Reproduction in Human Beings | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Reproduction? |

|
| Types of Reproduction |

|
| Reproduction in Human Beings |

|
| Reproductive Health |

|
| Population Control Methods |

|
| Competitive Window |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions |

|
What is Reproduction?
Reproduction is the process of producing offsprings that are biologically or genetically similar to the parent organism.
- Reproduction means to reproduce. It is a biological process by which an organism reproduces an offspring who is biologically similar to the organism.
- Reproduction enables and ensures the continuity of species, generation after generation. It is the main feature of life on earth.
Types of Reproduction
There are basically two types of reproduction:
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction refers to the type of reproduction in which only a single organism gives rise to a new individual.
- Asexual reproduction does not involve the fusion of gametes, and therefore, the offsprings produced are genetically identical to the parent. The organisms produced by asexual reproduction are less diverse in nature. This type of reproduction is practised widely by unicellular organisms.
- The process involves rapid population growth and no mate is required for the process. However, a lack of genetic diversity makes the organisms more susceptible to diseases and nutrition deficiencies.
Asexual reproduction is further divided into:
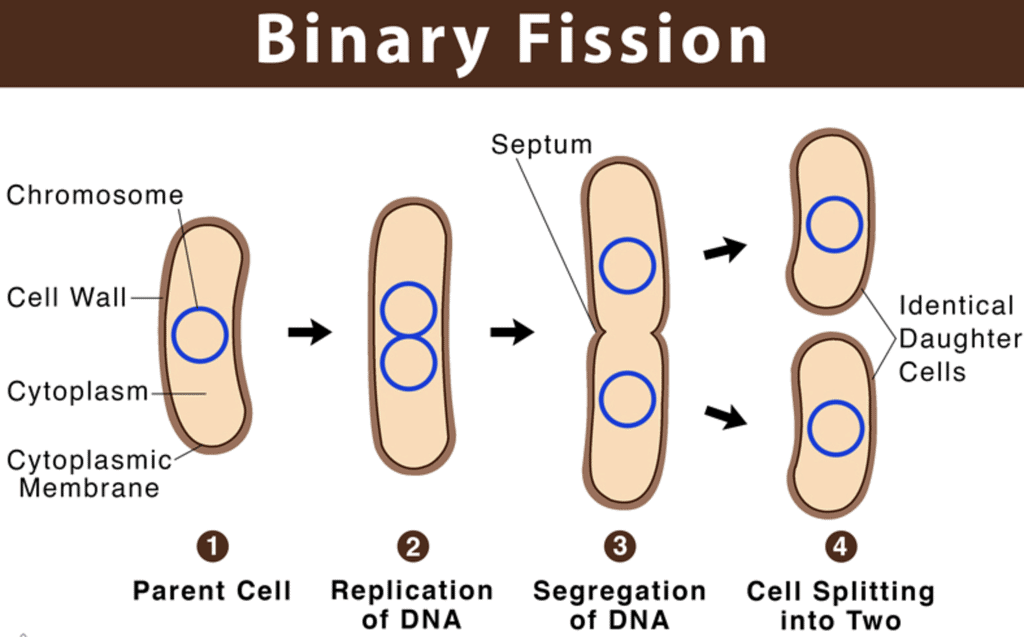
- Binary Fission: In this, the cell splits into two each cell carrying a copy of the DNA from the parent cell. Example: Amoeba
- Budding: In this, a small bud-like outgrowth gives rise to a new individual. The outgrowth remains attached to the organism until it is fully grown. It detaches itself as lives as an individual organism. Example: Hydra
- Fragmentation: In this, the parent organism splits into several parts and each part grows into a new individual. Example: Planaria
- Sporogenesis: In this type of reproduction, a new organism grows from the spores. These can be created without fertilization and can spread through wind and animals.
Sexual Reproduction
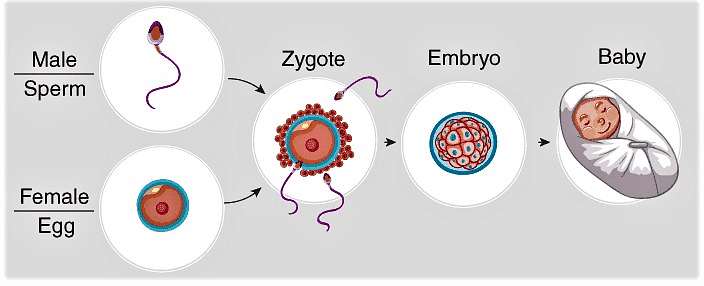
The type of reproduction in which the fusion of male gamete & female gamete occurs is called sexual reproduction.
