NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 - Linear Inequalities
Exercise 5.1
Q1: Solve 24x < 100, when (i) x is a natural number (ii) x is an integer
Ans: The given inequality is 24x < 100.
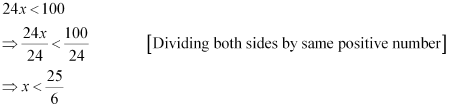
(i) It is evident that 1, 2, 3, and 4 are the only natural numbers less than 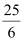 .
.
Thus, when x is a natural number, the solutions of the given inequality are 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Hence, in this case, the solution set is {1, 2, 3, 4}.
(ii) The integers less than 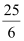 are …–3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
are …–3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
Thus, when x is an integer, the solutions of the given inequality are
…–3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
Hence, in this case, the solution set is {…–3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4}.
Q2: Solve –12x > 30, when
(i) x is a natural number (ii) x is an integer
Ans: The given inequality is –12x > 30.
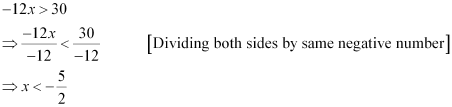
(i) There is no natural number less than 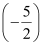 .
.
Thus, when x is a natural number, there is no solution of the given inequality.
(ii) The integers less than 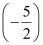 are …, –5, –4, –3.
are …, –5, –4, –3.
Thus, when x is an integer, the solutions of the given inequality are
…, –5, –4, –3.
Hence, in this case, the solution set is {…, –5, –4, –3}.
Q3: Solve 5x– 3 < 7, when
(i) x is an integer (ii) x is a real number
Ans: The given inequality is 5x– 3 < 7.
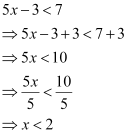
(i) The integers less than 2 are …, –4, –3, –2, –1, 0, 1.
Thus, when x is an integer, the solutions of the given inequality are
…, –4, –3, –2, –1, 0, 1.
Hence, in this case, the solution set is {…, –4, –3, –2, –1, 0, 1}.
(ii) When x is a real number, the solutions of the given inequality are given by x < 2, that is, all real numbers x which are less than 2.
Thus, the solution set of the given inequality is x ∈ (–∞, 2).
Q4: Solve 3x+8 > 2, when
(i) x is an integer (ii) x is a real number
Ans: The given inequality is 3x + 8 > 2.
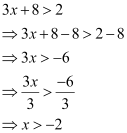
(i) The integers greater than –2 are –1, 0, 1, 2, …
Thus, when x is an integer, the solutions of the given inequality are
–1, 0, 1, 2 …
Hence, in this case, the solution set is {–1, 0, 1, 2, …}.
(ii) When x is a real number, the solutions of the given inequality are all the real numbers, which are greater than –2.
Thus, in this case, the solution set is (– 2, ∞).
Q5: Solve the given inequality for real x: 4x + 3 < 5x + 7
Ans: 4x + 3 < 5x + 7
⇒ 4x + 3 – 7 < 5x + 7 – 7
⇒ 4x – 4 < 5x
⇒ 4x – 4 – 4x < 5x – 4x
⇒ –4 < x
Thus, all real numbers x,which are greater than –4, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–4, ∞).
Q6: Solve the given inequality for real x: 3x – 7 > 5x – 1
Ans: 3x – 7 > 5x – 1
⇒ 3x – 7+ 7 > 5x – 1+ 7
⇒ 3x > 5x + 6
⇒ 3x – 5x > 5x + 6 – 5x
⇒ – 2x > 6
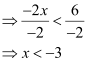
Thus, all real numbers x,which are less than –3, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–∞, –3).
Q7: Solve the given inequality for real x: 3(x – 1) ≤ 2 (x – 3)
Ans: 3(x – 1) ≤ 2(x – 3)
⇒ 3x – 3 ≤ 2x – 6
⇒ 3x – 3 +3 ≤ 2x – 6+ 3
⇒ 3x ≤ 2x – 3
⇒ 3x – 2x ≤ 2x – 3 – 2x
⇒ x ≤ – 3
Thus, all real numbers x,which are less than or equal to –3, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–∞, –3].
Q8: Solve the given inequality for real x: 3(2 – x) ≥ 2(1 – x)
Ans: 3(2 – x) ≥ 2(1 – x)
⇒ 6 – 3x ≥ 2 – 2x
⇒ 6 – 3x + 2x ≥ 2 – 2x + 2x
⇒ 6 – x ≥ 2
⇒ 6 – x – 6 ≥ 2 – 6
⇒ –x ≥ –4
⇒ x ≤ 4
Thus, all real numbers x,which are less than or equal to 4, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–∞, 4].
Q9: Solve the given inequality for real x: 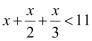
Ans:
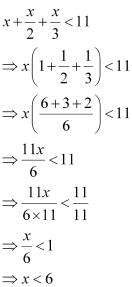
Thus, all real numbers x,which are less than 6, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–∞, 6).
