Transportation in Animals and Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 7
In unicellular organisms, the transportation of substances happens through diffusion and osmosis. Gases move in and out of the cell by diffusion. Other substances move by osmosis.
Diffusion: Random motion of particles in order to attain equilibrium of concentration is called diffusion. Diffusion can be observed in many aspects of day to day life. The aroma of food comes from the kitchen because of diffusion. A pleasant smell of flowers comes because of diffusion. The bad odour of garbage comes because of diffusion.
Osmosis: Osmosis is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. Seeds swell up when soaked in water, because of osmosis.
Review Questions
Q1. What is diffusion?
Answer: Random movement of particles in order to attain equilibrium of concentration is called diffusion.
Q2. What is osmosis?
Answer: Movement of water through semi-permeable membrane from high water concentration to low water concentration is called osmosis.
Circulatory System
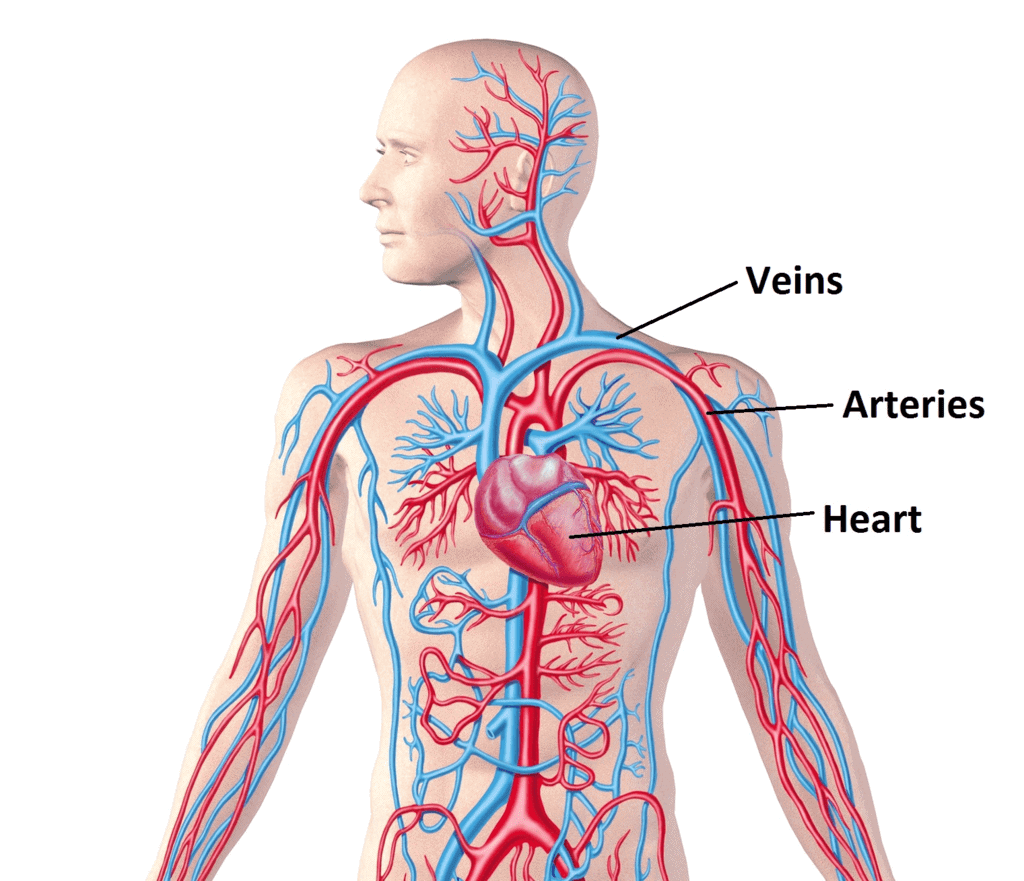
Diffusion and osmosis can result in the transportation of substances to short distances only. For bigger and complex organisms, there is a need of a more complex system for transportation of substances.
