Business Services NCERT Solutions | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Short Answer Question
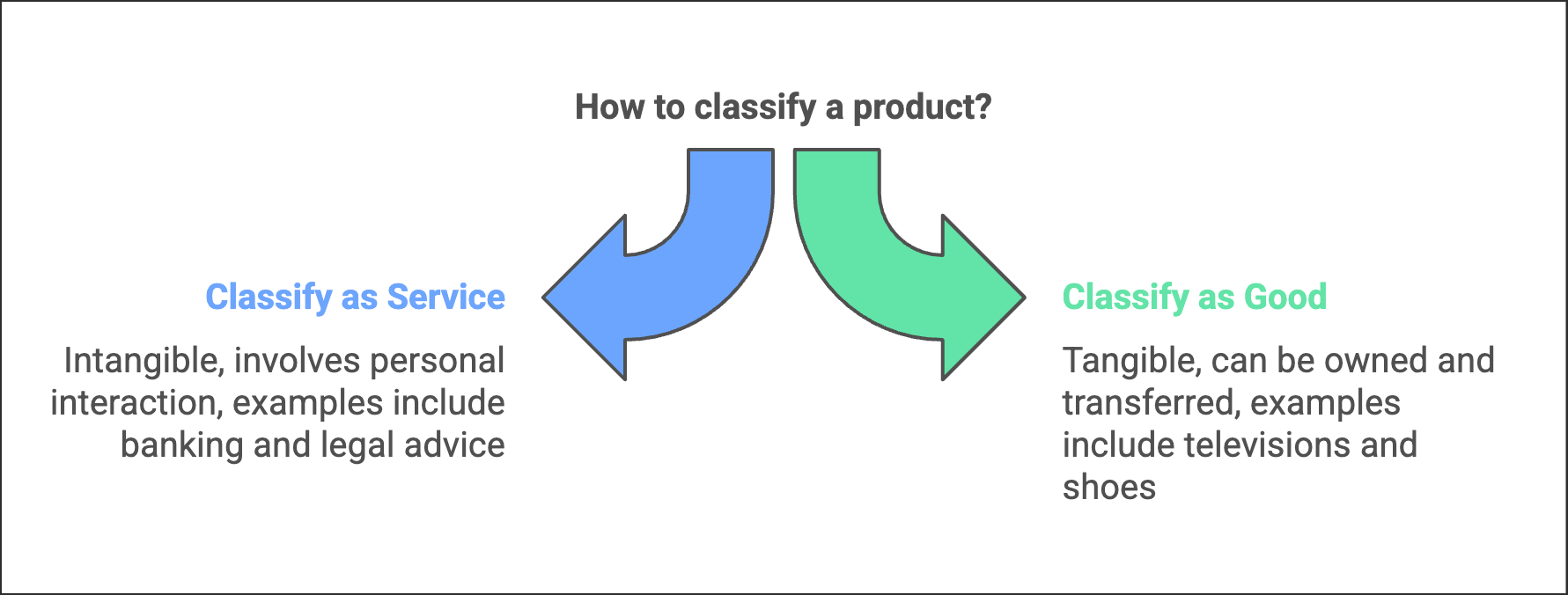
Q1. Define services and goods.
Ans: Services are activities that provide satisfaction to consumers and typically involve personal interaction between the consumer and the provider. They are intangible and do not result in ownership of a physical product. Services can be classified into two main categories:
- Business services: Examples include banking, insurance, and warehousing.
- Professional services: Examples include legal advice, medical consultations, and tax consultancy.
In contrast, goods are tangible items that can be owned and transferred upon purchase. Examples of goods include televisions, radios, and shoes.
Q2. What is e-banking. What are the advantages of e-banking?
Ans: e-banking refers to using electronic means to perform various banking tasks, such as:
- Transferring money
- Checking account balances
- Applying for loans
These services are offered by commercial banks, allowing customers to manage their banking needs online from anywhere, at any time. The advantages of e-banking include:
- 24/7 Availability: Customers can access their accounts and perform transactions at any time, providing flexibility and convenience.
- Easy Access: Banking can be done via mobile phones or computers, making it simple to manage finances.
- Reduced Workload: E-banking decreases the demand on bank branches, as many services can be completed electronically.
- Financial Discipline: E-banking records all transactions, helping users keep track of their spending.
- Enhanced Security: Customers can avoid carrying cash, reducing the risk of theft.
Q3. Write a note on various telecom services available for enhancing business.
Ans: The following are the various types of telecom services that enable a business to carry out its operations efficiently.