Q10: Solve the given inequality for real x: 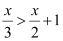
Ans:
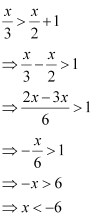
Thus, all real numbers x,which are less than –6, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–∞, –6).
Q11: Solve the given inequality for real x: 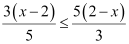
Ans:
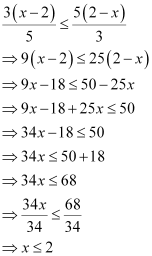
Thus, all real numbers x,which are less than or equal to 2, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–∞, 2].
Q12: Solve the given inequality for real x: 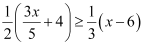
Ans:
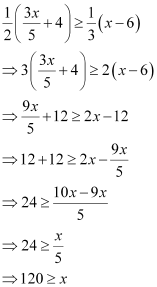
Thus, all real numbers x,which are less than or equal to 120, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–∞, 120].
Q13: Solve the given inequality for real x: 2(2x +3) – 10 < 6 (x – 2)
Ans:
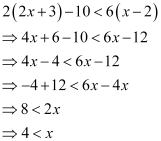
Thus, all real numbers x,which are greater than or equal to 4, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is [4, ∞).
Q14: Solve the given inequality for real x: 37 – (3x + 5) ≥ 9x – 8(x – 3)
Ans:
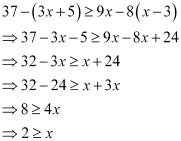
Thus, all real numbers x,which are less than or equal to 2, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–∞, 2].
Q15: Solve the given inequality for real x: 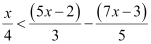
Ans:
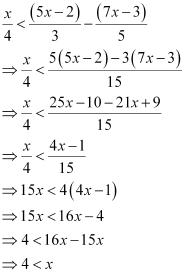
Thus, all real numbers x,which are greater than 4, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (4, ∞).
Q16: Solve the given inequality for real x: 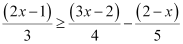
Ans:
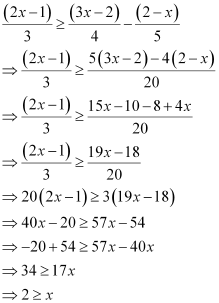
Thus, all real numbers x,which are less than or equal to 2, are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is (–∞, 2].
Q17: Solve the given inequality and show the graph of the solution on number line: 3x – 2 < 2x + 1
Ans: 3x – 2 < 2x + 1
⇒ 3x – 2x < 1 + 2
⇒ x < 3
The graphical representation of the solutions of the given inequality is as follows.
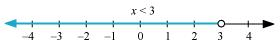
Q18: Solve the given inequality and show the graph of the solution on number line: 5x – 3 ≥ 3x – 5
Ans:
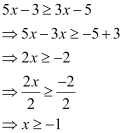
The graphical representation of the solutions of the given inequality is as follows.
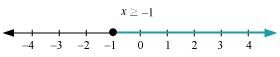
Q19: Solve the given inequality and show the graph of the solution on number line: 3(1 – x) < 2 (x + 4)
Ans:
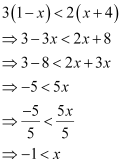
The graphical representation of the solutions of the given inequality is as follows.
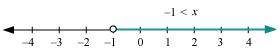
Q20: Solve the given inequality and show the graph of the solution on number line: 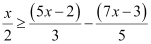
Ans:
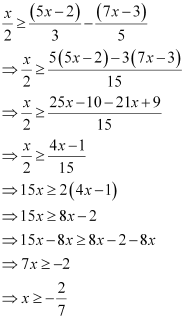
The graphical representation of the solutions of the given inequality is as follows.
Q21: Ravi obtained 70 and 75 marks in first two unit test. Find the minimum marks he should get in the third test to have an average of at least 60 marks.
Ans: Let x be the marks obtained by Ravi in the third unit test.
Since the student should have an average of at least 60 marks,
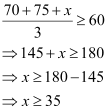
Thus, the student must obtain a minimum of 35 marks to have an average of at least 60 marks.
Q22: To receive Grade ‘A’ in a course, one must obtain an average of 90 marks or more in five examinations (each of 100 marks). If Sunita’s marks in first four examinations are 87, 92, 94 and 95, find minimum marks that Sunita must obtain in fifth examination to get grade ‘A’ in the course.
Ans: Let x be the marks obtained by Sunita in the fifth examination.
In order to receive grade ‘A’ in the course, she must obtain an average of 90 marks or more in five examinations.
Therefore,
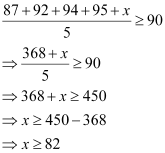
Thus, Sunita must obtain greater than or equal to 82 marks in the fifth examination.
Q23: Find all pairs of consecutive odd positive integers both of which are smaller than 10 such that their sum is more than 11.
Ans: Let x be the smaller of the two consecutive odd positive integers. Then, the other integer is
x + 2.
Since both the integers are smaller than 10,
x + 2 < 10
⇒ x < 10 – 2
⇒ x < 8 … (i)
Also, the sum of the two integers is more than 11.
