grow in size and height due to the constant updrafts of warm air. As the clouds become taller, they create an electrical charge which leads to lightning and thunder.
4. Why do earthquakes occur?
Ans. Earthquakes occur due to the movement of tectonic plates. These plates move around the Earth's surface, and when they rub against each other, they can cause a sudden release of energy. This energy is what causes the ground to shake and can lead to damage and destruction in the surrounding areas. $$$
5. How does a tsunami occur?
Ans. A tsunami is caused by a sudden displacement of water, usually due to an undersea earthquake or landslide. The displacement of water creates a powerful wave that can travel across the ocean at high speeds. As the wave approaches land, it can grow in height and cause significant damage to coastal areas.





















