Emerging Modes of Business Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
The method of conducting business has changed significantly over the past decade.
- In the digital age, money is now represented as electronic signals moving at incredible speeds, all thanks to the electronic funds transfer technology in e-commerce.
- It's fair to say that without the internet, the process of globalisation would have been much slower and limited.
- The internet has greatly decreased our reliance on paperwork and the associated bureaucracy.
This discussion focuses on the online trading process from a customer’s perspective.
Today, e-business has become an essential way to carry out transactions, setting itself apart from traditional business methods. The worldwide reach of the internet enables businesses to tap into global markets, while consumers have the freedom to select products from nearly anywhere in the world.
As we explore this topic further, we will look at the effects of these changes and how they influence our current business environment.
E-Business vs. Traditional Business
E-Business
If we understand business as a wide range of activities including industry, trade, and commerce, then e-business refers to conducting these activities through computer networks.
The most familiar network to students and consumers is the Internet. However, businesses also use private and secure networks for managing internal functions efficiently and safely.
E-Business vs. E-Commerce
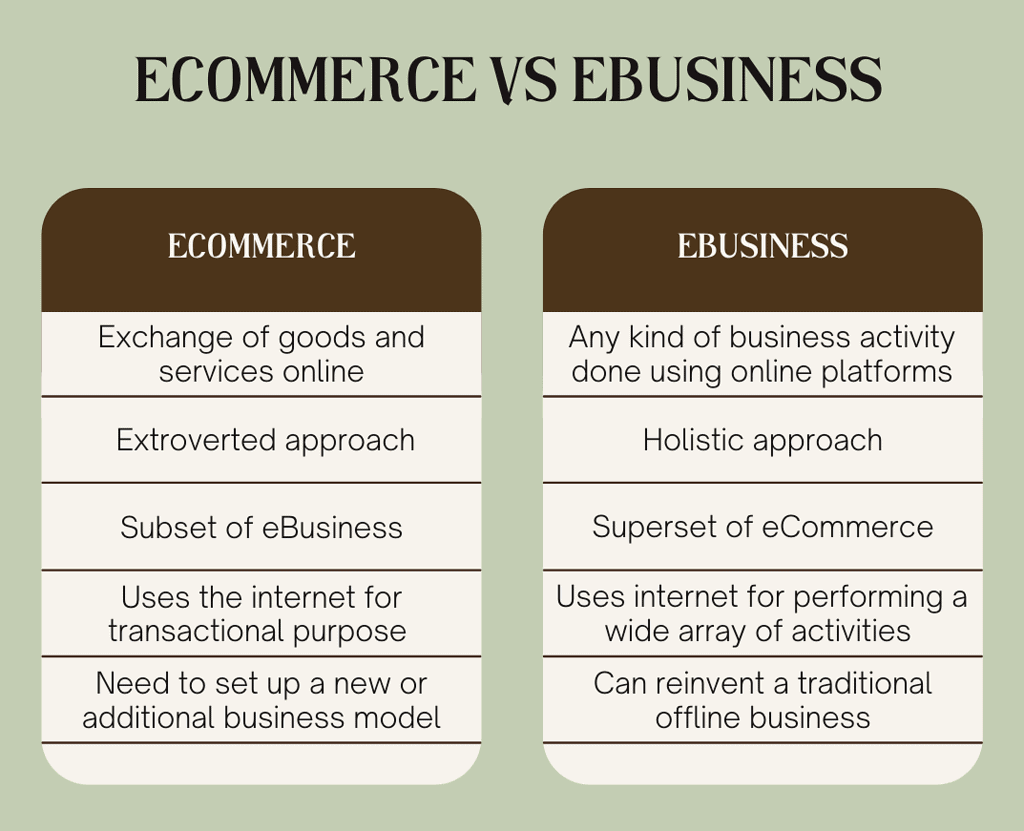
Although people often use e-business and e-commerce interchangeably, they are not exactly the same.
Just like business is a broader term than commerce,
e-business is broader than e-commerce.e-Commerce focuses on a firm's interactions with customers and suppliers over the internet — basically, buying and selling online.
e-Business, on the other hand, includes not just e-commerce but also other business functions like:
Production
Inventory Management
Product Development
Accounting and Finance
Human Resource Management
So, e-business is much more than just buying and selling — it’s the complete online management of a business.
