Principles Of Management Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Principles of Management: The Concept
Principles of Management are the broad and general guidelines for managerial decision making. They are different from principles of science as they deal with human behaviour. They are different from techniques of management as techniques are methods whereas principles are guidelines to action and decision making. Principles of management are different from values which are formed as generally accepted behaviour in society and are having moral coordination whereas principles are formed through research having technical nature. The management principles are derived from observation, analysis, experimental studies and personal experiences of the managers.

Nature of Principles of Management
The nature of principles of management can be described in the following points:
- Universal applicability i.e. they can be applied in all types of organizations, business as well as non-business, small as well as large enterprises.
- General Guidelines: They are general guidelines to action and decision making however they do not provide readymade solutions as the business environment is ever changing or dynamic.
- Formed by practice and experimentation: They are developed after thorough research work on the basis of experiences of managers.
- Flexible: Which can be adapted and modified by the practicing managers as per the demands of the situations as they are man-made principles.
- Mainly Behavioural: Since the principles aim at influencing complex human behaviour they are behavioural in nature.
- Cause and Effect relationship: They intend to establish relationship between cause & effect so that they can be used in similar situations.
- Contingent: Their applicability depends upon the prevailing situation at a particular point of time. According to Terry, “Management principles are ‘capsules’ of selected management wisdom to be used carefully and discretely”.
Significance of the Principles of Management
The significance of principles of management can be derived from their utility which can be understood from the following points:
- Providing managers with useful insights into reality: Management principles guide managers to take right decision at right time by improving their knowledge, ability and understanding of various managerial situations and circumstances.
- Optimum utilization of resources and effective administration: Management principles facilitate optimum use of resources by coordinating the physical, financial and human resources. They also help in better administration by discouraging personal prejudices and adopting an objective approach.
- Scientific decisions: Decisions based on management principles tend to be more realistic, balanced and free from personal bias.
- Meeting the changing environmental requirements: Management principles provide an effective and dynamic leadership and help the organization to implement the changes.
- Fulfilling social responsibility: Principles of management not only help in achieving organizational goals but also guide managers in performing social responsibilities.
Example: “Equity” and “Fair” remuneration. - Management training, education and research: Management principles are helpful in identifying the areas in which existing and future managers should be trained. They also provide the basis for future research.
Taylor’s Scientific Management
Fredrick Winslow Taylor (1856-1915) was a person who within a very short duration (1878-1884) rose from ranks of an ordinary apprentice to chief engineer in Midvale Steel Company, U.S.A. Taylor conducted a number of experiments and came to conclusion that workers were producing much less than the targeted standard task. Also, both the parties - Management and workers are hostile towards each other. He gave a number of suggestions to solve this problem and correctly propounded the theory of scientific management to emphasize the use of scientific approach in managing an enterprise instead of hit and trial method. For his contributions, he is well known as the “Father of the Scientific Management”. Scientific Management attempts to eliminate wastes to ensure maximum production at minimum cost.
Principles of Scientific Management
- Science, not rule of Thumb: There should be scientific study and analysis of each element of a job in order to replace the old rule of thumb approach or hit and miss method. We should be constantly experimenting to develop new techniques which make the work much simpler, easier and quicker.
- Harmony, not discord: It implies that there should be mental revolution on part of managers and workers in order to respect each other’s role and eliminate any class conflict to realize organizational objectives.
- Cooperation not individualism: It is an extension of the Principle of Harmony not discord whereby constructive suggestions of workers should be adopted and they should not go on strike as both management and workers share responsibility and perform together.
- Development of each and every person to his or her greatest Efficiency and Prosperity: It implies development of competencies of all persons of an organization after their scientific selection and assigning work suited to their temperament and abilities. This will increase the productivity by utilizing the skills of the workers to the fullest possible extent.
Techniques of Scientific Management
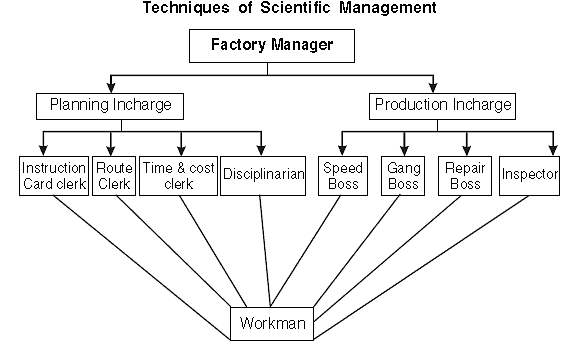
Functional Foremanship
Functional foremanship is a technique in which planning and execution are separated. There are eight types of specialized, professionals, four each under planning and execution who keep a watch on all workers to extract optimum performance.
Planning In charges:
(a) Route Clerk to specify the exact sequence and route of production.
(b) Instruction card clerk is responsible for drafting instructions for the workers.
(c) Time and cost clerk to prepare time and cost sheet for the job.
(d) Shop Disciplinarian to ensure discipline and enforcement of rules and regulations among the workers.
Production In charges:
(a) Gang boss is responsible for keeping tools and machines ready for operation.
(b)Speed boss is responsible for timely and accurate completion of job.
(c) Repair boss to ensure proper working conditions of tools and machines.
(d)Inspector to check quality of work.