Important features of sexual reproduction are given below:
- It involves two different parents, i.e. one male and one female.
- Each parent produces gametes.
- Male gametes are called sperms, while female gametes are called ova or eggs.
- The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilization. It results in the formation of a single diploid cell zygote.
- The zygote undergoes repeated mitotic divisions to form an embryo which differentiates to form a full organism.
- The organism produced in this type of reproduction are genetically different from both the parents and can resemble certain features with parents.
What is Puberty?
The age at which the gametes and sex hormones start getting produced and the boy and girl become sexually mature is called puberty.
➢ Pubertal Changes (Secondary Sexual Characters) in Male:
- Widening of shoulders.
- Deepening of voice.
- Growth of hairs under chest, armpits and around the pubic area.
- The appearance of beard and moustaches.
- Growth of sex organs, [Testes & Penis].
- Increased activity of sweat and sebaceous glands.
- Oily skin and appearance of pimples.
- Darkening in skin colour of the genital area.
➢ Pubertal Changes (Secondary Sexual Characters) in Female:
- Widening of pelvis and hips.
- High pitch voice.
- Growth of hairs under armpits and around the pubic area.
- Initiation of the menstrual cycle.
- Growth of mammary glands (breasts).
- Darkening in skin colour of the genital area.
- Maturation of secondary sex organs like fallopian tubes, uterus.
Reproduction in Human Beings
Reproduction in human beings involves the fusion of male and female gametes produced in their reproductive system. The male reproductive system is different from the female reproductive system, both in structure and in function.
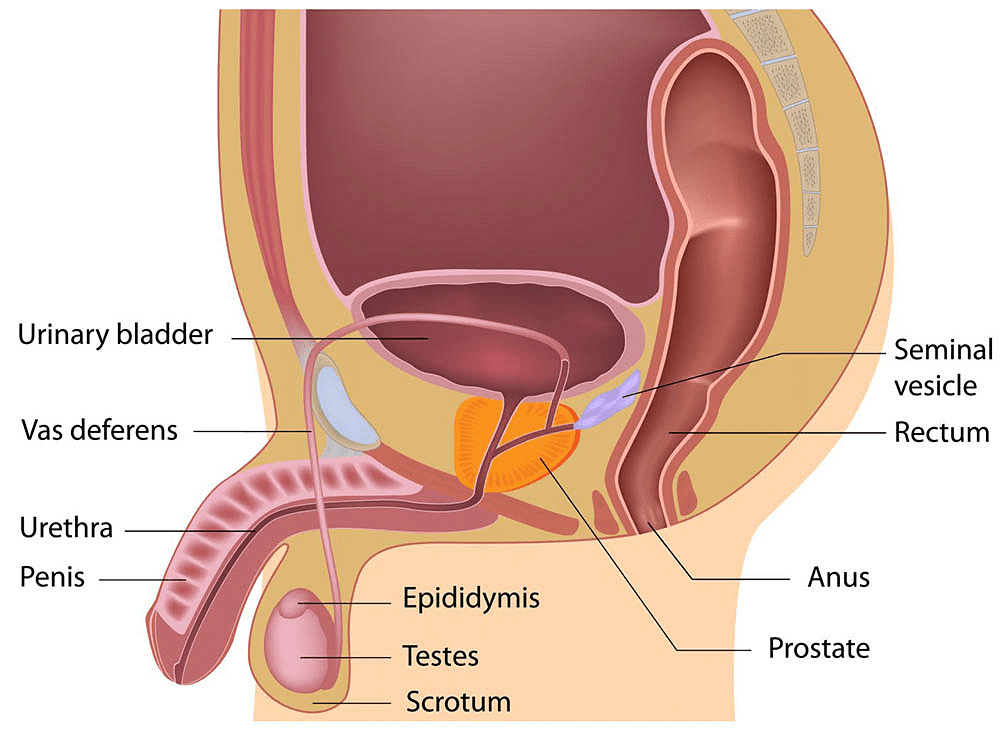
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system consists of portions that produce the germ cells and other portions that deliver the germ cells to the site of fertilization.
- The formation of germ cells or sperms takes place in the testis. These are located outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature [13°C] than the normal body temperature.

- Testes secrete a male sex hormone called testosterone. In addition to regulating the formation of sperms, testosterone brings about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. These changes are called secondary sexual characters.