Scope of E-Business
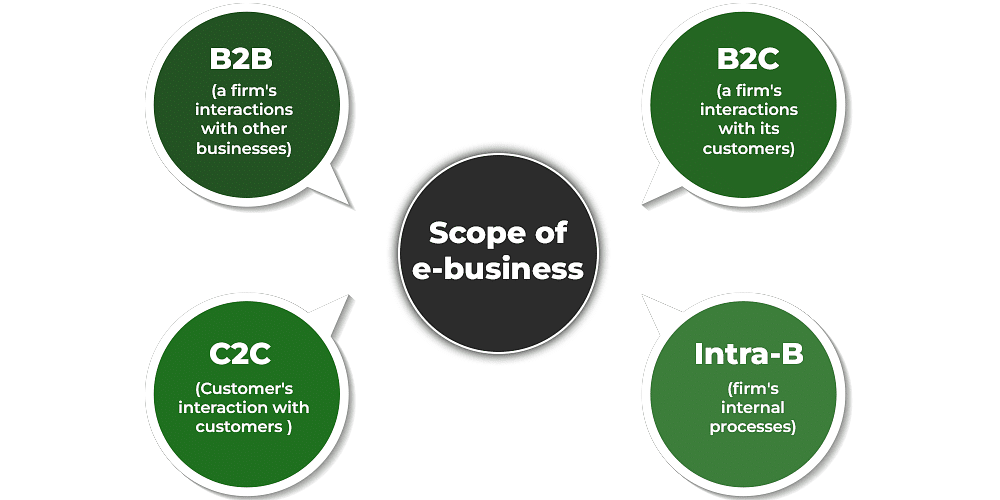
The scope of e-business is vast. Almost all business functions — including production, marketing, finance, and HR — as well as managerial tasks like planning, organising, and controlling can be done online.
Another way to understand the scope is by looking at the parties involved in e-transactions. e-Business can be categorized into three types based on this:
(i) B2B – Business to Business
In B2B commerce, both parties are businesses. For example:
An automobile company needs many parts (like tyres, seats, engines) from different suppliers. These suppliers are other businesses.
Companies use computer networks to:
Place orders
Monitor production
Track deliveries
Make payments
Benefits of B2B e-commerce:
Faster movement of information and documents
Real-time tracking of inventory
Quick money transfers
Customised production as per customer needs
Note: B2B e-commerce originally began with EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), which allowed businesses to send/receive documents like purchase orders and invoices electronically.
(ii) B2C – Business to Consumer
In B2C commerce, businesses deal directly with customers. While we usually think of online shopping, it involves much more:
B2C includes all marketing activities like:
Identifying customer needs
Promoting products
Delivering digital products (e.g., music, movies)
Conducting customer surveys
Receiving customer feedback
Advantages of B2C e-commerce:
Lower cost and faster speed
Personalised services and custom-made products
Convenience in delivery and payment options
24/7 customer interaction and support
For example, ATMs allow quick withdrawal of money — that’s B2C in action.
(iii) Intra-B Commerce – Within the Firm
In Intra-B commerce, all parties involved in the electronic transaction belong to the same company. That’s why it's called Intra-B (Intra-Business).
This is a key area where e-business differs from e-commerce:
E-commerce includes external interactions — with suppliers, distributors, and customers.
E-business also includes internal interactions — among departments and employees, using a private network called an intranet.
Benefits of Intra-B Commerce:
Enables flexible manufacturing – for example, the marketing department can inform the production department to make customized products based on customer needs.
Improves inventory and cash management
Allows better use of machines and plants
Enhances customer service and human resource management
Think of the intranet as a modern version of the intercom, but instead of just voice, it allows communication through multimedia and even 3D graphics — leading to better coordination and faster decision-making.
B2E (Business to Employee) – A Special Case of Intra-B
This refers to a firm's interaction with its own employees, often through online platforms.
