Principles Of Management Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Principles of Management: The Concept
Principles of Management are broad and general guidelines for decision-making and behaviour. They differ from scientific principles because they focus on human behaviour. These principles serve as guidelines for making decisions or taking actions, while techniques are specific methods used in those actions.
Values are general rules for individuals' behaviour in society, shaped by common practices. In contrast, principles of management are developed through research in work settings, which are technical in nature. The principles come from observation, analysis, experimental studies, and the personal experiences of managers.
Management principles have become increasingly important with the growing professionalisation of management. These principles are relevant to all types of organisations, including:
- Business and non-business
- Small and large
- Public and private sector
- Manufacturing and services sectors
Additionally, management principles offer managers valuable insights into reality, improving their ability to handle complex situations effectively.

Nature of Principles of Management
The nature of principles of management can be described in the following points:
- Universal applicability: The principles of management are designed to be relevant for all kinds of organisations, whether they are businesses or non-profits, large or small, public or private, and in both manufacturing and service sectors. However, how well they apply can differ based on the organisation's type, activities, and size.
- General Guidelines: These principles serve as broad guidelines for action but do not offer fixed solutions to every managerial issue.
- Formed by practice and experimentation: The principles of management are created from the experiences and collective knowledge of managers, as well as through experimentation. They are derived from careful research and the experiences of various managers.
- Flexible: They are adaptable and can be adjusted by the manager when necessary.
- Mainly Behavioural: Since these principles focus on influencing complex human behaviour, they are inherently behavioural.
- Cause and Effect relationship: They aim to identify relationships between causes and effects to apply them in similar situations effectively.
- Contingent: Their relevance depends on the current situation at any given time. As Terry stated, “Management principles are ‘capsules’ of selected management wisdom to be used carefully and discretely.”
Significance of the Principles of Management
The significance of principles of management can be derived from their utility which can be understood from the following points:
- Providing managers with useful insights into reality: Management principles help managers make timely and informed decisions by enhancing their knowledge and understanding of different managerial situations. Recognising the importance of these principles is crucial for effective decision-making.
- Optimum utilisation of resources and effective administration: Both human and material resources within a company are limited and must be used efficiently. This means resources should be managed to maximise benefits while minimising costs. Principles enable managers to predict the outcomes of their decisions and ensure that managerial actions are objective.
- Scientific decisions: Decisions grounded in management principles are typically more rational, well-balanced, and free from personal biases. These principles encourage logical thinking over mere belief. Decisions made with these principles are based on an objective evaluation of the situation.
- Meeting changing environmental requirements: While these principles serve as general guidelines, they can be adapted to help managers respond to evolving environmental needs.
- Fulfilling social responsibility: Management principles assist in achieving organisational objectives and also guide managers in fulfilling their social responsibilities.
- Management training, education, and research: These principles identify key areas for training current and future managers and lay the groundwork for ongoing research. Training is a vital element of management principles.
Taylor’s Scientific Management
Fredrick Winslow Taylor (1856-1915) quickly rose from an ordinary apprentice to chief engineer at Midvale Steel Company in the U.S.A. between 1878 and 1884. He performed a series of time and motion studies to find the most effective ways to carry out tasks, concluding that there are optimal methods of working that can greatly enhance productivity. Taylor believed that cooperation between management and workers was crucial to reduce hostility and boost productivity. He introduced the concept of scientific management as a replacement for the traditional rule of thumb approach. This method aims to minimise waste to achieve the highest production at the lowest cost. Taylor viewed contemporary management as unprofessional and advocated for its study as a proper discipline. He also highlighted the importance of scientific selection and education of workers, which are vital elements of his theory. The key principles of scientific management include:
- Development of a true science
- Scientific selection of workers
- Scientific education and development of workers
- Close and friendly cooperation between management and employees
Principles of Scientific Management
- Science, not rule of thumb: Each job should be studied scientifically to replace outdated methods. We need to keep experimenting to find new ways that make work simpler, easier, and faster.
- Harmony, not discord: There should be a mental shift among managers and workers to respect each other's roles and remove class conflicts to achieve organisational goals.
- Cooperation, not individualism: This principle extends the idea of 'Harmony, not discord,' where both management and workers take shared responsibility and work together. Suggestions from workers should be welcomed, and strikes should be avoided as both parties collaborate in their roles.
