Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 8 > Natural Vegetation & Wildlife - Land, Soil & Water Resources
Natural Vegetation & Wildlife - Land, Soil & Water Resources | Social Studies (SST) Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Biosphere |

|
| Importance of Wildlife |

|
| Distribution of Natural Vegetation |

|
| Evergreen & Deciduous Forests |

|
| Conservation of Natural Vegetation and Wildlife |

|
Biosphere
- Natural vegetation and wildlife exist only in the narrow zone of contact between the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere that we call biosphere.

- In the biosphere living beings are interrelated and interdependent on each other for survival.
- This life-supporting system is known as the ecosystem. Vegetation and wildlife are valuable resources.
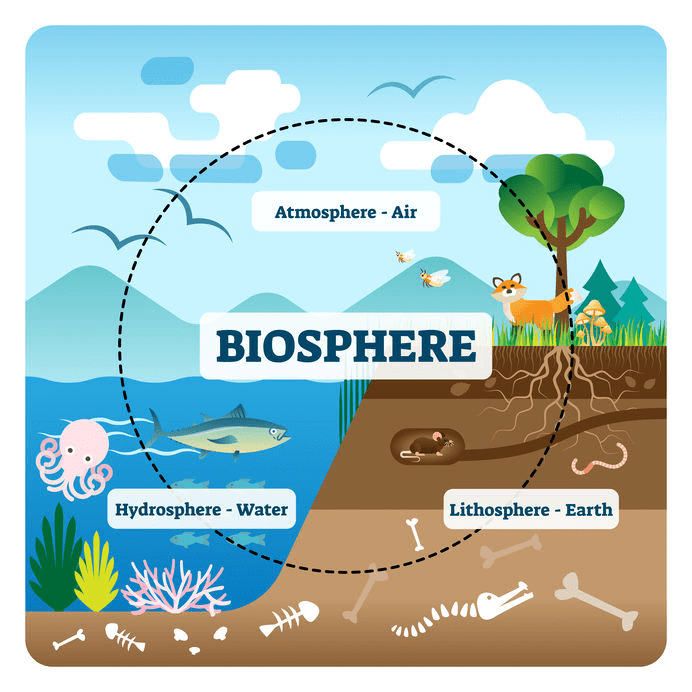
- Plants provide us with timber, give shelter to animals, produce oxygen we breathe, protect soils so essential for growing crops, act as shelter belts, help in storage of underground water, give us fruits, nuts, latex, turpentine oil, gum, medicinal plants and also the paper that is essential for your studies. There are innumerable uses of plants and you can add some more.
Question for Natural Vegetation & Wildlife - Land, Soil & Water ResourcesTry yourself: What are some of the valuable resources provided by plants in the biosphere?View Solution
Importance of Wildlife
- Wildlife includes animals, birds, insects as well as the aquatic life forms. They provide us with milk, meat, hides and wool.
- Insects like bees provide us honey, help in pollination of flowers and have an important role to play as decomposers in the ecosystem.
- The birds feed on insects and act as decomposers as well. Vulture due to its ability to feed on dead livestock is a scavenger and is considered a vital cleanser of the environment. So animals big or small, all are integral to maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
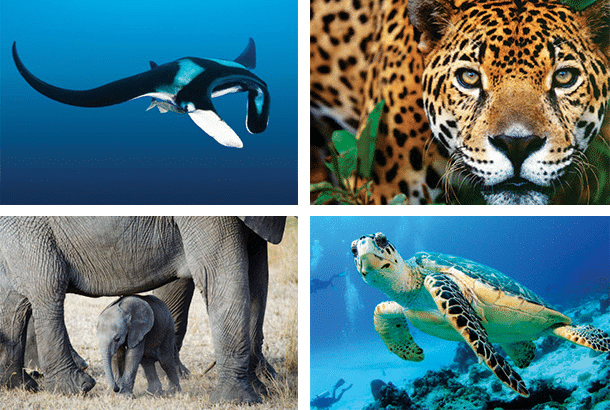 Wildlife
Wildlife
Distribution of Natural Vegetation
- The growth of vegetation depends primarily on temperature and moisture. The major vegetation types of the world are grouped as forests, grasslands, scrubs and tundra.
- In areas of heavy rainfall, huge trees may thrive. The forests are thus associated with areas having an abundant water supply.
- As the amount of moisture decreases the size of trees and their density reduces.
- In the regions of moderate rainfall, short stunted trees and grasses grow forming the grasslands of the world.
- In dry areas of low rainfall, thorny shrubs and scrubs grow. In such areas plants have deep roots and leaves have thorny and waxy surface to reduce loss of moisture by transpiration.
- Tundra vegetation of cold Polar Regions comprises of mosses and lichens.
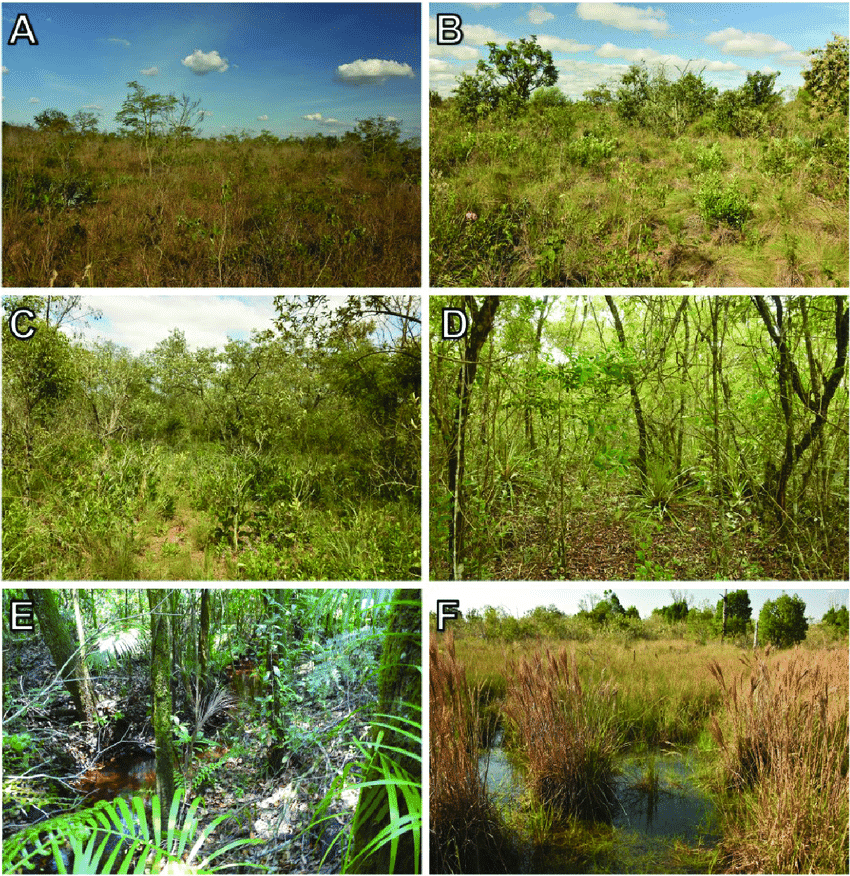 (A) Grassy scrubland, (B) Grassy scrubland with scattered trees, (C) Dense savanna, (D) Cerrado woodland, (E) Gallery forest, (F) Wet field.
(A) Grassy scrubland, (B) Grassy scrubland with scattered trees, (C) Dense savanna, (D) Cerrado woodland, (E) Gallery forest, (F) Wet field.
Evergreen & Deciduous Forests
- Forests are broadly classified as evergreen and deciduous depending on when they shed their leaves.
 Deciduous Forest
Deciduous Forest
- Evergreen forests do not shed their leaves simultaneously in any season of the year.
- Deciduous forests shed their leaves in a particular season to conserve loss of moisture through transpiration.
 Evergreen Forest
Evergreen Forest
- These forests are further classified as tropical or temperate based on their location in different latitudes.
Question for Natural Vegetation & Wildlife - Land, Soil & Water ResourcesTry yourself:How do bees contribute to the ecosystem?
View Solution
Conservation of Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