∴ x + (x + 2) > 11
⇒ 2x + 2 > 11
⇒ 2x > 11 – 2
⇒ 2x > 9

From (i) and (ii), we obtain .
Since x is an odd number, x can take the values, 5 and 7.
Thus, the required possible pairs are (5, 7) and (7, 9).
Q24: Find all pairs of consecutive even positive integers, both of which are larger than 5 such that their sum is less than 23.
Ans: Let x be the smaller of the two consecutive even positive integers. Then, the other integer is x+ 2.
Since both the integers are larger than 5,
x > 5 ... (1)
Also, the sum of the two integers is less than 23.
x + (x + 2) < 23
⇒ 2x + 2 < 23
⇒ 2x < 23 – 2
⇒ 2x < 21

From (1) and (2), we obtain 5 < x < 10.5.
Since x is an even number, x can take the values, 6, 8, and 10.
Thus, the required possible pairs are (6, 8), (8, 10), and (10, 12).
Q25: The longest side of a triangle is 3 times the shortest side and the third side is 2 cm shorter than the longest side. If the perimeter of the triangle is at least 61 cm, find the minimum length of the shortest side.
Ans: Let the length of the shortest side of the triangle be x cm.
Then, length of the longest side = 3x cm
Length of the third side = (3x – 2) cm
Since the perimeter of the triangle is at least 61 cm,
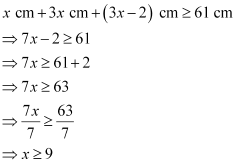
Thus, the minimum length of the shortest side is 9 cm.
Q26: A man wants to cut three lengths from a single piece of board of length 91 cm. The second length is to be 3 cm longer than the shortest and the third length is to be twice as long as the shortest. What are the possible lengths of the shortest board if the third piece is to be at least 5 cm longer than the second?
[Hint: If x is the length of the shortest board, then x, (x + 3) and 2x are the lengths of the second and third piece, respectively. Thus, x = (x + 3)+ 2x ≤ 91 and 2x ≥ (x + 3) +5]
Ans: Let the length of the shortest piece be x cm. Then, length of the second piece and the third piece are (x + 3) cm and 2x cm respectively.
Since the three lengths are to be cut from a single piece of board of length 91 cm,
x cm+ (x + 3) cm + 2x cm ≤ 91 cm
⇒ 4x + 3 ≤ 91
⇒ 4x ≤ 91 – 3
⇒ 4x ≤ 88

Also, the third piece is at least 5 cm longer than the second piece.
∴ 2x ≥ (x + 3)+ 5
⇒ 2x ≥ x + 8
⇒ x ≥ 8 … (2)
From (1) and (2), we obtain
8 ≤ x ≤ 22
Thus, the possible length of the shortest board is greater than or equal to 8 cm but less than or equal to 22 cm.
Miscellaneous Exercise
Q1: Solve the inequality 2 ≤ 3x – 4 ≤ 5
Ans: 2 ≤ 3x – 4 ≤ 5
⇒ 2 +4 ≤ 3x – 4+ 4 ≤ 5 +4
⇒ 6 ≤ 3x ≤ 9
⇒ 2 ≤ x ≤ 3
Thus, all the real numbers, x, which are greater than or equal to 2 but less than or equal to 3, are the solutions of the given inequality. The solution set for the given inequality is [2, 3].
Q2: Solve the inequality 6 ≤ –3(2x – 4) < 12
Ans: 6 ≤ – 3(2x – 4) < 12
⇒ 2 ≤ –(2x – 4) < 4
⇒ –2 ≥ 2x – 4 > –4
⇒ 4 – 2 ≥ 2x > 4 – 4
⇒ 2 ≥ 2x > 0
⇒1 ≥ x > 0
Thus, the solution set for the given inequalityis (0, 1].
Q3: Solve the inequality 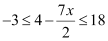
Ans:
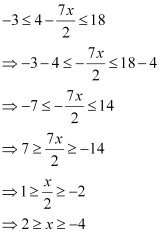
Thus, the solution set for the given inequalityis [–4, 2].
Q4: Solve the inequality 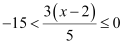
Ans:
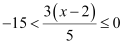
⇒ –75 < 3(x – 2) ≤ 0
⇒ –25 < x – 2 ≤ 0
⇒ – 25+ 2 < x ≤ 2
⇒ –23 < x ≤ 2
Thus, the solution set for the given inequalityis (–23, 2].
Q5: Solve the inequality 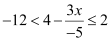
Ans:
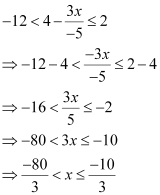
Thus, the solution set for the given inequality is 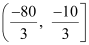 .
.
Q6: Solve the inequality 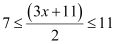
Ans:
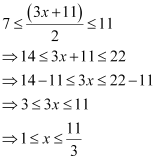
Thus, the solution set for the given inequality is 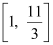 .
.
