Controlling Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Meaning of Controlling |

|
| Importance of Controlling |

|
| Limitations of Controlling |

|
| Relationship between Planning and Controlling |

|
| Controlling Process |

|
Meaning of Controlling
- Controlling is a crucial function of management aimed at ensuring planned results from subordinates.
- It involves effectively overseeing and regulating activities to align with organizational plans.
- Controlling guarantees efficient utilization of resources towards predetermined goals, making it goal-oriented.
- Controlling is pervasive and essential at all managerial levels, including top, middle, and lower management.
- It is indispensable across various sectors like education, military, healthcare, and business.
- Contrary to misconception, controlling isn't the final management function; it loops back to planning, aiding in future planning cycles.
- Controlling entails assessing performance against standards, identifying deviations, and implementing corrective measures.
- Analysis of deviations aids in enhancing future planning by addressing identified issues.
- By completing one management cycle, controlling contributes to refining planning for subsequent cycles.

Importance of Controlling
Control is a vital function in management that ensures activities proceed as planned. Without proper control, even the best strategies may fail. Here are the key ways an effective control system benefits an organisation:
1. Accomplishing Organisational Goals
- Control helps monitor progress towards goals by identifying deviations from the plan.
- It indicates corrective actions to keep the organisation on track toward achieving its objectives.
2. Judging the Accuracy of Standards
- A good control system checks if the set standards are achievable and fair.
- It enables management to review and change these standards when there are internal or external changes.
3. Making Efficient Use of Resources
- Control helps to reduce waste and prevent the misuse of resources.
- It ensures that every task is carried out according to set standards.
- This approach allows the organization to reach maximum productivity while using fewer resources.
4. Improving Employee Motivation
- Setting clear performance goals helps to motivate employees.
- Understanding the evaluation criteria makes employees strive for better outcomes.
5. Ensuring Order and Discipline
- Control helps create a work environment that is disciplined by keeping a close watch on what people do.
- It discourages dishonesty by making sure employees are responsible for their actions.
6. Facilitating Coordination in Action
- Control helps different departments and people work together towards shared goals.
- Coordinating activities using standard procedures makes sure the organization runs smoothly.
Limitations of Controlling
1. Difficulty in setting quantitative standards
- Control system effectiveness diminishes when standards lack quantitative definitions, complicating performance measurement and comparison with standards.
- Areas like employee morale, job satisfaction, and human behaviour can be particularly challenging in this regard.
2. Little control on external factors
- Enterprises often face limitations in controlling external factors such as government policies, technological changes, and competition.
3. Resistance from employees
- Employees may resist control, viewing it as a restriction on their freedom.
- For example, employees might object to stringent surveillance through Closed Circuit Televisions (CCTVs).
4. Costly affair
- Control incurs significant costs in terms of expenditure, time, and effort.
- Small enterprises may find it challenging to afford expensive control systems and must ensure that the costs do not outweigh the benefits.
Relationship between Planning and Controlling
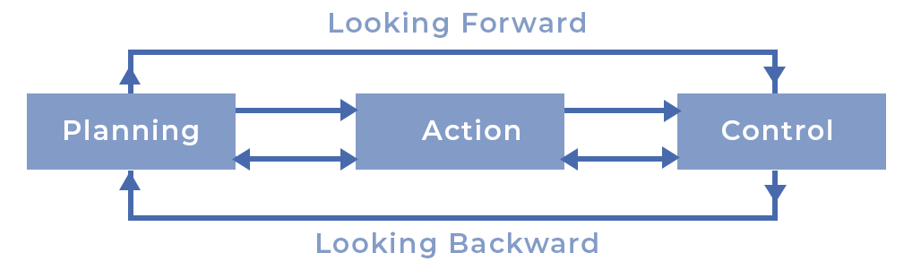
- Planning and controlling are important parts of management that are closely related and essential for an organization's success.
- A control system relies on predefined standards created during the planning stage, which act as the basis for control.
- Once a plan is put into action, controlling becomes important for checking progress, assessing performance, identifying any deviations, and taking corrective actions to stay aligned with the plan.
- Effective planning is necessary for meaningful controlling because the control process needs predetermined standards as a reference point.
- On the other hand, controlling without planning doesn’t work well because it lacks the necessary guidance and benchmarks for evaluation.
- Planning is a proactive process that involves thinking strategically, clearly communicating, and analyzing how to reach goals. In contrast, controlling is a reactive process that checks if decisions are made as intended.
- While planning looks toward the future, controlling reviews past performance to find any deviations from set standards.
- Even though people often think planning is about looking ahead and controlling is about looking back, both functions are connected and work together to improve future performance.
Planning and controlling complement each other:
- Planning based on accurate data facilitates the controlling process, making it more efficient and effective.
- Controlling provides insights from past experiences that can be used to enhance future planning, creating a cyclical and reinforcing relationship between the two functions.
Controlling Process
Controlling is a systematic process involving the following steps:
- Setting performance standards
- Measurement of actual performance
- Comparison of actual performance with standards
- Analysing deviations
- Taking corrective action