Examples:
Recruitment, interviews, training, and e-learning
Employees using e-catalogues or inventory systems to serve customers better
Sending real-time field reports through emails
Working from home using Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Holding meetings online via video conferencing
(iv) C2C Commerce – Consumer to Consumer
In C2C commerce, both the buyer and seller are individual consumers. This happens when people sell items like:
Used books
Second-hand clothes
Or any goods without a formal market
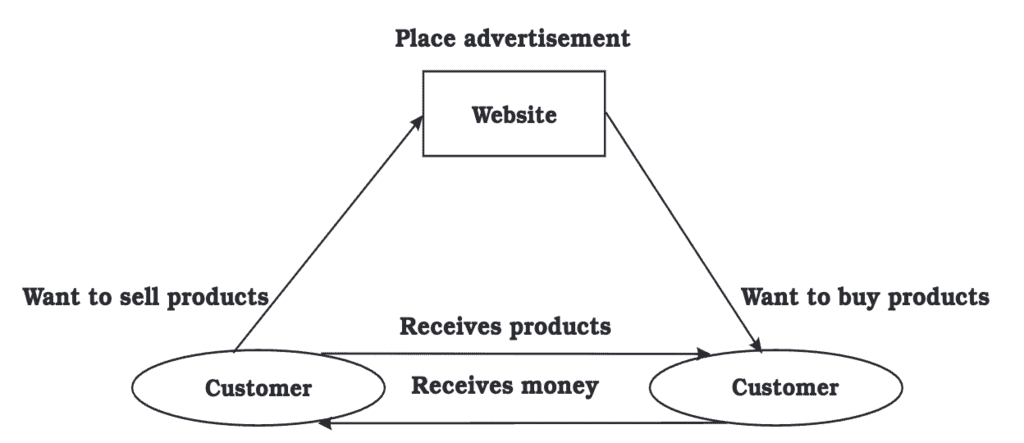
C2C Commerce Benefits:
The internet connects buyers and sellers from around the world.
Platforms like eBay provide a secure and trusted system for these transactions.
Safety Features:
Ratings and reviews – buyers can see how trustworthy a seller is based on past feedback.
Payment intermediaries like PayPal – which hold the buyer's money safely until the goods are received.
C2C Interactive Forums
Consumers can form forums and pressure groups online (e.g., Yahoo groups).
People can share experiences or warn others about bad products or services.
Just like a driver alerts others on traffic FM about jams, a customer can alert others about poor services through online posts.
Group pressure can even lead to a resolution of issues.
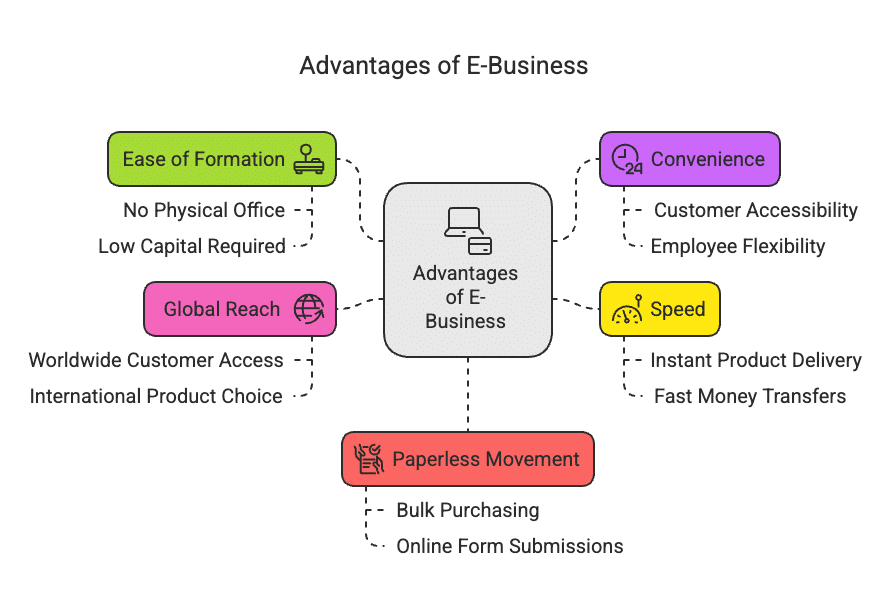
Benefits of E-Business
(i) Ease of Formation and Lower Investment Requirements
Setting up an e-business is much easier and cheaper compared to starting a traditional business.
It doesn’t need a physical office or shop.
Even people with low capital (money) but good networks (contacts) can do successful business online.
