Nature and Significance of Management
Management is the process of creating and maintaining an environment where people work together in groups to reach specific goals efficiently.
It is important for all types of organisations—big or small, profit or non-profit—and shows how individuals play a role in achieving common goals.
Management is both a science (with a structured set of knowledge) and an art (through practical application). It is a dynamic function, which means it must change and adjust with time and situations.
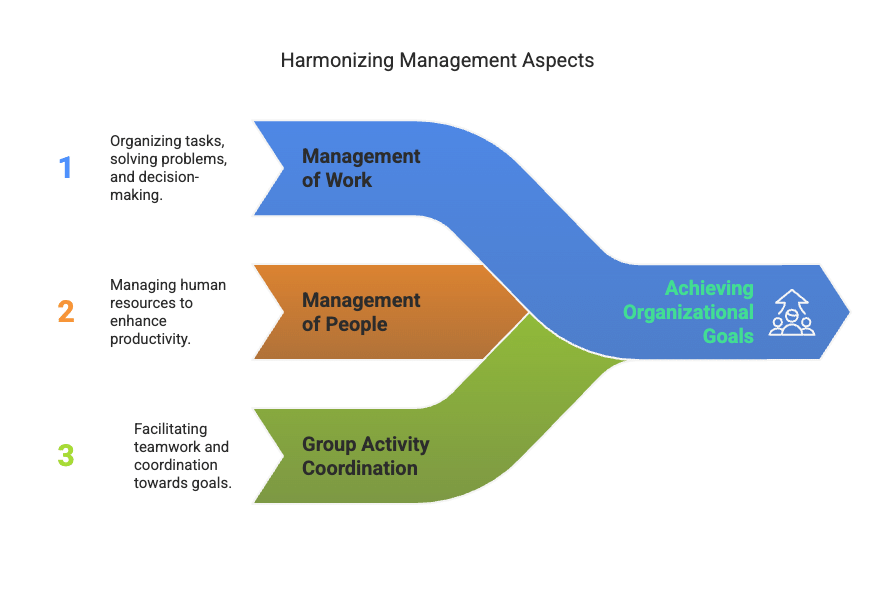
Management is complex and has three main parts:
- Management of work: Every organisation exists to do certain tasks. For example, a factory makes products, a garment store serves customers, and a hospital treats patients. Management includes solving problems, making decisions, planning, budgeting, assigning responsibilities, and giving authority to others.
- Management of people: People are the most valuable part of any organisation. Even with advanced technology, the main challenge is still getting work done through people.
- Management as a group activity: An organisation is made up of different individuals with different needs. Each person may have their own reason for joining, but they all work together toward a common goal, which requires teamwork and coordination.
Efficiency and Effectiveness
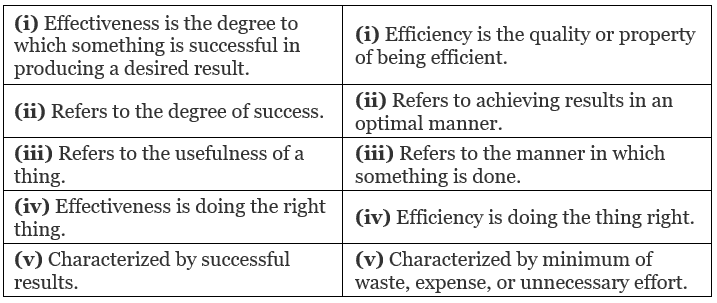
Efficiency means doing a task correctly using the least amount of resources and cost. It focuses on how the work is done. Effectiveness means achieving the desired result by finishing the task on time. It focuses on what is achieved. Though efficiency and effectiveness are different, they are connected. Good management must maintain a balance between both to be successful.
Question for Chapter Notes - Nature and Significance of Management
Try yourself:
Which term refers to completing a task correctly within stipulated time?Explanation
Effectiveness is concerned with achieving the desired end result, which involves completing a task correctly within the specified timeframe. It focuses on accomplishing goals and objectives successfully. Efficiency, on the other hand, relates to minimizing costs and optimizing resource utilization. While efficiency and effectiveness are interrelated, effectiveness specifically pertains to timely task completion.
Report a problem
Effectiveness V/s Efficiency
Characteristics of Management
(i) Management is a Goal-oriented Process which is undertaken to achieve already specified and desired objectives by proper utilisation of available resources.