- Development of Each and Every Person to His or Her Greatest Efficiency and Prosperity: Scientific management promotes worker development, with necessary training to learn the best methods. Efficiency should be considered from the employee selection process to ensure that workers are chosen and assigned tasks that match their skills and abilities, maximising productivity.
Techniques of Scientific Management
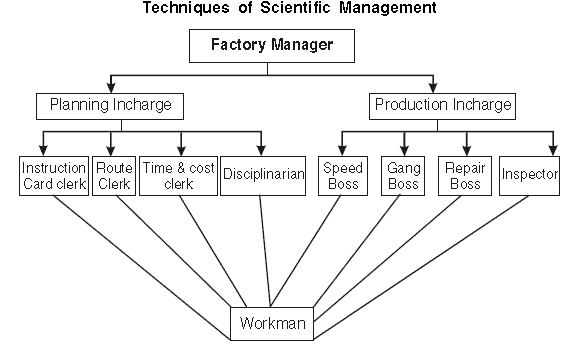
Functional Foremanship
Functional foremanship is a technique in which planning and execution are separated. There are eight types of specialised professionals, four each under planning and execution,who keep a watch on all workers to extract optimum performance.
Planning In charges:
(a) Route Clerk to specify the exact sequence and route of production.
(b) The instruction card clerk is responsible for drafting instructions for the workers.
(c) Time and cost clerk to prepare the time and cost sheet for the job.
(d) Shop Disciplinarian to ensure discipline and enforcement of rules and regulations among the workers.
Production In charges:
Under the production in-charge, the following roles exist:
- Speed boss: Ensures the job is completed accurately and on time.
- Gang boss: Keeps tools and machines ready for use.
- Repair boss: Maintains tools and machines in good working order.
- Inspector: Checks the quality of the completed work.
Standardisation and Simplification of Work
Standardization refers to developing standards for every business activity whereas Simplification refers to eliminating superfluous varieties of product or service. It results in savings of cost of labour, machines and tools. It leads to fuller utilization of equipment and increase in turnover.
Method Study
The objective of method study is to find out one best way of doing the job to maximize efficiency in the use of materials, machinery, manpower and capital.
Motion Study
Motion study looks at movements such as lifting, placing objects, sitting, and changing positions while performing a job. The aim is to remove unnecessary movements to make the job more efficient and quicker. For instance, Taylor and his associate Frank Gilbreth reduced the motions in bricklaying from 18 to just 5. This change led to a productivity increase of about four times. By closely examining body motions, it is possible to identify:
- Productive motions
- Incidental motions (e.g., trips to the store)
- Unproductive motions
Taylor employed stopwatches along with various symbols and colours to categorise different motions. Through these studies, he designed appropriate tools and equipment to instruct workers effectively. The results were impressive.
Time Study
Time study establishes the standard time required to complete a specific task. Devices are used to measure the time taken for each part of the job. The total time for the entire task is determined by averaging several readings. The process of time study depends on factors such as the volume and frequency of the task, the cycle time of the operation, and the costs of time measurement. The goal of time study is to ascertain:
- The number of workers needed
- Appropriate incentive schemes
- Labour costs
For example, if observations show that a worker takes 20 minutes to make one cardboard box, they can produce 3 boxes in an hour. If a worker works 8 hours a shift, with 1 hour deducted for breaks, they would complete 21 boxes in 7 hours at this rate. This sets the standard task for the worker, which in turn helps determine wages.
Fatigue Study
Fatigue study aims to find out how much rest is needed to maintain performance during a task. These rest breaks enable workers to regain energy and continue working effectively, leading to better productivity. Factors that can cause fatigue include:
- Long working hours
- Unsuitable tasks
- Poor relationships with supervisors
- Unpleasant working conditions
Addressing these issues can remove barriers to good performance.
Differential Piece Wage System
- This system connects wages to productivity.
- The standard time and other factors are set based on work-study.
- Two-piece rates are applied:
- A higher rate for those meeting or exceeding the standard output, rewarding efficient workers.
- A lower rate for slower, less efficient workers.
- This encourages efficient workers and aims to motivate slower workers with a difference of Rs. 190.
Mental Revolution
- This involves a complete shift in the attitudes of workers and management from competition to cooperation.
- Both parties should focus on increasing the surplus rather than fighting over it.
- Management should share part of the surplus, while workers should contribute their efforts.
Fayol versus Taylor
- Taylor's work focused on the shop floor, while Fayol's principles apply to all situations.