Example:
Imagine an online food delivery website that takes orders and routes them to nearby restaurants.
The website owner doesn’t cook or deliver food — just earns a commission for connecting customers with restaurants.
(ii) Convenience
E-business is open 24×7×365 — all day, every day of the year!
Customers can shop anytime, even at midnight.
Employees can also work from anywhere, at a time that suits them.
This flexibility is a big advantage over traditional businesses.
(iii) Speed
E-business is very fast, especially for exchanging information.
Products like software, music, e-books, movies, etc., can be delivered instantly online.
Business processes become faster and more efficient — multiple tasks can happen simultaneously.
Cycle time (time from placing an order to delivery) is greatly reduced.
Money transfers are also quick through electronic funds transfer (EFT).
(iv) Global Reach / Access
The Internet removes geographical boundaries:
Sellers can reach customers anywhere in the world.
Buyers can choose products from any country.
Without the internet, globalization would have grown much slower.
(v) Movement Towards a Paperless Society
E-business helps in reducing paperwork:
Companies like Maruti do bulk purchasing without using paper.
Government departments now allow online submissions of forms and returns.
This reduces delays and makes approvals and licenses faster.
The Information Technology Act, 2000 supports these changes by giving legal recognition to digital records and communication.

Limitations of E-Business
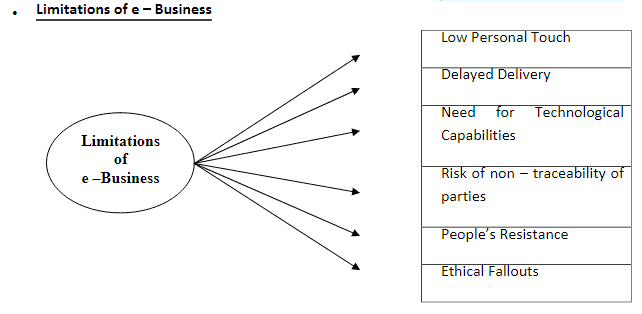
(i) Low Personal Touch
E-business lacks face-to-face interaction.
It is less suitable for products that need personal experience, like clothes, perfumes, or cosmetics.
Customers often want to see, touch, or try products before buying.
(ii) Mismatch Between Order and Delivery Speed
Information travels instantly online, but the physical delivery of goods takes time.
Sometimes, websites are slow to load, adding to customer frustration.
This mismatch can annoy customers, especially when they expect quick service.
(iii) Need for Technology Skills
E-business needs computer skills and access to digital technology.
Not everyone is comfortable with technology.
This creates a digital divide — a gap between those who know how to use technology and those who don’t.
This makes e-business less inclusive for people unfamiliar with computers or the internet.
(iv) Risk Due to Anonymity and Security Issues
Online transactions are done between cyber identities, not real people.
It’s hard to verify identities or track locations.
Risks include:
Impersonation (someone else using your identity)
Theft of data (like credit card info)
Viruses and hacking
This makes trust a big issue in e-business.
(v) People Resistance
Employees may resist new technology because:
It causes stress.
They may fear losing their jobs.
They may feel insecure or uncomfortable with change.
This resistance can slow down the company’s move to e-business.
(vi) Ethical Issues
Companies often monitor employee activities online:
Tracking emails, websites visited, and files accessed.
This raises ethical concerns:
Is it right to watch someone’s private communication?
Where is the line between safety and privacy?