(ii) Management is All Pervasive and is used in all types of organisations, whether economic, social or political, irrespective of their size, nature and location and at every level.
(iii) Management is Multidimensional: It does not contain one activity. It is a complex activity including three main activities.
(a) Management of work
(b) Management of people
(c) Management of operations
(iv) Management is a Continuous Process: It is a never-ending process. It consists of a series of interrelated functions which perform continuously. The process of management continues until an organisation exists to attain its objectives.
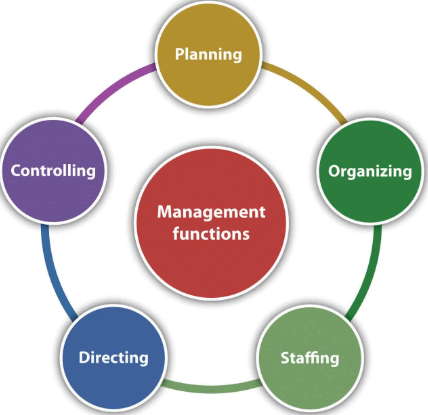 Fig: Continuous Loop of Management
Fig: Continuous Loop of Management
(v) Management is a Group Activity: An organisation is a collection of many individuals, and every individual contributes towards achieving the goal.
(vi) Management is a Dynamic function: It is a dynamic function since it has to adapt according to the needs, time and situation of the changing environment.
Example: McDonald's made major changes in its ‘Menu’ to survive in the Indian market.
(vii) Management is an Intangible Force: It cannot be seen or touched; it can only be felt in the way the organisation functions.
Objectives of Management
Objectives can be classified into organisational, social or personal
(i) Organisational Objectives
- Survival: The main goal of any business is to stay alive. Management must make sure the organisation earns enough income to cover its costs.
- Profit: Just surviving is not enough. The business must also make a profit. Profit is important for long-term success, as it helps cover expenses and risks.
- Growth: A business is considered successful when it grows and expands. To stay competitive, management must use the organisation’s full growth potential and plan for the future.
(ii) Social Objectives
Social objectives focus on benefiting society, such as adopting environmentally friendly practices and creating jobs for underprivileged groups. Companies like TISCO, ITC, and Asian Paints are examples of this.
(iii) Personal Objectives
Organisations consist of individuals with varied personalities, backgrounds, experiences, and aims. Management needs to align personal objectives with organisational objectives to maintain harmony within the organisation.
Question for Chapter Notes - Nature and Significance of Management
Try yourself:
What is the main characteristic of management?Explanation
Management is a continuous process that consists of a series of interrelated functions which are performed continuously until an organization exists for attaining its objectives. It involves ongoing planning, organizing, leading, and controlling activities to achieve desired goals. This characteristic highlights the dynamic nature of management and the need for managers to adapt to changing circumstances and environments.
Report a problem
Importance of Management
(i) Helps in achieving Group Goals: Management creates teamwork and coordination in the group. Managers give common direction to individual efforts in achieving the overall goals of the organisation.
(ii) Increases Efficiency: Management increases efficiency by using resources in the best possible manner to reduce cost and increase productivity.
(iii) Management creates a Dynamic organisation: Management helps the employees overcome their resistance to change and adapt to changing situations to ensure its survival and growth.
(iv) Management helps in achieving personal objectives: Management helps individuals achieve their personal goals while working towards organisational objectives.
(v) Development of Society: Management helps in the development of society by producing good quality products, creating employment opportunities and adopting new technology.
Management as an Art
Art means using one’s skills and knowledge effectively to reach a goal. These skills can be developed through learning, observing, and experience. Management has grown over time with the help of both practical experience and theories, making it a dynamic and unique field.
Main features of art include:
- Existence of theoretical knowledge: Every art is based on some theoretical knowledge. Experts have created basic principles that guide the art.
- Personalised application: This knowledge is used differently by each person, making art personal and unique.
- Based on practice and creativity: Art is practical and needs creativity. For example, all music is based on just seven notes, but a musician creates something special through their creative use of those notes.
Management is considered an art because it meets these points:
- A successful manager uses the art of management every day by learning from study, observation, and experience. There is a lot of knowledge in areas like marketing, finance, and human resources that managers need to learn, showing that theoretical knowledge exists.
