NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Nutrition in Animals
Exercises
Q1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) The main steps of nutrition in humans are _____, ____, _____, _____ and ______.
Ans: The main steps of nutrition in humans are Ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion.
 View Answer
View AnswerNutrition in humans is a multi-step process to obtain and utilize food for energy and growth. The five main steps are:
- Ingestion: Taking in food through the mouth.
- Digestion: Breaking down food into smaller, absorbable molecules.
- Absorption: Nutrients from the food pass into the blood from the digestive tract.
- Assimilation: Cells in the body use these absorbed nutrients for various functions.
- Egestion: Expelling the undigested waste from the body.
 Digestion
Digestion
(b) The largest gland in the human body is _______.
Ans: The largest gland in human body is liver.
 View Answer
View Answer- The liver is the largest gland in the human body.
- It plays a crucial role in digestion by producing bile, which helps break down fats.
- It also performs various other functions, such as detoxifying the blood and storing vitamins and minerals.
(c) The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and _____ juices which act on food.
Ans: The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and digestive juices which act on food.
 View Answer
View Answer- The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and digestive juices.
- These juices contain enzymes like pepsin that help break down proteins into simpler forms, aiding in the overall process of digestion.
 Digestive Juices in Stomach
Digestive Juices in Stomach
(d) The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger-like outgrowths called _______.
Ans: The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger-like outgrowths called villi.
 View Answer
View Answer- The inner wall of the small intestine has finger-like outgrowths called villi.
- Villi increase the surface area for absorption, allowing nutrients to pass efficiently into the bloodstream.
(e) Amoeba digests its food in the ________
Ans: Amoeba digest its food in the food vacuole.
 View Answer
View Answer- Amoeba digests its food in the food vacuole.
- Amoeba engulfs food by forming a vacuole around it, where enzymes break down the food for absorption and energy.
 Amoeba
Amoeba
Q2. Mark T if the statement is true and F if it is false.
(a) Digestion of starch starts in the stomach.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer- The digestion of starch actually starts in the mouth, not the stomach.
- Saliva contains an enzyme called amylase, which begins breaking down starch into simpler sugars as soon as food is chewed and mixed with saliva.
(b) The tongue helps in mixing food with saliva.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer- The tongue is essential in the process of mixing food with saliva, which moistens the food and starts the breakdown of starch.
- The tongue also helps move the food around the mouth, making it easier to swallow.
(c) The gallbladder temporarily stores bile.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer- The gallbladder is a small organ that temporarily stores bile produced by the liver.
- Bile is released from the gallbladder into the small intestine to help digest fats.
(d) The ruminants bring back swallowed grass into their mouth and chew it for some time.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer- Ruminants, such as cows and goats, have a unique digestive process called "rumination."
- After swallowing grass, they bring it back into their mouth to chew it again thoroughly, which helps break down the food further and aids in digestion.
 Digestive system of ruminant
Digestive system of ruminant
Q.3. Tick (√) mark the correct answer in each of the following.
(a) Fat is completely digested in the
(i) Stomach
(ii) Mouth
(iii) Small intestine
(iv) Large intestine
Ans: (iii) Small intestine
 View Answer
View Answer- The small intestine is where fat digestion is completed.
- Bile, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, is released into the small intestine to emulsify fats, breaking them down into smaller droplets.
- Pancreatic enzymes then act on these droplets, allowing for complete digestion and absorption.
 The Digestive System
The Digestive System
(b) Water from the undigested food is absorbed mainly in the
(i) Stomach
(ii) Food pipe
(iii) Small intestine
(iv) Large intestine
Ans: (iv) Large intestine
 View Answer
View Answer- The large intestine is responsible for absorbing water from undigested food material.
- As the undigested food passes through the large intestine, most of the water is absorbed back into the body, leaving a more solid waste product for elimination.
Q4. Match the column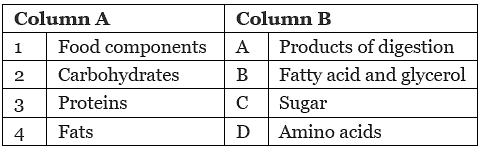
Ans: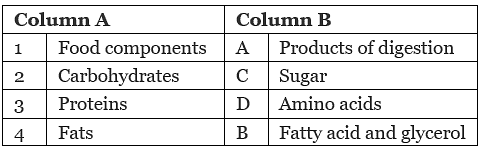
 View Answer
View AnswerCarbohydrates - Sugar
- Carbohydrates are broken down into simpler sugars, primarily glucose, during digestion.