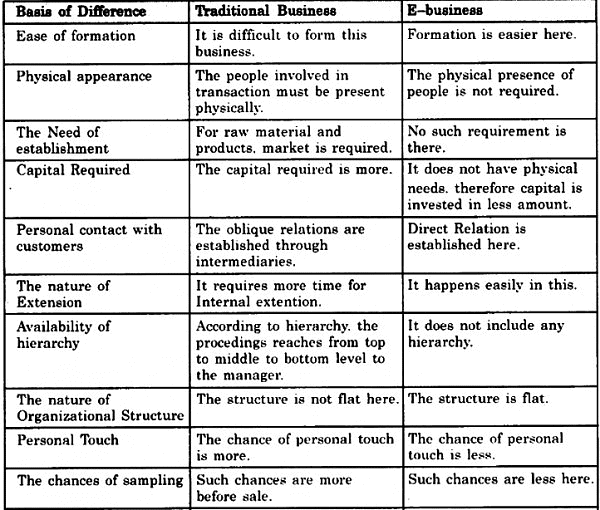
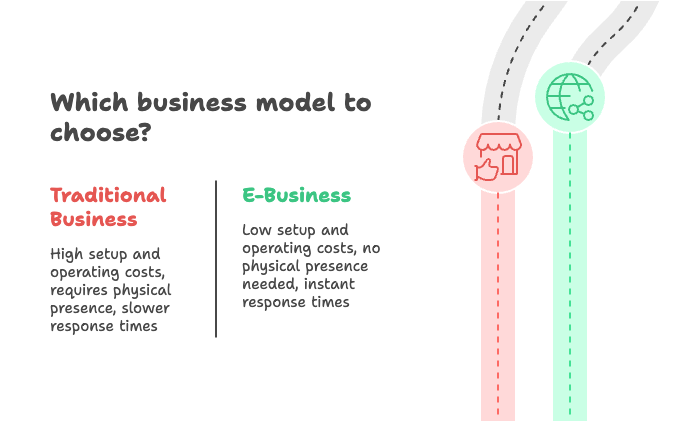
Traditional Business Vs. E-Business (Comparison)
Ease of Formation:
Traditional Business: Difficult to set up
E-Business: Simple and quick to start
Physical Presence:
Traditional Business: Requires a physical location
E-Business: Does not need a physical presence
Locational Requirements:
Traditional Business: Needs to be close to raw materials or target markets
E-Business: No such location constraint
Cost of Setting Up:
Traditional Business: High, due to infrastructure costs
E-Business: Low, as it doesn’t need physical setup
Operating Cost:
Traditional Business: High, due to costs of storage, production, and marketing
E-Business: Low, as it uses digital networks instead of ownership
Contact with Suppliers & Customers:
Traditional Business: Indirect, through intermediaries
E-Business: Direct, through websites or digital platforms
Internal Communication:
Traditional Business: Hierarchical (top-down)
E-Business: Non-hierarchical and more flexible
Response Time:
Traditional Business: Slower response
E-Business: Instant response
Organisational Structure:
Traditional Business: Vertical/tall with many levels
E-Business: Horizontal/flat with direct communication
Business Process Cycle:
Traditional Business: Step-by-step (sequential)
E-Business: Many steps happen at once (simultaneous)
Interpersonal Touch:
Traditional Business: High (more face-to-face interaction)
E-Business: Low (less personal interaction)
Physical Pre-sampling of Products:
Traditional Business: Possible and common
E-Business: Limited, except for digital products like music or e-books
Global Reach:
Traditional Business: Limited by geography
E-Business: Wide, global accessibility
Government Support:
Traditional Business: Decreasing support
E-Business: Increasing support, especially in IT sector
Human Capital Needs:
Traditional Business: Can work with semi-skilled or unskilled workers
E-Business: Needs technically skilled professionals
Transaction Risk:
Traditional Business: Low risk due to face-to-face interaction
E-Business: Higher risk due to anonymity, fraud, and data breaches
Despite limitations, E-Commerce is the way
It can be noted that many of the challenges faced by e-business are being addressed. When you want to buy something, especially from overseas or from a seller far away, the issues encountered in traditional business are often greater than those in E-Commerce. This is due to factors like travelling, carrying cash, time needed, speed, and payment methods.