- Many management theories from different thinkers provide general principles. A manager must adapt these principles to fit their own organisation. Since management principles are not as exact as scientific laws, they are not always the same for every situation. Still, these principles give managers standard techniques that work in many cases and help in training and developing managers.
Management as a Science
Science is a well-organised set of knowledge based on general truths that can be tested anytime and anywhere. Features of science are:
(i) Systematised body of knowledge: Science has organised knowledge based on principles and experiments.
(ii) Principles based on experiments and observation: Scientific principles come from careful experiments and observations.
(iii) Universal validity: Scientific principles apply everywhere and at all times.
Management also has a systematised body of knowledge, and its principles are developed over time through many observations and experiments that apply broadly. However, these principles must be adjusted depending on the situation. Since management principles are not as exact as pure science, management is called an inexact science.
Management as a Profession
A profession is a job that needs special knowledge and skills, and has limits on who can enter it. Main features of a profession are:
- Well-defined body of knowledge: Every profession is based on clear knowledge that you learn through training.
- Restricted entry: Entry to a profession is limited by exams or education requirements. For example, doctors and lawyers must have valid degrees, but anyone can be called a manager in business without such restrictions.
- Professional associations: In India, there are groups like AIMA (All India Management Association) for managers. They create a code of conduct for members, but joining is not compulsory, and these groups have no legal power.
- Ethical code of conduct: Most professions have a code of ethics to guide behaviour. While not always required by law, many professional groups have their own codes.
- Service motive: The main goal of a profession is to serve clients by providing dedicated service.
Management is not a completely professional field, but it has some similar features. Around the world, management is growing fast. It is seen as both an art and a science, based on a well-organised body of knowledge with clear principles that apply to many business situations. This knowledge is taught in many colleges and professional institutes, and is available in many books and journals. Some places, like the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), focus especially on management education, and usually require passing an exam to get admission.
Levels of Management
“Levels of management” means different categories of managers, from the lowest to the highest on the basis of their relative responsibilities, authority and status.
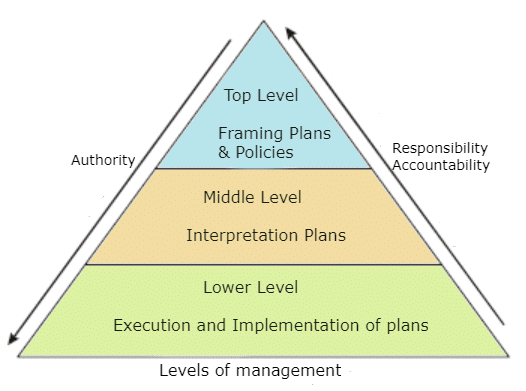
(i) Top Level or Top Management includes the Chairperson, Chief Executive Officer, Chief Operating Officer, and their team. Their main job is to:
- Integrate and coordinate various business activities.
- Frame policies and formulate organisational goals and strategies.
- Analyse the business environment and understand how it affects the firm’s survival.
The role of top management is complex and stressful, requiring long hours and a strong commitment to the organisation.
(ii) Middle Level or Middle Management consists of divisional or departmental heads, plant superintendents, and operation managers. Their key responsibilities include:
Carry out plans made by top managers.
Explain policies created by top management.
Make sure their department has enough staff.
Assign duties and responsibilities to team members.
Motivate staff to reach their goals.
Work with other departments to keep things running smoothly.
(iii) Lower Level and Supervisory Level or Operational Management include foremen and supervisors. Their main tasks are to:
Make sure policies are actually followed.
Handle workers’ grievances with management.
Maintain discipline among workers.
Supervisory management plays a crucial role in the organisation as they interact with the workforce and convey instructions from middle management to the workers.