Q7: Solve the inequalities and represent the solution graphically on number line: 5x + 1 > –24, 5x – 1 < 24
Ans: ⇒ 5x + 1 > –24
⇒ 5x > –25
⇒ x > –5 … (1)
5x – 1 < 24
⇒ 5x < 25
⇒ x < 5 … (2)
From (1) and (2), it can be concluded that the solution set for the given system of inequalities is (–5, 5). The solution of the given system of inequalities can be represented on number line as
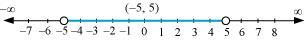
Q8: Solve the inequalities and represent the solution graphically on number line: 2(x – 1) < x + 5, 3(x + 2) > 2 – x
Ans: 2(x – 1) < x + 5
⇒ 2x – 2 < x + 5
⇒ 2x – x < 5+ 2
⇒ x < 7 … (1)
3(x + 2) > 2 – x
⇒ 3x + 6 > 2 – x
⇒ 3x + x > 2 – 6
⇒ 4x > – 4
⇒ x > – 1 … (2)
From (1) and (2), it can be concluded that the solution set for the given system of inequalities is (–1, 7). The solution of the given system of inequalities can be represented on number line as
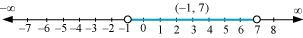
Q9: Solve the following inequalities and represent the solution graphically on number line:
3x – 7 > 2(x – 6), 6 – x > 11 – 2x
Ans: 3x – 7 > 2(x – 6)
⇒ 3x – 7 > 2x – 12
⇒ 3x – 2x > – 12 +7
⇒ x > –5 … (1)
6 – x > 11 – 2x
⇒ –x + 2x > 11 – 6
⇒ x > 5 … (2)
From (1) and (2), it can be concluded that the solution set for the given system of inequalities is 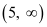 . The solution of the given system of inequalities can be represented on number line as
. The solution of the given system of inequalities can be represented on number line as
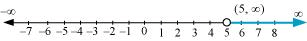
Q10: Solve the inequalities and represent the solution graphically on number line: 5(2x – 7) – 3(2x + 3) ≤ 0, 2x + 19 ≤ 6x +47
Ans: 5(2x – 7) – 3(2x + 3) ≤ 0
⇒ 10x – 35 – 6x – 9 ≤ 0
⇒ 4x – 44 ≤ 0
⇒ 4x ≤ 44
⇒ x ≤ 11 … (1)
2x + 19 ≤ 6x + 47
⇒ 19 – 47 ≤ 6x – 2x
⇒ –28 ≤ 4x
⇒ –7 ≤ x … (2)
From (1) and (2), it can be concluded that the solution set for the given system of inequalities is [–7, 11]. The solution of the given system of inequalities can be represented on number line as
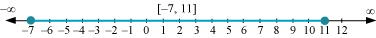
Q11: A solution is to be kept between 68°F and 77°F. What is the range in temperature in degree Celsius (C) if the Celsius/Fahrenheit (F) conversion formula is given by 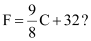
Ans: Since the solution is to be kept between 68°F and 77°F,
68 < F < 77
Putting 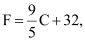 we obtain
we obtain
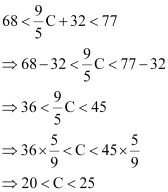
Thus, the required range of temperature in degree Celsius is between 20°C and 25°C.
Q12: A solution of 8% boric acid is to be diluted by adding a 2% boric acid solution to it. The resulting mixture is to be more than 4% but less than 6% boric acid. If we have 640 litres of the 8% solution, how many litres of the 2% solution will have to be added?
Ans: Let x litres of 2% boric acid solution is required to be added.
Then, total mixture = (x + 640) litres
This resulting mixture is to be more than 4% but less than 6% boric acid.
∴ 2%x + 8% of 640 > 4% of (x + 640)
And, 2% x + 8% of 640 < 6% of (x + 640)
2%x + 8% of 640 > 4% of (x + 640)
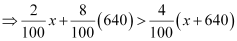
⇒ 2x + 5120 > 4x + 2560
⇒ 5120 – 2560 > 4x – 2x
⇒ 5120 – 2560 > 2x
⇒ 2560 > 2x
⇒ 1280 > x
2% x + 8% of 640 < 6% of (x 640)
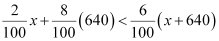
⇒ 2x + 5120 < 6x + 3840
⇒ 5120 – 3840 < 6x – 2x
⇒ 1280 < 4x
⇒ 320 < x
∴ 320 < x < 1280
Thus, the number of litres of 2% of boric acid solution that is to be added will have to be more than 320 litres but less than 1280 litres.
Q13: How many litres of water will have to be added to 1125 litres of the 45% solution of acid so that the resulting mixture will contain more than 25% but less than 30% acid content?
Ans: Let x litres of water is required to be added.
Then, total mixture = (x + 1125) litres
It is evident that the amount of acid contained in the resulting mixture is 45% of 1125 litres.
This resulting mixture will contain more than 25% but less than 30% acid content.