- Cellular mobile service: It includes voice and non-voice transmission services and data transmission services.
- Radio paging service: It is a one-way communication service by which information is transmitted in the form of a tone or numeric or alphanumeric message.
- Fixed-line service: Under this kind, fibre optic cables are laid across the country for transmitting information including both voice and non-voice messages.
- Cable service: This service is used to transmit media-related information to a defined area of operation for which a licence has been acquired. In this type of telecom service, the flow of information is one way.
- VSAT service: The abbreviation ‘VSAT’ stands for ‘very small aperture terminal’—it is a satellite-based communication service through which information can be transmitted to far-flung and remote areas. Therefore, it provides a wider reach and a high degree of flexibility to businesses.
- DTH service: The abbreviation ‘DTH’ stands for direct-to−home—DTH service is a type of telecom service provided by DTH companies. The companies transmit TV channels to customers through satellites. Customers can watch multiple channels by installing a small dish antenna and a set-top box connected to their television set.
Q4. Explain briefly the principles of insurance with suitable examples?
Ans:
- Utmost good faith: Both the insurer and the insured must trust each other and the contract.
Example: Rahul, a heart patient, should disclose his health issues when purchasing a life insurance policy. - Insurable interest: It implies that the insured must have some interest vested in the object which is being insured by him.
Example: A businessperson has an insurable interest in his or her land, house and other properties. - Indemnity: According to the principle of indemnity, the purpose of an insurance contract is to bring back the insured to the same financial position as he or she was before the loss occurred to him or her (because of a mishap).
Example: If an individual suffers a loss of Rs. 1 lakh in a fire accident, then the insurance company will accept a claim up to Rs. 1 lakh and not more. - Proximate cause: The reason for the loss must be related to the insured item.
Example: If a fire causes damage, this event must be covered in the insurance policy for a claim to be valid. - Subrogation: Once the compensation is paid, the right of ownership of the damaged property passes on to the insurer, so that the insured cannot sell the damaged property to make profits.
Example: If a person receives Rs. 1 lakh for his or her damaged stock, then the ownership of the stock will be transferred to the insurance company and the person will hold no control over the stock. - Contribution: If multiple policies exist for the same item, insurers share the compensation.
Example: If person A insures their house for Rs. 2 lakh with insurer B and Rs. 1 lakh with insurer C, and suffers a loss of Rs. 90,000, both insurers will pay a total of Rs. 90,000, not more. - Mitigation: The insured should take care of the insured object in the same way as he or she would have in the absence of the insurance.
Example: If a person has insured his house against fire, then, in case of fire, he or she should take all possible measures to minimise the damage to the property exactly in the manner he or she would have done in the absence of the insurance.
Q5. Explain warehousing and its functions.
Ans: Warehousing is the process of storing goods in a systematic way to preserve their quality and value. Modern warehouses have evolved from simple storage spaces to comprehensive logistical service providers, ensuring that products are available at the right time, place, and cost. The main functions of warehousing include:
- Storage: Warehouses facilitate the storage of goods and raw materials that are not required immediately for sale or for manufacturing, and protect them from spoilage or damage.
- Value-added services: They perform value-added services, such as grading the quality of products, packaging and labelling, for producers.
- Financing: The owner of the goods or raw materials stored in a warehouse can use the warehouse receipt as a security for borrowing money from banks or other financial institutions.