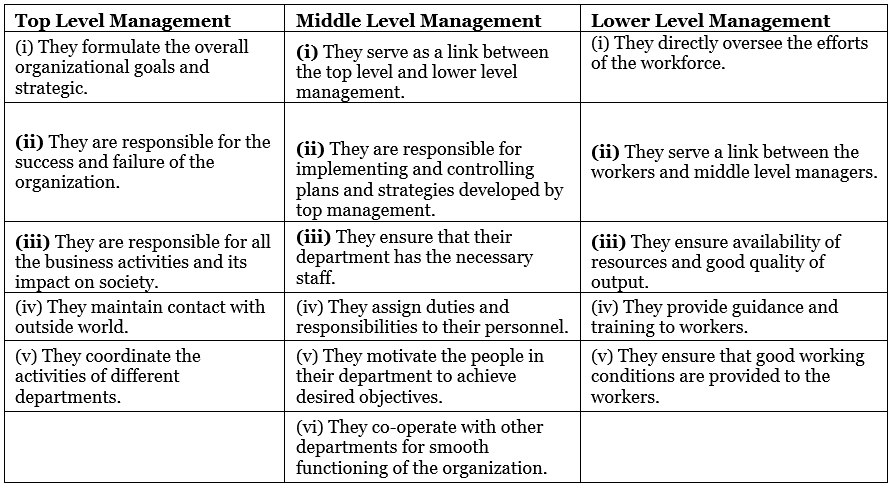
Functions of Management
- Planning: It refers to deciding in advance what to do, how to do and developing a way of achieving goals efficiently and effectively.
- Organising: It refers to the assigning of duties, grouping tasks, establishing authority and allocating of resources required to carry out a specific plan.
- Staffing: It implies the right people for the right job.
- Directing: It involves leading, influencing, and motivating employees to perform the task assigned to them.
- Controlling: It refers to the performance measurement and follow-up actions that keep the actual performance on the path of the plan.
Question for Chapter Notes - Nature and Significance of Management
Try yourself:
Which level of management is responsible for formulating organizational goals and strategies?Explanation
Top Level or Top Management is responsible for integrating and coordinating the various activities of the business, as well as formulating organizational goals and strategies. They consist of the Chairperson, Chief Executive Officer, Chief Operating Officer, or equivalent positions.
Report a problem
Coordination (the Essence of Management)
Coordination is the force which synchronises all the functions of management and activities of different departments. Lack of coordination results in overlapping, duplication, delays and chaos. It is concerned with all three levels of management, as if all the levels of management are looked at together, they become a group, and as in the case of every group, they also require coordination among themselves. So, it is not a separate function of management, rather, it is the essence of management.
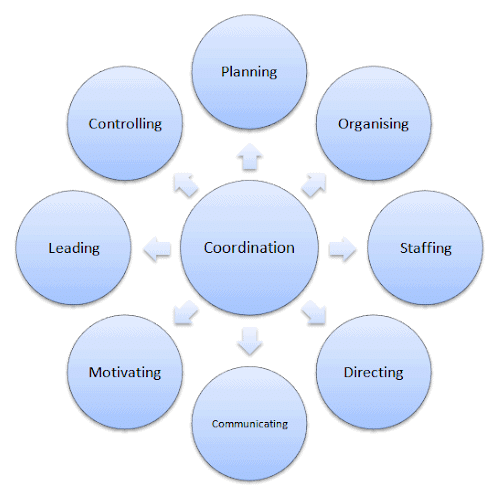
Characteristics of Coordination
(i) Coordination integrates group efforts: It integrates diverse business activities into purposeful group activity, ensuring that all people work in one direction to achieve organisational goals.
(ii) Coordination ensures unity of action: It directs the activities of different departments and employees towards the achievement of common goals and brings unity to individual efforts.
(iii) Coordination is a continuous process: It is not a specific activity matter it is required at all levels, in all departments, till the organisation continues its operations.
(iv) Coordination is an all-pervasive function: It is universal in nature. It synchronises the activities of all levels and departments as they are interdependent to maintain organisational balance.
(v) Coordination is the responsibility of all managers: It is equally important at all three levels of management. Thus, it is the responsibility of all managers they make efforts to establish coordination.
(vi) Coordination is a deliberate function: Coordination is never established by itself; rather, it is a conscious effort on the part of every manager. Cooperation is the voluntary effort of employees to help one another. Effective coordination cannot be achieved without the cooperation of group members.
Importance of Coordination
(i) Growth in Size: When there is a growth in size, the number of people employed by the organisation also increases. Thus, to integrate the efforts, coordination is needed.
(ii) Functional Differentiation: In an organisation, there are separate departments and different goals. The process of linking those activities is achieved by coordination.
(iii) Specialisation: Modern organisation is characterised by a high degree of specialisation. Coordination is required among different specialists because of their different approaches, judgment, etc.






