- The sperms formed are delivered through the vas deferens which unites with a tube coming from the urinary bladder. The urethra thus forms a common passage for both the sperms and urine. Hence urethra is also known as a urinogenital tract.
- Along the path of the vas deferens, glands like the prostate gland and the seminal vesicle add their secretions so that the sperms are now in a fluid that makes their transport easier and this fluid also provides nutrition.
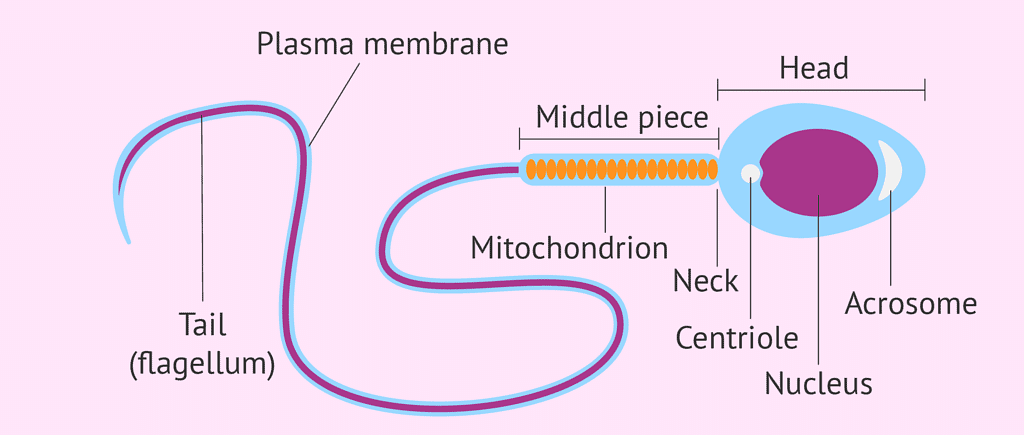
 Structure of Sperm
Structure of Sperm - The sperms are tiny bodies consisting of mainly genetic material and a long tail that helps them move towards the female germ cell (ovum).Question for Reproduction in Human BeingsTry yourself:In human males, the testes lie in the scrotum, because it helps in the:View Solution
The male reproductive system consists of :
- Testicles (testes): A pair of oval-shaped organs masked in a pouch called the scrotum. They are responsible for the production of sperms and the male hormone testosterone.
- Scrotum: It is a sac-like organ that hangs below the penis and behind it. It is the houses of the testicles, or testes, and maintains a temperature that is required for the production of sperm by it.
- Vas deferens: The sperms produced in testes are stored in a tube called the epididymis. Here the sperms get matured and pass to the urethra through the muscular tube called vas deferens.
- Accessory glands: This includes three glands, namely seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and Cowper’s gland. The secretions from the three glands mix to form a fluid called semen. Semen nourishes the sperm, increases the volume and helps in lubrication.
- Penis: The penis is a cylindrical tube that serves as both a reproductive organ and an excretory organ. It delivers sperms into the vagina during sexual intercourse.
Female Reproductive System
- The female germ cells or eggs are made in the ovaries. They are also responsible for the production of female sex hormones, i.e., Oestrogen and Progesterone.
- When a girl child is born, the ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs. On reaching puberty, some of these start maturing. One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
- The egg is carried from the ovary to the womb through a thin oviduct or fallopian tube.
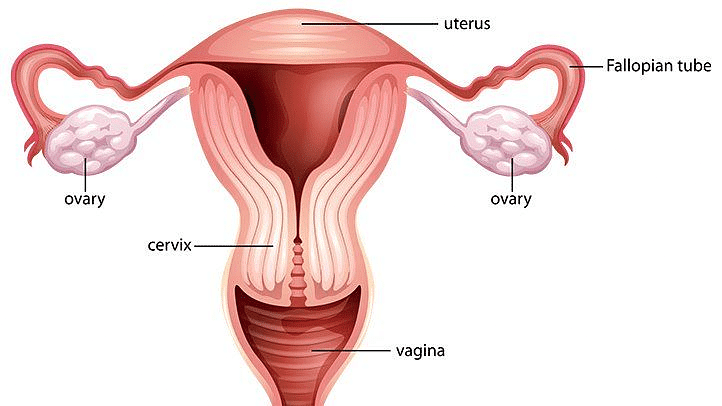 Female Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System- The two oviducts unite into an elastic bag-like structure known as the uterus.
- The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix.
- The sperms enter through the vaginal passage during sexual intercourse. They travel upwards and reach the oviduct where they may encounter the egg.