- This breakdown begins in the mouth with the enzyme amylase and is completed in the small intestine.
- Glucose serves as the primary energy source for the body's cells.
Proteins - Amino acids
- Proteins are digested into amino acids, which are their basic building blocks.
- Protein digestion begins in the stomach with enzymes like pepsin and continues in the small intestine.
- Amino acids are then absorbed and used for growth, repair, and various cellular functions.
Fats - Fatty acids and glycerol
- Fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol in the small intestine.
- Bile from the liver emulsifies fats, while pancreatic enzymes break them down further.
- These smaller molecules are absorbed and used as an energy source or stored for future use.
Q5. What are villi? What are their location and function?
Ans:
- Definition: Villi are small, finger-like projections.
- Location: Found in the inner walls of the small intestine.
- Function: Increase the surface area for absorption. Help in absorbing nutrients from digested food into the bloodstream.
 Villi
Villi
Q6. Where is the bile produced? Which component of the food does it digest?
Ans:
- Produced in: The liver.
- Stored in: The gallbladder.
- Function in digestion: Aids in the digestion of fats by breaking them into smaller droplets, a process called emulsification.
Q7. Name the type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Give the reason also.
Ans:
- Cellulose is the type of carbohydrates which is digested in ruminants but not in humans.
- Ruminants have a large sac–like structure between the small intestine and large intestine, in which cellulose of the food is digested by the action of certain bacteria.
- Such structure is not present in humans. Hence humans cannot digest cellulose while ruminants can.
Q8. Why do we get instant energy from glucose?
Ans:
- Glucose is a simple sugar that can be easily absorbed into the bloodstream.
- It quickly enters cells and undergoes cellular respiration, releasing energy instantly.
Q.9. Which part of the digestive canal is involved in:
(a) Absorption of food ________.
Ans: Absorption of food Small Intestine.
 View Answer
View Answer- The small intestine is the primary site for the absorption of nutrients.
- Its inner walls have villi and microvilli, which increase the surface area, allowing nutrients from digested food to be absorbed efficiently into the bloodstream.
(b) Chewing of food________.
Ans: Chewing of food Buccal cavity.
 View Answer
View Answer- The buccal cavity, or mouth, is where food is initially broken down by chewing (mastication) with the help of teeth.
- Saliva mixes with the food, softening it and beginning the digestion of carbohydrates.
 Parts of Buccal Cavity
Parts of Buccal Cavity
(c) Killing of bacteria ________.
Ans: Killing of bacteria Stomach.
 View Answer
View Answer- The stomach secretes hydrochloric acid (HCl), which creates an acidic environment.
- This acid not only aids in digestion but also kills bacteria and other pathogens present in food, providing protection against infections.
(d) Complete digestion of food _______.
Ans: Complete digestion of food Small intestine.
 View Answer
View Answer- The small intestine is where complete digestion occurs.
- Digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver further break down food, allowing all nutrients to be fully digested and absorbed.
(e) Formation of faeces _________.
Ans: Formation of faeces Large Intestine.
 View Answer
View Answer- In the large intestine, undigested food residue and waste are processed.
- Water is absorbed, and the remaining material solidifies, forming faeces, which are stored until elimination from the body.
Q10. Write one similarity and one difference between the nutrition in amoeba and human beings.
Ans: Similarity: Both Amoeba and human have holozoic type of nutrition.
Difference: Human beings have complex structure for the ingestion, digestion and egestion of food while Amoeba has simple process in which it engulfs the with the help of pseudopodia and food get trapped in food vacuoles.
Q11. Match the following column
Ans: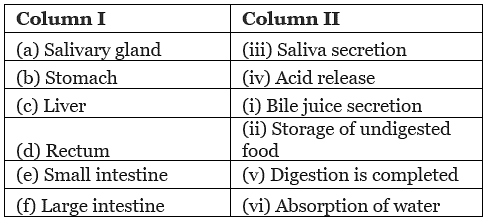
 View Answer
View Answer(a) Salivary gland - (iii) Saliva secretion
- The salivary glands, located in the mouth, produce and release saliva. Saliva contains enzymes like amylase that begin the digestion of starches in food.
(b) Stomach - (iv) Acid release
- The stomach secretes gastric acid (hydrochloric acid), which helps in breaking down food, creating an acidic environment that activates digestive enzymes and kills harmful bacteria.