Standardization and Simplification of Work
Standardization refers to developing standards for every business activity whereas Simplification refers to eliminating superfluous varieties of product or service. It results in savings of cost of labour, machines and tools. It leads to fuller utilization of equipment and increase in turnover.
Method Study
The objective of method study is to find out one best way of doing the job to maximize efficiency in the use of materials, machinery, manpower and capital.
Motion Study
It is the science of eliminating wastefulness resulting from using unnecessary, ill-directed and inefficient motions by workers and machines to identify best method of work.
Time Study
It determines the standard time taken to perform a well-defined job. The objective of time study is to determine the number of workers to be employed, frame suitable incentive schemes & determine labour costs.
Fatigue Study
Fatigue study seeks to determine time and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task. The rest interval will enable workers to regain their lost stamina thereby avoiding accidents, rejections and industrial sickness.
Differential Piece Wage System
This system links wages and productivity. The standard output per day is established and two piece rates are used: higher for those who achieve up to and more than standard output i.e. efficient workers and lower for inefficient and slow workers. Thus, efficient workers will be rewarded & inefficient will be motivated to improve their performance. Mental Revolution: It involves a complete change in mental outlook and attitude of workers and management towards one another from competition to cooperation. The management should create pleasant working conditions & workers should work with devotion and loyalty. Instead of fighting over distribution of profits, they must focus attention on increasing it. Fayol versus Taylor: While the work of Taylor concerned shop floor, the work of Fayol concerned General Principles applicable to all types of situations. So, their principles are mutually complementary to each other.
Fayol’s Principles of Management
About Henry Fayol: Henry Fayol (1841-1925) got degree in Mining Engineering and joined French Mining Company in 1860 as an Engineer. He rose to the position of Managing Director in 1988. When the company was on the verge of bankruptcy. He accepted the challenge and by using rich and broad administrative experience, he turned the fortune of the company. For his contributions, he is well known as the “Father of General Management”.
Principles of Management developed by Fayol
1. Division of work: Work is divided in small tasks/job and each work is done by a trained specialist which leads to greater efficiency, specialization, increased productivity and reduction of unnecessary wastage and movements.
2. Authority and Responsibility: Authority means power to take decisions and responsibility means obligation to complete the job assigned on time. Authority and responsibility should go hand in hand. Mere responsibility without authority, makes an executive less interested in discharging his duties. Similarly giving authority without assigning responsibility makes him arrogant and there is fear of misuse of power.
3. Discipline: t is the obedience to organizational rules by the subordinates. Discipline requires good supervisors at all levels, clear and fair agreements and judicious application of penalties.
4. Unity of Command: It implies that every worker should receive orders and instructions from one superior only, otherwise it will create confusion, conflict, disturbance and overlapping of activit.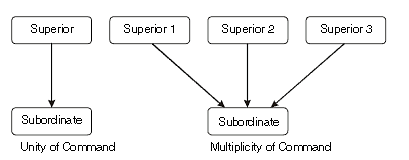
5. Unity of Direction: Each group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan. This ensures unity of action and coordination.
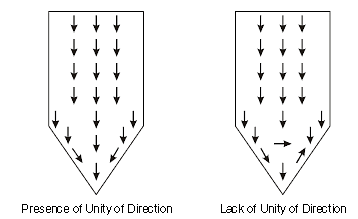
Difference between Unity of Command and Unity of Direction 
6. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest: The interest of an organization should take priority over the interest of any one individual employee.
7. Remuneration of Employees: The overall pay and compensation should be, fair to both employees and the organization. The wages should encourage the workers to work more and better.
8. Centralization and Decentralization: Centralization means concentration of decisions making authority in few hands at top level. Decentralization means evenly distribution of power at every level of management. Both should be balanced as no organization can be completely centralized or completely decentralized.
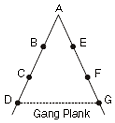
9. Scalar Chain: The formal lines of authority between superiors and subordinates from the highest to the lowest ranks is known as scalar chain. This chain should not be violated but in emergency employees at same level can contact through Gang Plank by informing their immediate superiors.
10. Order: A place for everything and everyone and everything and everyone should be in its designated place. People & material must be in suitable places at appropriate time for maximum efficiency.
11. Equity: The working environment of any organization should be free from all forms of discrimination (religion, language, caste, sex, belief or Basis Unity of Command Unity of Direction nationality) and principles of justice and fair play should be followed. No worker should be unduly favoured or punished.
12. Stability of Personnel: Fayol emphasizes minimizing employee turnover to maintain organizational efficiency. Employees should be carefully selected and given a fixed minimum tenure to ensure stability and allow them to produce results. Frequent changes cause instability, increase costs, and prompt employees to leave. Therefore, stable tenure is beneficial for the business.
13. Initiative: Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plan for improvements. Initiative means taking the first step with self-motivation. It is thinking out and executing the plan.
14. Espirit De Corps: Management should promote team spirit, unity and harmony among employees. Management should promote a team work.
|
52 videos|198 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Principles Of Management Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the key principles of management discussed in the chapter? |  |
| 2. How does scientific management differ from traditional management approaches? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of how the principles of management can be applied in real-world business scenarios? |  |
| 4. How can managers effectively implement the principles of management in a diverse workforce? |  |
| 5. What are the potential challenges or obstacles that managers may face when trying to apply the principles of management in their organizations? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|


