- The fertilized egg (zygote) gets implanted in the lining of the uterus.
The female reproductive system consists of :
- A pair of ovaries: Ovaries produce and store ovum in them. They also produce a female hormone called estrogen.
- Fallopian tubes (Oviducts): They are the site of fertilization. They connect the ovaries with the uterus.
- Uterus: Uterus is the site of development for the embryo.
- Vagina: It is the part that connects the cervix to the external female body parts. It is the route for the penis during coitus as well as a fetus during delivery.
The mother's body is designed to undertake the development of the child:
- The uterus prepares itself every month to receive and nurture the blood to nourish the growing embryo. The lining thickens and is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo.
- The embryo gets nutrition from the mother's blood with the help of a special tissue called the placenta. This is a disc that is embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi.
- On the mother's side are blood spaces, which surround the villi. This provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo.
- The developing embryo will also generate waste substances that can be removed by transferring them into the mother's blood through the placenta.
- The development of the child inside the mother's body takes approximately nine months. The child is born due to rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus, called labour pain.Question for Reproduction in Human BeingsTry yourself:Which of the following statements are incorrect?View Solution
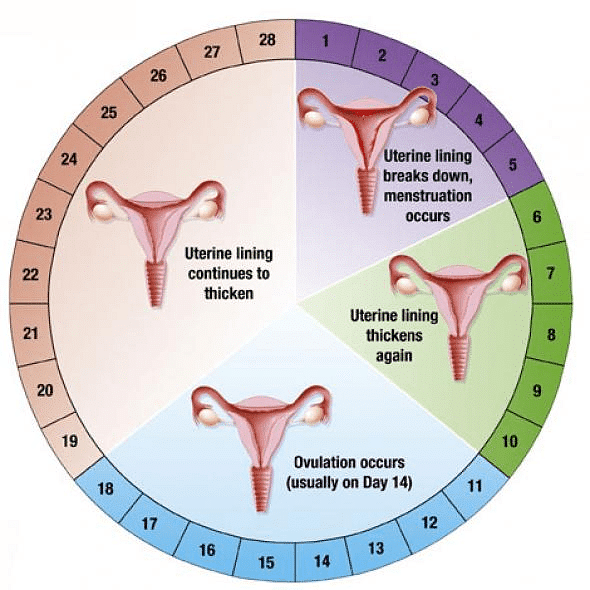
What happens when the egg is not fertilized?
- If the egg is not fertilized, it lives for about one day. Since the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself every month to receive a fertilized egg.
- Thus its lining becomes thick and spongy. This would be required for nourishing the embryo if fertilization had taken place.
- This lining is not needed any longer. So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous.
- This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as menstruation. It usually lasts for about two to eight days.
 Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual Cycle
Reproductive Health
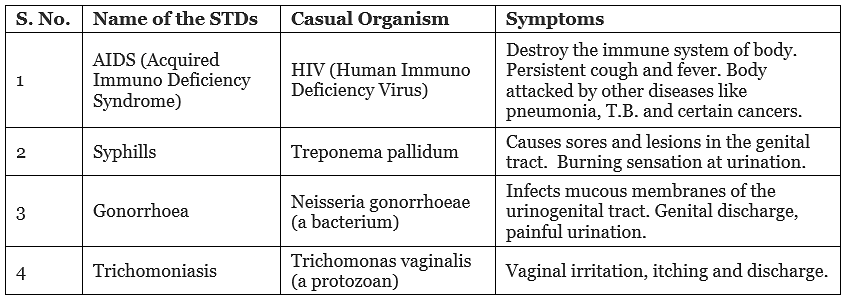
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
- There are many infectious diseases that are spread by sexual contact, called Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs).
Example: AIDS, Hepatitis.STDs occur mostly in individuals who are involved in sexual activities with many partners. - Some common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs):

Methods of prevention of STDs:
(i) The people should be educated about various STDs.
(ii) Extramarital relations should be avoided.
(iii) No sex without proper precaution.
(iv) High standard of moral education should be given to the people.
Population Control Methods
The prevention of pregnancy in women is called contraception.
(i) Planned Control of the Population
- By educating people about the advantages of a small family.
- Raising the age of marriage can help in reducing population growth.
- By family planning.
(ii) Natural Method
- Intercourse is safe for a week before and a week after menstruation.
- Coitus interruptus involves withdrawing the penis before ejaculation.
(iii) Mechanical Methods
- It includes the use of condoms which are the rubber or plastic sheets put on the penis before coital activity.