Online Transactions
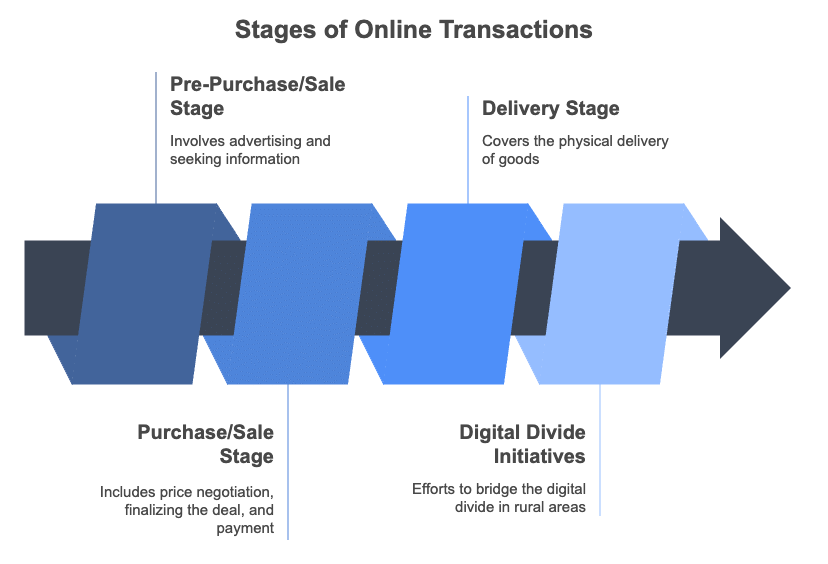
Stages of Online Transactions
- Pre-Purchase/Sale Stage – Involves advertising and seeking information.
- Purchase/Sale Stage – Includes price negotiation, finalising the deal, and payment.
- Delivery Stage – Covers the physical delivery of goods.
In traditional business transactions, information is shared through direct contact. The first two stages involve interaction and can therefore be effectively managed online.
Efforts are being made to bridge the digital divide. For example, community telecentres are being established in rural areas of India, supported by government agencies, NGOs, and international organisations. India has initiated around 150 such projects to promote e-commerce across various regions.
Steps Involved in the Online Purchase
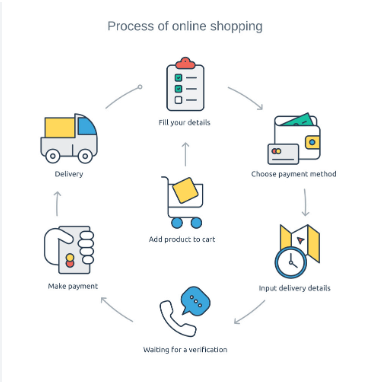
1. Registration
- Before you can shop online, you need to register with the vendor by filling out a form.
- Registration creates an 'account' with the online vendor.
- You will need to choose a 'password' to protect your account and shopping cart.
- This means only you can access your account and make purchases.
2. Placing an Order
- You can select items to add to your shopping cart.
- The shopping cart keeps track of what you want to buy while browsing.
- Like in a physical store, you can add or remove items from your cart.
- Once you are ready to buy, you can proceed to 'checkout' and choose how to pay.
3. Payment Options
a. Cash on Delivery (COD): Pay cash when the goods are delivered.
b. Cheque: The vendor may collect the cheque from you, and delivery will happen once it clears.
c. Net-Banking Transfer: Use online banking to transfer funds via services like IMPS, NEFT, or RTGS directly to the vendor's account.
d. Credit/Debit Cards: Credit cards allow purchases on credit, while debit cards let you spend what you have in your account.
e. Digital Cash: This is electronic money that you can use after paying a bank an equivalent amount.
Approximately 95 percent of online transactions are made with a credit card, highlighting its common use in online shopping. Vendors must ensure a secure method for collecting credit card details to prevent misuse.
Security and Safety of e-Transactions: e-Business Risks
Online transactions can be risky because they don’t happen face-to-face. These risks may lead to financial loss, damaged reputation, or stress. That’s why security is a major concern in e-business.