∴ 30% of (1125 + x) > 45% of 1125
And, 25% of (1125 + x) < 45% of 1125
30% of (1125 + x) > 45% of 1125
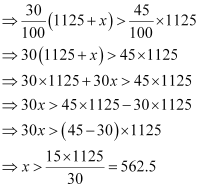
25% of (1125 + x) < 45% of 1125
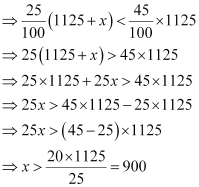
∴ 562.5 < x < 900
Thus, the required number of litres of water that is to be added will have to be more than 562.5 but less than 900.
Q14: IQ of a person is given by the formula
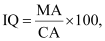
Where MA is mental age and CA is chronological age. If 80 ≤ IQ ≤ 140 for a group of 12 years old children, find the range of their mental age.
Ans: It is given that for a group of 12 years old children, 80 ≤ IQ ≤ 140 … (i)
For a group of 12 years old children, CA = 12 years
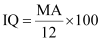
Putting this value of IQ in (i), we obtain

Thus, the range of mental age of the group of 12 ye
Old NCERT Questions
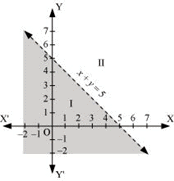
Q1: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: x + y < 5
Ans: The graphical representation of x + y = 5 is given as dotted line in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes, I and II.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
0 +0 < 5 or, 0 < 5, which is true
Therefore, half plane II is not the solution region of the given inequality. Also, it is evident that any point on the line does not satisfy the given strict inequality.
Thus, the solution region of the given inequality is the shaded half plane I excluding the points on the line.
This can be represented as follows.
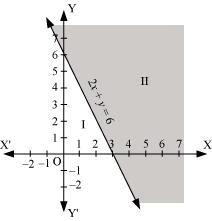
Q2: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: 2x + y ≥ 6
Ans: The graphical representation of 2x + y = 6 is given in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes, I and II.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
2(0) 0 ≥ 6 or 0 ≥ 6, which is false
Therefore, half plane I is not the solution region of the given inequality. Also, it is evident that any point on the line satisfies the given inequality.
Thus, the solution region of the given inequality is the shaded half plane II including the points on the line.
This can be represented as follows.
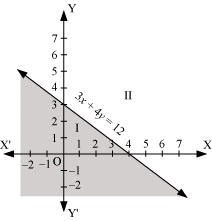
Q3: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: 3x + 4y ≤ 12
Ans: 3x + 4y ≤ 12
The graphical representation of 3x + 4y = 12 is given in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes, I and II.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
3(0) +4(0) ≤ 12 or 0 ≤ 12, which is true
Therefore, half plane II is not the solution region of the given inequality. Also, it is evident that any point on the line satisfies the given inequality.
Thus, the solution region of the given inequality is the shaded half plane I including the points on the line.
This can be represented as follows.
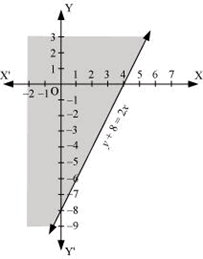
Q4: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: y + 8 ≥ 2x
Ans: The graphical representation of y 8 = 2x is given in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
0 +8 ≥ 2(0) or 8 ≥ 0, which is true
Therefore, lower half plane is not the solution region of the given inequality. Also, it is evident that any point on the line satisfies the given inequality.
Thus, the solution region of the given inequality is the half plane containing the point (0, 0) including the line.
The solution region is represented by the shaded region as follows.
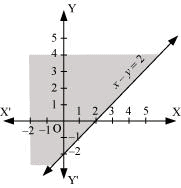
Q5: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: x – y ≤ 2
Ans: The graphical representation of x – y = 2 is given in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
0 – 0 ≤ 2 or 0 ≤ 2, which is true
Therefore, the lower half plane is not the solution region of the given inequality. Also, it is clear that any point on the line satisfies the given inequality.
Thus, the solution region of the given inequality is the half plane containing the point (0, 0) including the line.
The solution region is represented by the shaded region as follows.
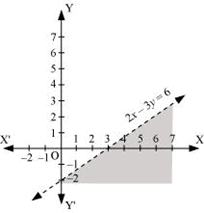
Q6: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: 2x – 3y > 6
Ans: The graphical representation of 2x – 3y = 6 is given as dotted line in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
2(0) – 3(0) > 6 or 0 > 6, which is false
Therefore, the upper half plane is not the solution region of the given inequality. Also, it is clear that any point on the line does not satisfy the given inequality.
Thus, the solution region of the given inequality is the half plane that does not contain the point (0, 0) excluding the line.
The solution region is represented by the shaded region as follows.
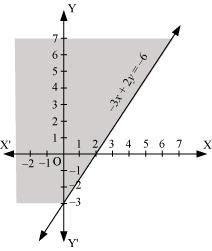
 Q7: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: –3x + 2y ≥ –6
Q7: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: –3x + 2y ≥ –6
Ans: The graphical representation of – 3x + 2y = – 6 is given in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
– 3(0) 2(0) ≥ – 6 or 0 ≥ –6, which is true
Therefore, the lower half plane is not the solution region of the given inequality. Also, it is evident that any point on the line satisfies the given inequality.