Step 1: Setting Performance Standards
- Performance standards are benchmarks against which actual performance is measured.
- Standards can be quantitative (e.g., cost, revenue, product units) or qualitative (e.g., employee motivation).
- Managers should set precise quantitative standards for easier comparison.
- Qualitative standards should be defined in a way that makes measurement easier.
- Standards should be flexible and modified when required due to changing business environments.
Step 2: Measurement of Actual Performance
- Performance should be measured objectively and reliably.
- Techniques for measurement include personal observation, sample checking, and performance reports.
- Measurement should ideally be in the same units as the standards for easier comparison.
- Measurement can be done during or after task completion, depending on the nature of the work.
Step 3: Comparing Actual Performance with Standards
- The comparison involves revealing deviations between actual and desired results.
- Quantitative standards make comparison easier.
- For example, a worker's weekly output can be compared to the standard output.
Step 4: Analyzing Deviations
1. Critical Point Control
- This focuses on key result areas (KRAs) critical to organizational success.
- Monitoring critical points where issues can significantly impact the organization.
- Example: In a manufacturing setting, a 5% increase in labour costs may be more critical than a 15% increase in postal charges.
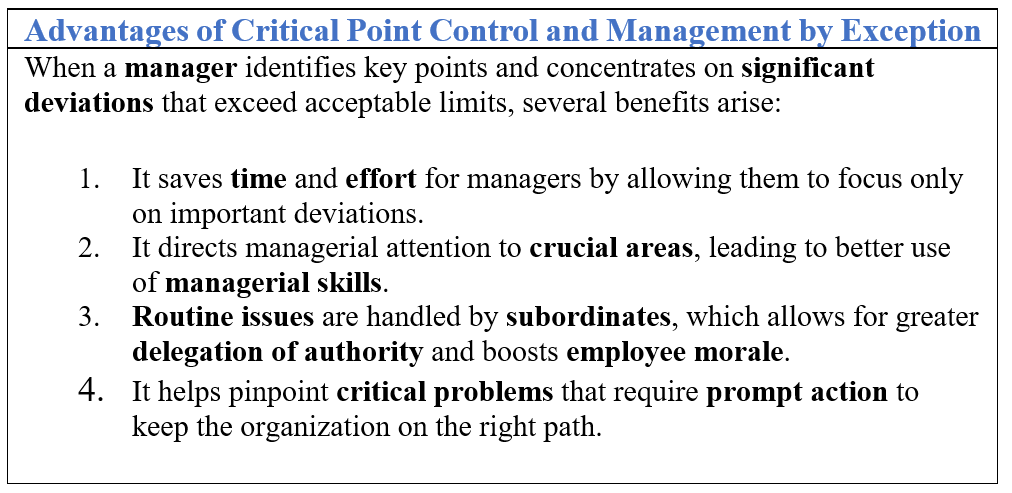
2. Management by Exception
- Control principle based on addressing significant deviations beyond permissible limits.
- Bringing only major deviations to management's attention for immediate action.
Identifying and Analyzing Deviations
- Deviation causes unrealistic standards, defective processes, resource inadequacy, structural drawbacks, organizational constraints, and external factors.
Importance of Identifying Causes:
- It is important to take the right steps to fix any mistakes that have occurred.
- We need to report any deviations and the reasons behind them so that we can implement corrective actions.
Step 5: Taking Corrective Action
When Corrective Action is Needed
- Required when changes go beyond acceptable limits, especially in important areas.
- Immediate managerial attention is needed to stop these issues from happening again and to make sure standards are followed.
Examples of Corrective Actions
- Training employees to meet production goals that have not been achieved.
- Providing extra resources for projects that are not on track.
- Changing standards if problems continue even after management steps in.
|
52 videos|198 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Controlling Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the meaning of controlling in a business context? |  |
| 2. Why is controlling considered important in management? |  |
| 3. What are some limitations of the controlling function in management? |  |
| 4. How is planning related to controlling in management? |  |
| 5. What are the key steps in the controlling process? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|


