Long Answer Question
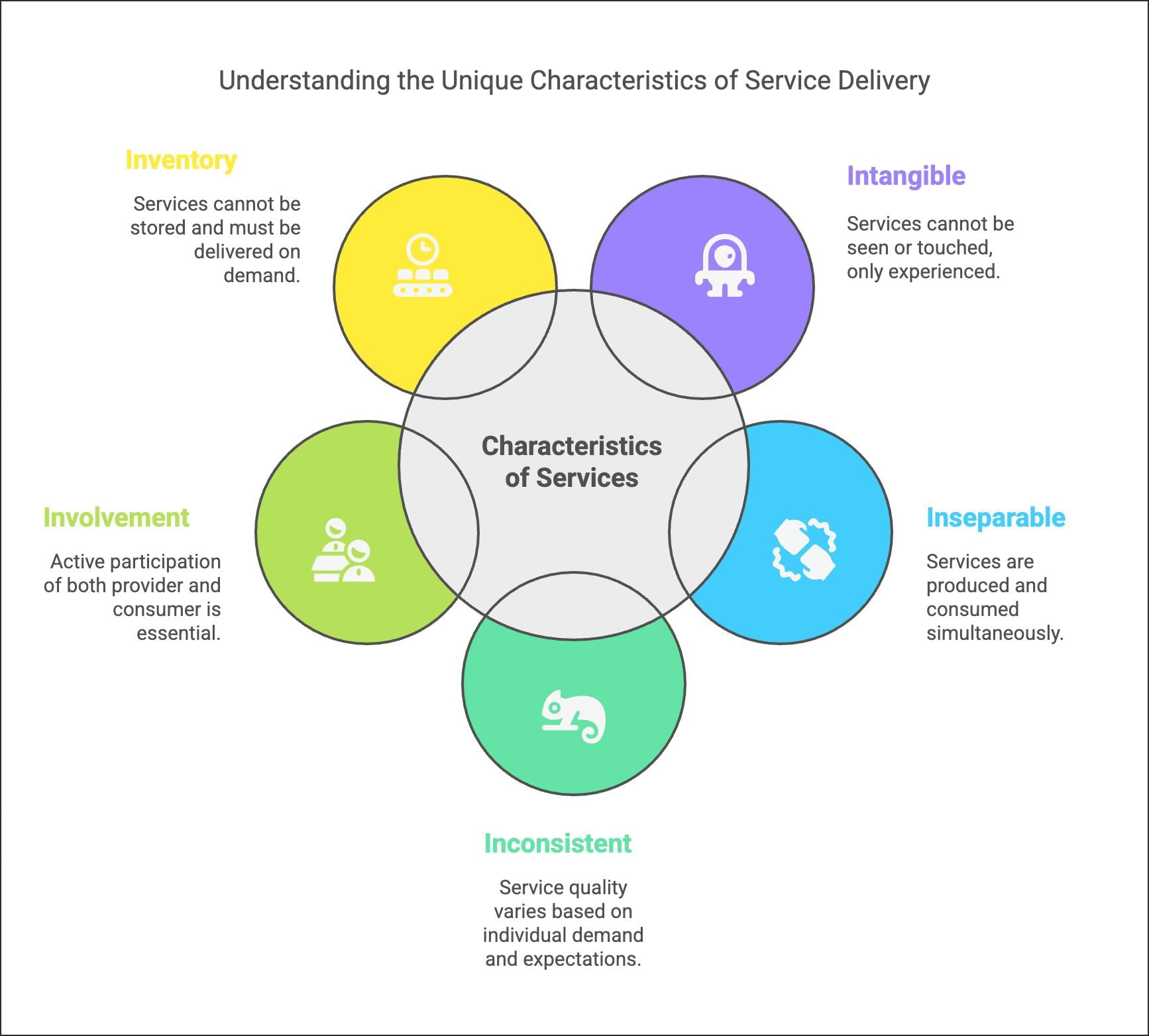
Q1. What are services? Explain their distinct characteristics.
Ans: Services are intangible economic activities that require personal interaction between the consumer and the service provider at the time of delivery of the services. Services need not involve any kind of production or sale of goods and are mainly provided to satisfy individuals’ wants. Services are generally classified into business services (including banking, insurance and warehousing) and professional services (including legal services, medical advice and tax consultancy).
Features of services are as follows:
- Intangible: Services are intangible as they cannot be seen or touched. One can only experience them. This implies that the quality of services cannot be checked before their use. Thus, it becomes imperative for service providers to offer services to the satisfaction of the individuals concerned.
- Inseparable: Services have to be produced and used simultaneously. Unlike goods, which are produced today for sale later, services have to be used at the same time as they are made available.
- Inconsistent: No standards can be set for services; they have to be provided each time according to the demand and expectations of the service users. As each service user has different tastes and preferences, the type and quality of services provided differ according to the user.
- Involvement: The involvement of the service user and the service provider is a prerequisite at the time of delivery of the services. For instance, in a school, the teacher and the students are actively involved in the exchange of the service of imparting knowledge.
- Inventory: Services cannot be stored for sale at a future date. They need to be provided as and when the service users ask for them. This is because if services are not consumed immediately then they lose their value.
Q2. Explain the functions of commercial banks with an example of each.
Ans: The following functions are performed by commercial banks:
- Collection of deposits: Banks accept various types of deposits from the public, including savings accounts, current accounts, and fixed deposits. They pay interest on these deposits and are obligated to return the deposited amount.
- Lending of funds: Banks provide loans and advances based on their total deposits. These can include overdrafts, discounted trade bills, and consumer credits. The interest from these loans is a key source of profit for banks.