Thus, the solution region of the given inequality is the half plane containing the point (0, 0) including the line.
The solution region is represented by the shaded region as follows.
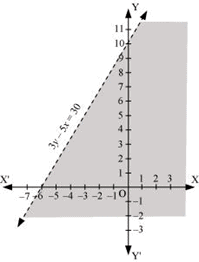
Q8: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: 3y – 5x < 30
Ans: The graphical representation of 3y – 5x = 30 is given as dotted line in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
3(0) – 5(0) < 30 or 0 < 30, which is true
Therefore, the upper half plane is not the solution region of the given inequality. Also, it is evident that any point on the line does not satisfy the given inequality.
Thus, the solution region of the given inequality is the half plane containing the point (0, 0) excluding the line.
The solution region is represented by the shaded region as follows.
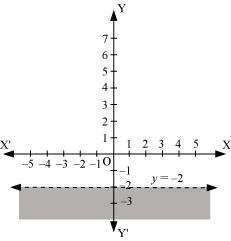
Q9: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: y < –2
Ans: The graphical representation of y = –2 is given as dotted line in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
0 < –2, which is false
Also, it is evident that any point on the line does not satisfy the given inequality.
Hence, every point below the line, y = –2 (excluding all the points on the line), determines the solution of the given inequality.
The solution region is represented by the shaded region as follows.
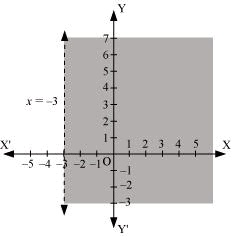
 Q10: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: x > –3
Q10: Solve the given inequality graphically in two-dimensional plane: x > –3
Ans: The graphical representation of x = –3 is given as dotted line in the figure below.
This line divides the xy-plane in two half planes.
Select a point (not on the line), which lies in one of the half planes, to determine whether the point satisfies the given inequality or not.
We select the point as (0, 0).
It is observed that,
0 > –3, which is true
Also, it is evident that any point on the line does not satisfy the given inequality.
Hence, every point on the right side of the line, x = –3 (excluding all the points on the line), determines the solution of the given inequality.
The solution region is represented by the shaded region as follows.
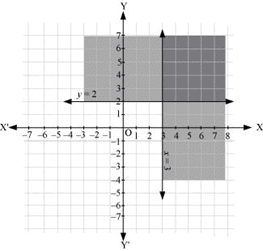
Q11: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: x ≥ 3, y ≥ 2
Ans: x ≥ 3 … (1)
y ≥ 2 … (2)
The graph of the lines, x = 3 and y = 2, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region on the right hand side of the line, x = 3 (including the line x = 3), and inequality (2) represents the region above the line, y = 2 (including the line y = 2).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the respective lines as follows.
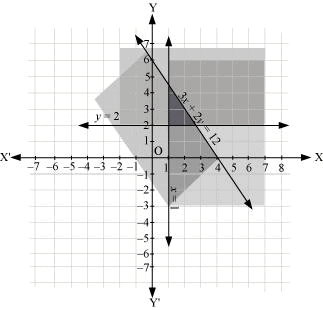
Q12: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x ≥ 1, y ≥ 2
Ans: 3x + 2y ≤ 12 … (1)
x ≥ 1 … (2)
y ≥ 2 … (3)
The graphs of the lines, 3x + 2y = 12, x = 1, and y = 2, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region below the line, 3x + 2y = 12 (including the line 3x + 2y = 12).
Inequality (2) represents the region on the right side of the line, x = 1 (including the line x = 1).
Inequality (3) represents the region above the line, y = 2 (including the line y = 2).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the respective lines as follows.
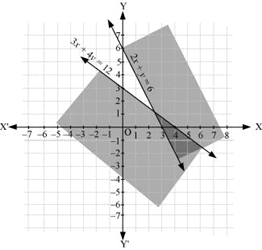
Q13: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: 2x y≥ 6, 3x 4y ≤ 12
Ans: 2x + y≥ 6 … (1)
3x + 4y ≤ 12 … (2)
The graph of the lines, 2x + y= 6 and 3x + 4y = 12, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region above the line, 2x + y= 6 (including the line 2x + y= 6), and inequality (2) represents the region below the line, 3x + 4y =12 (including the line 3x + 4y =12).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the respective lines as follows.
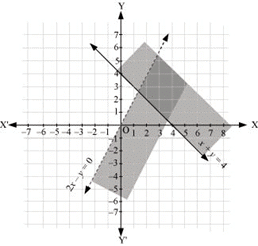
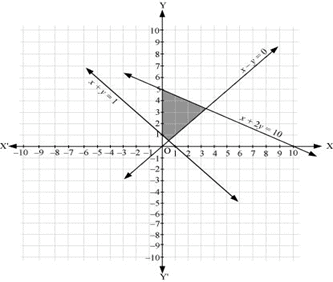
Q14: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: x + y≥ 4, 2x – y > 0
Ans: x + y≥ 4 … (1)
2x – y > 0 … (2)
The graph of the lines, x + y = 4 and 2x – y = 0, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region above the line, x + y = 4 (including the line x + y = 4).