- Their principles complement each other.
- For example, Taylor describes a worker named Schmidt, who earned significantly more by improving productivity, showcasing the effectiveness of the differential piece wage system.
Fayol’s Principles of Management
About Henry Fayol: Henry Fayol (1841-1925) earned a degree in Mining Engineering and began working for a French Mining Company in 1860 as an Engineer. He advanced to Managing Director in 1888. When the company faced bankruptcy, he accepted the challenge and, drawing on his extensive administrative experience, turned its fortunes around. He is often referred to as the “Father of General Management.” Fayol's 14 principles of management are widely relevant to managerial challenges today and have significantly influenced management thought.
Principles of Management developed by Fayol
1. Division of work:
- Work is split into smaller tasks, with each handled by a trained specialist.
- This approach leads to higher efficiency, increased productivity, and less wasted effort.
2. Authority and Responsibility:
- Authority is the power to make decisions, while responsibility is the duty to complete assigned tasks on time.
- Authority and responsibility should be aligned; without authority, responsibility may seem unimportant, and without responsibility, authority can lead to misuse.
3. Discipline: It is the obedience to organisational rules by the subordinates. Discipline requires good supervisors at all levels, clear and fair agreements and judicious application of penalties.
4. Unity of Command:
- Each worker should take instructions from one superior only.
- This prevents confusion and conflict.
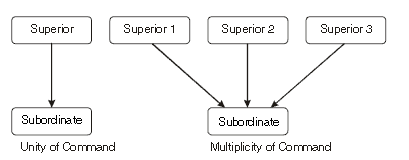
5. Unity of Direction:
- All activities aimed at the same goal should be managed by one leader and follow a single plan.
- This ensures coordinated efforts.
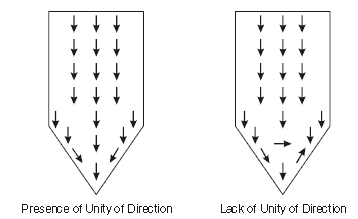
Difference between Unity of Command and Unity of Direction 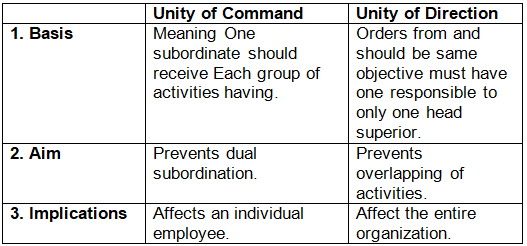
6. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest: The interest of an organisation should take priority over the interest of any one individual employee.
7. Remuneration of Employees:
- Pay and benefits should be fair to both the employees and the organisation.
- Wages should motivate workers to perform better.
8. Centralisation and Decentralisation:
- Centralisation refers to the concentration of decision-making at the top level.
- Decentralisation distributes power across all management levels.
- A balance of both is essential for effective management.
9. Scalar Chain:
- The scalar chain represents the formal lines of authority from the top to the bottom of the organisation.
- This chain should generally be followed, but in emergencies, employees at the same level can communicate directly with each other after informing their immediate supervisors.
10. Order: A place for everything and everyone, and everything and everyone should be in their designated place. People & material must be in suitable places at the appropriate time for maximum efficiency.
11. Equity:
- The scalar chain represents the formal lines of authority from the top to the bottom of the organisation.
- This chain should generally be followed, but in emergencies, employees at the same level can communicate directly with each other after informing their immediate supervisors.
12. Stability of Personnel:
- Fayol stressed the importance of reducing employee turnover to maintain efficiency.
- Employees should be well-selected and have stable tenures for better productivity.
- Frequent changes can lead to instability and increased costs.
13. Initiative:
- Workers should be encouraged to propose and implement their ideas for improvement.
- Initiative involves taking the first step with self-motivation.
14. Espirit De Corps:
- Management should foster a spirit of teamwork, unity, and harmony among employees.
- Encouraging collaboration is crucial for a positive working environment.
|
51 videos|230 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Principles Of Management Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the key principles of management discussed in the chapter? |  |
| 2. How does scientific management differ from traditional management approaches? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of how the principles of management can be applied in real-world business scenarios? |  |
| 4. How can managers effectively implement the principles of management in a diverse workforce? |  |
| 5. What are the potential challenges or obstacles that managers may face when trying to apply the principles of management in their organizations? |  |

