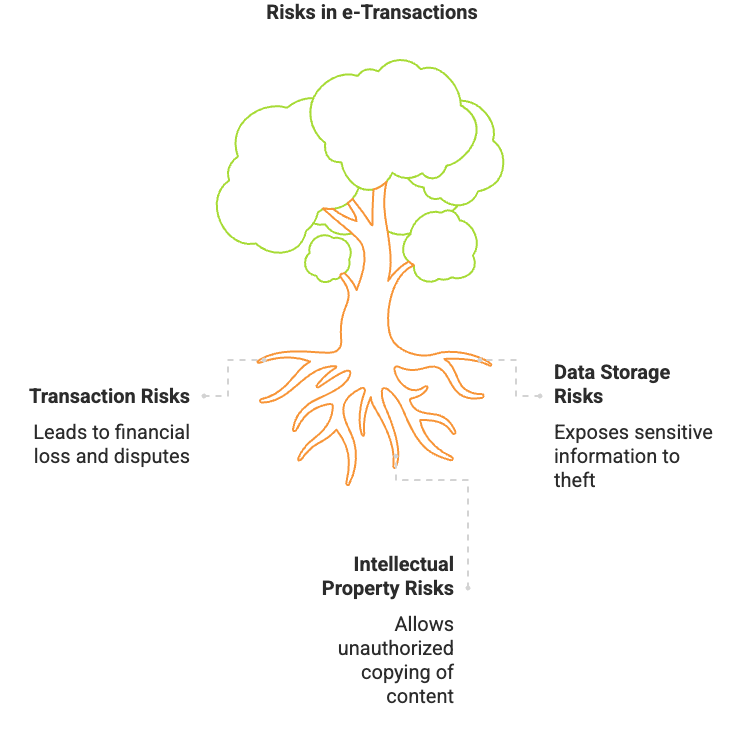
We can understand the risks in three broad categories:
1. Transaction Risks
These are problems that occur while placing an order, making a payment, or receiving delivery.
Order Problems:
A customer or seller may deny that the order was placed at all.Delivery Issues:
Goods may not be delivered, may go to the wrong address, or may be different from what was ordered.Payment Problems:
The seller may not receive the money even if the buyer claims to have paid.
How to reduce these risks:
Verify the customer’s identity and address at the time of registration.
Use cookies (like caller IDs) to check past activity.
Shop only from trusted websites that show seller details, ratings, and past records.
Use secure payment methods and trusted platforms like credit card companies with secure systems (e.g. SSL).
2. Data Storage and Transmission Risks
Important data (like personal details and payment info) is stored or shared online. If this data gets into the wrong hands, it can be misused.
Common risks:
Virus: A harmful program that can damage your files or even your entire computer.
Example: A Level-1 virus just shows messages; a Level-4 virus can destroy your system.Hacking: Someone breaks into your system to steal or change information.
How to stay safe:
Install anti-virus software and keep it updated.
Use encryption (cryptography) to protect data.
Encryption changes the message into unreadable code (cyphertext), which only the right person with a secret key can read (decrypt it back to plaintext).
3. Risks to Intellectual Property and Privacy
Once you put content online, anyone can copy it. This is a risk to your intellectual property.
Your personal details can be shared or sold, leading to spam emails and unwanted ads.
Resources Needed to Start an E-Business
To set up any business, you need:
Money (capital)
People (human resources)
Machines (hardware)
In addition, for e-business, you need:
A proper website – This is your company’s space on the internet.
It is not a physical place but an online location where your products, services, and information are shared.
You also need:
Technical support to develop, run, and update the website.
Tools to make sure your website is safe and secure for customers.
Key Terms
- e-Business: Doing business using the internet – includes buying, selling, customer service, etc.
- e-Commerce: Part of e-business that deals mainly with buying and selling goods and services online.
- Browser: A software (like Chrome or Firefox) used to access websites on the internet.
- Virus: A harmful computer program that can damage files or slow down systems.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): A security technology used to protect information (like passwords and card details) during online transactions.
- Online Trading: Buying and selling things (like shares or goods) over the internet.
- e-Trading: Another word for online trading – trading electronically instead of physically.
- e-Procurement: Using the internet to buy goods and services for a business (usually used by companies).
- e-Bidding: A process where suppliers bid online to sell goods/services, and the best offer is chosen.
- e-Cash: Digital money used for making payments online. It’s not in physical form but works like real money.
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO): When a business hires another company to do some of its work (e.g. customer care, data entry).
- Call Centres: Places where employees handle customer calls for sales, support, etc., often outsourced.
- Verticals: BPOs that focus on one specific industry, like banking or healthcare.
- Horizontals: BPOs that handle general tasks like HR or finance across many industries.
- Captive BPO Units: When a company sets up its own BPO in another country instead of giving it to an outside company.
- Sweat-shopping: When workers are made to work long hours for low wages in poor conditions – an unethical form of outsourcing.
|
38 videos|180 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Emerging Modes of Business Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is the difference between e-business and traditional business? |  |
| 2. What are the key concepts of e-business? |  |
| 3. How does e-business differ from e-commerce? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of e-business? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of e-business? |  |






