It is observed that (1, 0) satisfies the inequality, 2x – y > 0. [2(1) – 0 = 2 > 0]
Therefore, inequality (2) represents the half plane corresponding to the line, 2x – y = 0, containing the point (1, 0) [excluding the line 2x – y > 0].
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on line x + y = 4 and excluding the points on line 2x – y = 0 as follows.
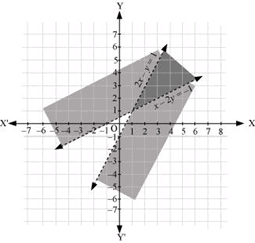
Q15: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: 2x – y > 1, x – 2y < –1
Ans: 2x – y > 1 … (1)
x – 2y < –1 … (2)
The graph of the lines, 2x – y = 1 and x – 2y = –1, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region below the line, 2x – y = 1 (excluding the line 2x – y = 1), and inequality (2) represents the region above the line, x – 2y = –1 (excluding the line x – 2y = –1).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region excluding the points on the respective lines as follows.
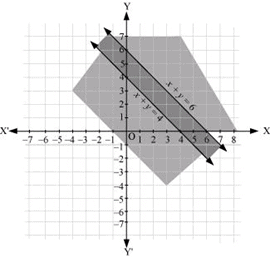
Q16: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: x + y ≤ 6, x + y ≥ 4
Ans: x + y ≤ 6 … (1)
x + y ≥ 4 … (2)
The graph of the lines, x y = 6 and x y = 4, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region below the line, x + y = 6 (including the line x + y = 6), and inequality (2) represents the region above the line, x + y = 4 (including the line x + y = 4).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the respective lines as follows.
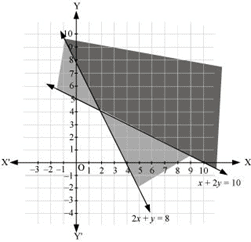
Q17: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: 2x + y≥ 8, x + 2y ≥ 10
Ans: 2x + y= 8 … (1)
x + 2y = 10 … (2)
The graph of the lines, 2x + y= 8 and x + 2y = 10, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region above the line, 2x + y = 8, and inequality (2) represents the region above the line, x + 2y = 10.
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the respective lines as follows.
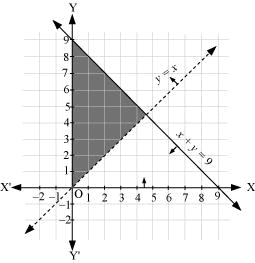
Q18 Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: x + y ≤ 9, y > x, x ≥ 0
Ans: x + y ≤ 9... (1)
y > x ... (2)
x ≥ 0 ... (3)
The graph of the lines, x + y= 9 and y = x, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region below the line, x + y = 9 (including the line x + y = 9).
It is observed that (0, 1) satisfies the inequality, y > x. [1 > 0]
Therefore, inequality (2) represents the half plane corresponding to the line, y = x, containing the point (0, 1) [excluding the line y = x].
Inequality (3) represents the region on the right hand side of the line, x = 0 or y-axis (including y-axis).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the lines, x y = 9 and x = 0, and excluding the points on line y = x as follows.
Q19: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: 5x + 4y ≤ 20, x ≥ 1, y ≥ 2
Ans: 5x + 4y ≤ 20 … (1)
x ≥ 1 … (2)
y ≥ 2 … (3)
The graph of the lines, 5x 4y = 20, x = 1, and y = 2, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region below the line, 5x + 4y = 20 (including the line 5x + 4y = 20).
Inequality (2) represents the region on the right hand side of the line, x = 1 (including the line x = 1).
Inequality (3) represents the region above the line, y = 2 (including the line y = 2).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the respective lines as follows.
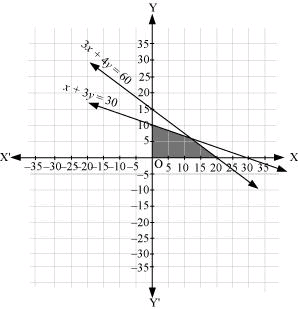
Q20: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: 3x + 4y ≤ 60, x 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Ans: 3x + 4y ≤ 60 … (1)
x + 3y ≤ 30 … (2)
The graph of the lines, 3x + 4y = 60 and x + 3y = 30, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region below the line, 3x + 4y = 60 (including the line 3x + 4y = 60), and inequality (2) represents the region below the line, x + 3y = 30 (including the line x + 3y = 30).
Since x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0, every point in the common shaded region in the first quadrant including the points on the respective line and the axes represents the solution of the given system of linear inequalities.
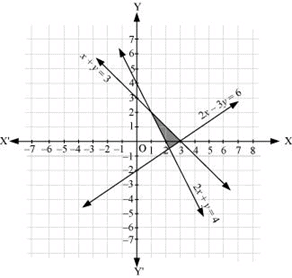
Q21: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: 2x + y ≥ 4, x + y ≤ 3, 2x – 3y ≤ 6
Ans: 2x + y≥ 4 … (1)
x + y ≤ 3 … (2)
2x – 3y ≤ 6 … (3)
The graph of the lines, 2x y= 4, x y = 3, and 2x – 3y = 6, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region above the line, 2x + y= 4 (including the line 2x + y= 4).