- Use of diaphragms or cervical caps fitted in the vagina of females to check the entry of sperms into the uterus and avoid conception.
- Use of IUCD, i.e., Intra-Uterine Contraceptive Devices like copper-T and loops fitted in the uterus, helps prevent fertilization. They can cause side effects due to the irritation of the uterus.
(iv) Chemical Methods
- It consists of using some chemicals which are spermicidal. They may be in the form of tablets, jellies, paste and creams introduced in the vagina before coital activity.
- Another chemical method is the use of oral contraceptive (OC) pills which inhibit the secretion of FSH (Follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (Luteinizing hormone) from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland and thus inhibiting ovulation from the ovary.
- Therefore, these contraceptive methods change the hormonal balance so that the egg cell is not released and hence prevent fertilization.
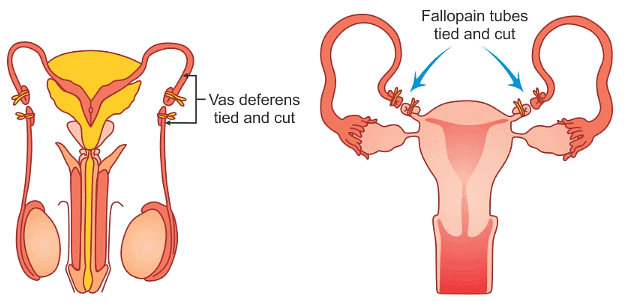
(v) Surgical Methods
- Tubectomy involves cutting of fallopian tubes in females.
- Vasectomy involves cutting of vas deferens of each side in males.
 (a) Vasectomy and (b) Tubectomy
(a) Vasectomy and (b) Tubectomy - Removal of ovaries surgically is known as ovariectomy, and removal of testes is known as castration.
- Another surgical method is MTP, i.e. Medical Termination of Pregnancy or abortion.
- Another method is tubal ligation in which an instrument blocks fallopian tubes called a laparoscope. Question for Reproduction in Human BeingsTry yourself:Which of the following method of contraception protects from acquiring sexually transmitted diseases?View Solution
Competitive Window
- India was the first country to adopt family planning as a government-sponsored programme in 1951.
- Menarche: The onset of menstruation in a young female at about the age of 13 years is termed menarche.
- Menopause: The permanent stoppage of menstruation at about the age of 45 years is termed menopause.
- The menstrual cycle is also called the ovarian cycle.
- In the human female, ovulation starts only after puberty and occurs once a month and midway through the menstrual cycle.
- The menstrual cycle is absent before puberty and temporarily stopped during pregnancy.
- The menstrual cycle occurs only in the primates among mammals.
- Parthenogenesis: A primitive type of sexual reproduction in which unfertilized eggs develop to form haploid adult organisms. It is found in female aphids, drones (males) of honey bees and termites, and certain lizards.
- In freshwater sponges (Spongilla), internal buds are formed within the parent body. Such buds are called gemmules. The gemmules, on the arrival of favourable conditions, develop into a sponge colony.
- After fertilization, the membrane appears around the egg to prevent further entry of sperms. It is called monospermy. After the entry of sperm, the ovum completes its maturation division.
- Amniocentesis: Amniocentesis is a prenatal diagnostic technique to determine the genetic disorders, if any, of the foetus. Unfortunately, the useful technique of amniocentesis is being misused to kill the normal female foetuses as it can help to detect the sex of the foetus also. The determination of sex by amniocentesis has been banned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1: Differentiate between binary fission and multiple fission.
Ans: Binary Fission:
1.In this type of fission, the parent cell gives rise to two daughter cells.
2.It is expressed by organisms like amoeba, paramecium, etc.
Multiple Fission:
1.In this type of fission , the parent cell gives rise to more than two daughter cells.
2.It is expressed by organisms plasmodium.
Q.2: Define fertilization.
Ans: The process of fusion of the male gamete with the female gamete of the same species, i.e., the sperm with the ovum is known as fertilization. After fertilization, the product obtained is the zygote, which eventually develops into a complete organism.
Q.3: What is syngamy?
Ans: The process of fusion of the two gametes is known as syngamy. It is the initial step in the process of fertilization.
|
110 videos|93 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Reproduction in Human Beings - Biology for Grade 10
| 1. What is the process of reproduction in human beings? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of reproduction in human beings? |  |
| 3. What is reproductive health and why is it important? |  |
| 4. What are some methods of population control? |  |
| 5. What is the competitive window in reproduction? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|