- Forests are our wealth. Plants give shelter to the animals and together they maintain the ecosystem.
- Changes in climate and human interference can cause the loss of natural habitats for plants and animals.
- Many species have become vulnerable or endangered and some are on the verge of extinction.
 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
- Deforestation, soil erosion, constructional activities, forest fires, tsunamis and landslides are some of the human-made and natural factors which together accelerate the process of extinction of these great natural resources.
- One of the major concerns is the increasing incidents of poaching that result in a sharp decline in the number of particular species.
- The animals are poached for collection and illegal trade of hides, skins, nails, teeth, horns as well as feathers. Some of these animals are tigers, lions, elephants, deer, blackbuck, crocodile, rhinoceros, snow leopard, ostrich and peacock.
- There is a balance in the environment if the relative number of species is not disturbed.
- Human activities in several parts of the world have disturbed the natural habitats of many species.
- Due to indiscriminate killings, several birds and animals have either become extinct or are on the verge of extinction.
- Awareness programs like social forestry and Vanmohatasava should be encouraged at the regional and community level.
- School children should be encouraged to watch birds and visit nature campus so that they appreciate the habitat of varied species.
The document Natural Vegetation & Wildlife - Land, Soil & Water Resources | Social Studies (SST) Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
65 videos|424 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Natural Vegetation & Wildlife - Land, Soil & Water Resources - Social Studies (SST) Class 8
| 1. What is the biosphere and why is it important? |  |
Ans. The biosphere refers to the global sum of all ecosystems, where life exists on Earth, including land, water, and the atmosphere. It is important because it supports all living organisms by providing essential resources such as food, water, and oxygen. The biosphere also plays a crucial role in regulating climate and maintaining ecological balance.
| 2. How does wildlife contribute to the ecosystem? |  |
Ans. Wildlife contributes to the ecosystem in various ways, such as pollination, seed dispersal, and maintaining food chains. Different species interact with one another and their environment, helping to sustain biodiversity, which is vital for ecosystem resilience and the overall health of the planet.
| 3. What are the main types of natural vegetation found around the world? |  |
Ans. The main types of natural vegetation include forests (such as evergreen and deciduous forests), grasslands, deserts, and tundra. Each type of vegetation is adapted to its environment and plays a unique role in supporting wildlife and maintaining ecological balance.
| 4. What is the difference between evergreen and deciduous forests? |  |
Ans. Evergreen forests are characterized by trees that retain their leaves throughout the year, allowing for continuous photosynthesis. In contrast, deciduous forests consist of trees that shed their leaves during certain seasons, usually in response to cold or dry conditions. This difference affects the biodiversity and types of wildlife each forest type can support.
| 5. Why is the conservation of natural vegetation and wildlife essential? |  |
Ans. The conservation of natural vegetation and wildlife is essential for several reasons, including maintaining biodiversity, ensuring ecosystem stability, and providing resources for human survival. Protecting these natural resources helps combat climate change, prevents habitat destruction, and supports the overall health of the planet for future generations.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches



