(c) Liver - (i) Bile juice secretion
- The liver produces bile, a digestive fluid that helps in emulsifying fats. Bile is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine to aid fat digestion.
(d) Rectum - (vii) Release of faeces
- The rectum is the last part of the large intestine, where faeces are stored temporarily until they are expelled from the body through the anus.
(e) Small intestine - (v) Digestion is completed
- In the small intestine, enzymes and bile work to complete the digestion of food. Nutrients are then absorbed through the intestinal walls into the bloodstream.
(f) Large intestine - (vi) Absorption of water
- The large intestine absorbs water and salts from undigested food, turning it into a more solid form, which becomes faeces, before it moves to the rectum for elimination.
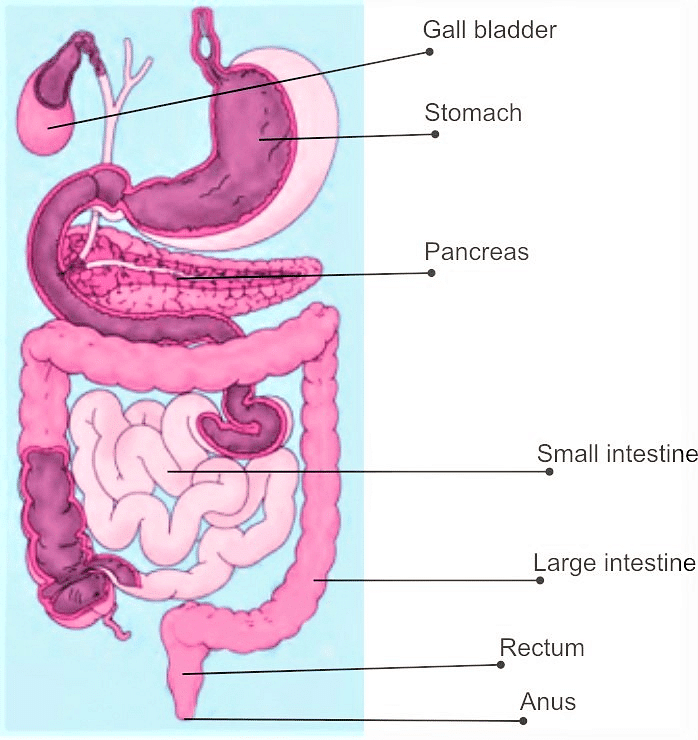
Q12. Label the diagram of the digestive system.
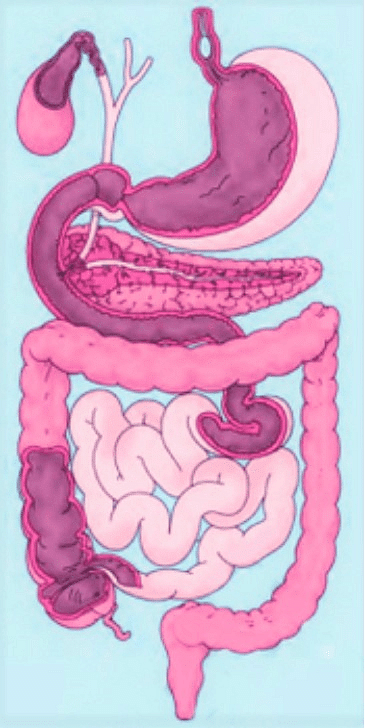 Ans:
Ans:
Q13. Can we survive only on raw, leafy vegetables/grass? Discuss.
Ans: No, we cannot survive only on raw, leafy vegetables or grass. Here’s why:
Human Digestive Limitations: Humans can’t digest cellulose in plants like cows do, so we don’t get enough nutrients from grass and leafy vegetables alone.
Lack of Key Nutrients: Leafy vegetables don’t have all the nutrients we need, like proteins, fats, vitamin B12, and iron.
Low in Calories: These foods don’t provide enough energy. We’d have to eat a huge amount to meet our energy needs, which would be hard to digest.
Risk of Malnutrition: A diet of only leafy vegetables could make us weak over time. Our bodies need a mix of foods for balanced nutrition and health.
So, we need a variety of foods to stay healthy and get all the nutrients we need.
|
111 videos|246 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Nutrition in Animals
| 1. What is the process of nutrition in animals? |  |
| 2. How do different animals obtain their food? |  |
| 3. What is the role of enzymes in animal nutrition? |  |
| 4. What are the main types of digestive systems found in animals? |  |
| 5. How does the nutrition process differ between humans and ruminants? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|


