The circulatory system in humans is composed of three main components, viz. heart, blood vessels and blood.

Blood
Blood is a type of tissue which is responsible for transportation of substances. Blood works as the carrier of various substances. Following are the main components of blood.
Plasma: Plasma makes the liquid part of the blood. It makes the largest part of the blood. Plasma is pale in colour.
Blood Cells: There are two main kinds of blood cells in the human blood, viz. Red Blood Cells and White Blood Cells.
- Red Blood Cells or Red Blood Corpuscles (RBC): These are in the shape of discs. They contain a pigment; called haemoglobin. Haemobglobin binds with oxygen and thus is mainly responsible for transportation of oxygen in the body. Haemoglobin also transports some amount of carbon dioxide.
- White Blood Cells or White Blood Corpuscles (WBC): These are present in various shapes. WBCs engulf foreign particles and harmful microbes. Thus, WBCs help in fighting the diseases. WBCs make the immune system of the body.
Platelets: Platelets are responsible for clotting or coagulation of blood. In case of an injury, the blood clots after some time. This prevents excess loss of blood. Clotting of blood is a defense mechanism in the body.
Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are of three main types, viz. arteries, veins and capillaries. Arteries: Arteries are made of thicker walls. Arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to different organs. Pulmonary artery is an exception, because it carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Arteries: Arteries are made of thicker walls. Arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to different organs. Pulmonary artery is an exception, because it carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Veins: Veins are made of thinner walls. Veins carry deoxygenated blood from different organs to the heart. Pulmonary vein is an exception, because it carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Capillaries: Capillaries are very tiny blood vessels — so small that a single red blood cell can barely fit through them. They help to connect your arteries and veins in addition to facilitating the exchange of certain elements between your blood and tissues.
Review Questions
Q1. What is blood?
Answer: Blood is a type of tissue which is responsible for transportation of substances.
Q2. What is the role of RBCs?
Answer: Transportation of oxygen.
Heart
 Human Heart
Human HeartThe heart is a small muscular organ which is responsible for pumping the blood. The human heart has four chambers, viz. the right auricle, the right ventricle, the left auricle and the left ventricle. The upper chambers are called auricle or atrium. The lower chambers are called ventricle.
The following flow chart shows the movement of blood through the heart (the blue colour shows deoxygenated blood and the red colour shows oxygenated blood):
From the body → Right Auricle → Right Ventricle → Pulmonary Artery → Lungs → Pulmonary Vein → Left Auricle → Left Ventricle → To the body

Heartbeat
While pumping the blood, different chambers of the heart contract and relax in turns. The contraction and relaxation of different chambers produces a thumping sound. This sound can be heard as heart beat. One heart beat indicates one cycle of pumping action by all the four chambers. The heart of a normal human beats for 72 times in a minute. The heart pumps about 70 mL blood in one beat. This means that heart pumps a whopping 5 liter blood in a minute.
Pulse: At certain locations in the body, a pulse, similar to heart beat can be felt. This happens because of blood rushing in with every heart beat. The pulse rate is same as the heart rate. Pulse can be felt near the wrist, neck, ankle, etc.
Stethoscope: This is a device which is used by doctors to listen to the heart beat and pulse. Stethoscope is composed of a long rubber tube, two ear pieces and a diaphragm.
Review Questions
Q1. Which organ in the human body is responsible for pumping of blood?
Answer: heart
Q2. Which type of blood is carried by arteries?
Answer: Oxygenated Blood
Excretion in Animals
Various activities always go on inside the body of a living being. These activities are collectively called metabolism. Many harmful substances are created during metabolic activities. These substances can prove lethal if not removed from the body in time. Removal of waste from the body is called excretion.
Excretory System in Humans
 The human excretory system is composed of a pair of kidneys, two tubes; called ureter and a urinary bladder.