Inequality (2) represents the region below the line, x + y = 3 (including the line x + y = 3).
Inequality (3) represents the region above the line, 2x – 3y = 6 (including the line 2x – 3y = 6).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the respective lines as follows.
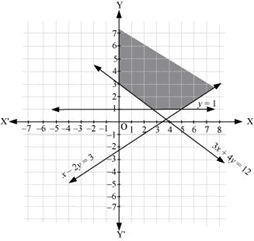
Q22: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically:
x – 2y ≤ 3, 3x +4y ≥ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 1
Ans: x – 2y ≤ 3 … (1)
3x + 4y ≥ 12 … (2)
y ≥ 1 … (3)
The graph of the lines, x – 2y = 3, 3x + 4y = 12, and y = 1, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region above the line, x – 2y = 3 (including the line x – 2y = 3).
Inequality (2) represents the region above the line, 3x + 4y = 12 (including the line 3x + 4y= 12).
Inequality (3) represents the region above the line, y = 1 (including the line y = 1).
The inequality, x ≥ 0, represents the region on the right hand side of y-axis (including y-axis).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the respective lines and y- axis as follows.
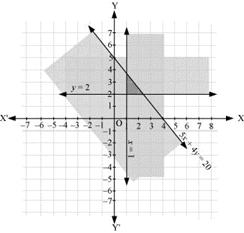
Q23: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically:
4x + 3y ≤ 60, y ≥ 2x, x ≥ 3, x, y ≥ 0
Ans: 4x + 3y ≤ 60 … (1)
y ≥ 2x … (2)
x ≥ 3 … (3)
The graph of the lines, 4x 3y = 60, y = 2x, and x = 3, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region below the line, 4x + 3y = 60 (including the line 4x 3y = 60).
Inequality (2) represents the region above the line, y = 2x (including the line y = 2x).
Inequality (3) represents the region on the right hand side of the line, x = 3 (including the line x = 3).
Hence, the solution of the given system of linear inequalities is represented by the common shaded region including the points on the respective lines as follows.
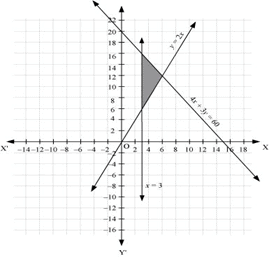 Q24: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: 3x + 2y ≤ 150,
Q24: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: 3x + 2y ≤ 150,
x +4y ≤ 80, x ≤ 15, y ≥ 0, x ≥ 0
Ans: 3x + 2y ≤ 150 … (1)
x + 4y ≤ 80 … (2)
x ≤ 15 … (3)
The graph of the lines, 3x + 2y = 150, x + 4y = 80, and x = 15, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region below the line, 3x + 2y = 150 (including the line 3x + 2y = 150).
Inequality (2) represents the region below the line, x + 4y = 80 (including the line x+ 4y = 80).
Inequality (3) represents the region on the left hand side of the line, x = 15 (including the line x = 15).
Since x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0, every point in the common shaded region in the first quadrant including the points on the respective lines and the axes represents the solution of the given system of linear inequalities.
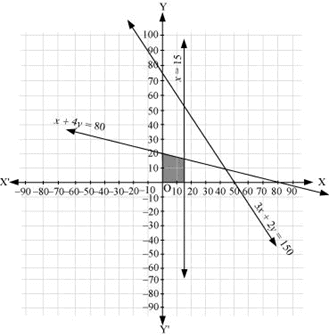
Q25: Solve the following system of inequalities graphically: x + 2y ≤ 10,
x + y ≥ 1, x – y ≤ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Ans: x + 2y ≤ 10 … (1)
x + y ≥ 1 … (2)
x – y ≤ 0 … (3)
The graph of the lines, x + 2y = 10, x + y = 1, and x – y = 0, are drawn in the figure below.
Inequality (1) represents the region below the line, x + 2y = 10 (including the line x + 2y = 10).
Inequality (2) represents the region above the line, x + y = 1 (including the line x + y = 1).
Inequality (3) represents the region above the line, x – y = 0 (including the line x – y = 0).
Since x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0, every point in the common shaded region in the first quadrant including the points on the respective lines and the axes represents the solution of the given system of linear inequalities.
ars old children is 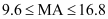 .
.
|
172 videos|503 docs|154 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 - Linear Inequalities
| 1. What are linear inequalities and how do they differ from linear equations? |  |
| 2. How can I solve a linear inequality graphically? |  |
| 3. Can you provide an example of a real-life situation that can be modeled using linear inequalities? |  |
| 4. What are the steps to solve a linear inequality algebraically? |  |
| 5. How do you represent the solution of a linear inequality on a number line? |  |

