- Cheque facility: Banks facilitate the collection of cheques drawn on other banks, acting as a clearing house. There are two main types of cheques:
- Bearer cheques: Encashable immediately at bank counters.
- Crossed cheques: These can only be deposited into the payee’s account.
- Remittance of funds: Banks assist in transferring customer funds from one location to another, using bank drafts and pay orders for a nominal fee.
- Provision of allied services: In addition to the above functions, banks offer services such as locker facilities, underwriting services, and bill payments. They also handle the buying and selling of shares and debentures on behalf of customers.
Q3. Write a detailed note on various facilities offered by the Indian Postal Department.
Ans: The Indian Postal Department offers a range of facilities, which can be categorised as follows:
Financial Facilities:
- Public Provident Fund (PPF)
- Kisan Vikas Patra
- National Saving Certificate (NSC)
- Recurring Deposit Scheme
- Fixed Deposit Scheme
- Money Order Facility
Mail Facilities:
Mail facilities primarily include the following three kinds of services:
(i)Parcel facilities: They facilitate the movement of an article from one place to another.
(ii) Registration facilities: They provide security to the article being transmitted.
(iii) Insurance facilities: They cover the risks involved in transmission by post.
Some of the mail facilities provided by the banks are as follows:
(i) Postcards: It is the cheapest form of postal service.
(ii) Letter: It ensures the secrecy of the information conveyed, and is placed in an envelope.
(iii) Registered post: Registered post ensures that the mail registered is delivered to the addressee or returned to the sender if it is not delivered.
Allied Facilities:
- Passport Service: Accepts passport applications for the Ministry of External Affairs.
- Media Post: Allows corporate advertising through postcards and letters.
- Direct Post: Delivers brochures, pamphlets, and CDs for advertising.
- Speed Post: Ensures rapid delivery of articles within a specified timeframe.
Q4. Describe various types of insurance and examine the nature of risks protected by each type of insurance.
Ans: Insurance can be classified into three main types:
- Life Insurance
- Fire Insurance
- Marine Insurance
1. Life Insurance
- Life insurance is an agreement between the insurer and the insured.
- In this agreement, the insurerpromises to pay a specific amount of money when either of two events occurs:
- The death of the insured.
- The end of the insurance contract period.
- If the insured dies before the contract ends, their family will receive the agreed amount of money.
- If the insured lives until the contract matures, they will receive the specified sum of money at that time.
- To get this financial protection, the insured must pay a regular fee known as a premium to the insurer.
- The reason for needing a life insurance policy is due to the uncertainties of life.
- It protects against two main risks:
- Risk of dying too early - providing financial support to the family.
- Risk of dying too late - ensuring funds for retirement.
2. Fire Insurance: This type of insurance covers loss or damage caused by fire. Important aspects include:
- The insurer compensates for losses during a specified period, up to a pre-defined limit.
- Insured must take reasonable steps to minimise damage, or risk losing the claim.
3. Marine Insurance: This insurance protects against losses related to ships or cargo at sea. Key features include:
- Covers complete or partial loss due to various marine perils like collisions or piracy.
- Insured pays a premium for this protection.
In summary, each type of insurance serves to mitigate specific risks, providing financial security in uncertain situations.
Q5. Explain in detail the warehousing services.
Ans: Warehousing involves the systematic storage of goods to preserve their quality and value over time. A warehouse serves as a facility not only for storage but also for logistical services, ensuring that the right quantity of goods is available at the right time and cost. The main functions of warehousing include:
- Consolidation: Warehouses collect goods from various sources and dispatch them together. This reduces shipping time and costs.
- Bulk Breaking: Goods are received in large quantities and divided into smaller amounts for delivery to different customers based on their needs.
- Stockpiling: Warehouses store goods that are not immediately needed for sale or production, protecting them from spoilage or damage.
- Price Stabilisation: By storing excess goods during high supply periods, warehouses help prevent price drops. Conversely, they can release goods during shortages to control price increases.
- Value-added Services: Warehouses may provide additional services such as grading, packaging, and labelling to enhance the quality of stored goods.
- Financing: Warehouse receipts can serve as collateral for loans, allowing owners to secure financing against their stored goods.
|
38 videos|269 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Business Services NCERT Solutions - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are business services? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of business services? |  |
| 3. How can businesses benefit from outsourcing business services? |  |
| 4. What factors should businesses consider when selecting a business services provider? |  |
| 5. How can businesses ensure the quality of business services received? |  |

