The human excretory system is composed of a pair of kidneys, two tubes; called ureter and a urinary bladder.Kidney: Kidneys are bean-shaped. They work like filters. Blood; laden with waste materials enters the kidney. The waste is filtered from the blood and the purified blood is sent to the normal circulation. The waste; along with water; is transferred to the urinary bladder through the ureters. The content of the ureter is called urine. Urine contains 95% water, 2.5% urea and 2.5% other wastes. Urine is expelled out from time to time.
Type of waste and mode of excretion: Protein is made up of nitrogen. Metabolism of protein creates nitrogenous wastes in the body. The nitrogenous waste is the main waste in animals. The nitrogenous waste takes different forms in different animals. These are; ammonia, urea and uric acid. Based on the type of nitrogenous waste, /animals can be divided into following categories:
Ammonotelic: Ammonia is the main nitrogenous waste in these animals. Lot of water is required for removal of ammonia. Ammonotelism is present in aquatic animals, e.g. fish, frogs, etc.
Ureotelism: Urea is the main nitrogenous waste in these animals. Less water is required for removal of urea. Ureotelism is present in mammals.
Urecotelism: Uric acid is the main nitrogenous waste in these animals. Removal of uric acid requires negligible amount of water. Urecotelism is present in reptiles and aves.
Note: Some of the wastes are removed along with sweat. Carbon dioxide is an important waste which is removed through the lungs.
Review Questions
Q1. Which is the main excretory organ in humans?
Answer: Kidneys
Q2. Which is the main excretory product in humans?
Answer: Urea
Transport of Substances in Plants
For transportation in plants, there are two main tissues, viz. xylem and phloem. These are composed of narrow tube-like structures. Xylem is responsible for transport of water, while phloem is responsible for transport of food.
Transport of Water
Plants take water from soil. Following are the main steps in transport of water in plants.
In Roots: From soil, the water enters the root hairs because of osmosis. From root hairs water enters further because of root pressure.
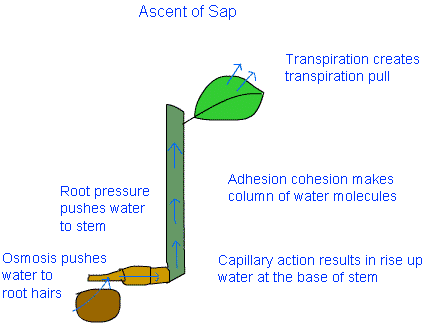
In stem: Various factors are at play during transportation of water through xylem in stems. The transport of water through xylem is also called ‘Ascent of Sap’.
- Root pressure is responsible for the rise of water to some height.
- Capillary action pushes the water further up. The rise of liquid in a very narrow tube is called capillary action. Capillary action happens because of very small diameter of the tube.
- Adhesion Cohesion: Water molecules stick to each other and make a continuous column inside the xylem tubes.
- Transpiration pull: There are numerous small pores on the surface of leaves. These pores are called stomata. Water vapour is continuously removed through stomata during daytime. Removal of water vapour in plants is called transpiration. This creates a pull in the underlying xylem tissues. The pull is called transpiration pull. Transpiration pull creates a suction effect on the water column inside the xylem.
Transport of Food: Food is prepared in leaves and needs to be transported to different plant parts for use and for storage. The transport of food takes place through phloem. Some biological force is used in transport of food in plants.
Review Questions
Q1. Transport of water and minerals in plants happens through which tissues?
Answer: Xylem
Q2. Transport of food in plants happens through which tissues?
Answer: Phloem
|
111 videos|246 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Transportation in Animals and Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 7
| 1. What is the primary function of the circulatory system in animals? |  |
| 2. How do plants transport substances, and what are the main components involved? |  |
| 3. What are the major organs involved in the excretion process in animals? |  |
| 4. How does the transport of substances differ between animals and plants? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system of animals? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|


















