Sources of Business Finance NCERT Solutions | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What is business finance? Why do businesses need funds? Explain.
Ans: Business finance refers to the funds required to carry out the establishment and running of operations of a business. These operations include the purchase of premises and payment of wages and salaries. The funds required to finance the expansion of a business are also considered a part of business finance.
The following are the reasons why a business needs funds.
- Fixed capital requirements: For setting up a business, fixed assets such as building, machinery, furniture and fixtures are required. The requirement of funds to purchase these assets is known as fixed capital requirement. The level of requirement of funds depends upon the size and nature of a business.
- Working capital requirements: Firms require funds for financing their day-to-day operations, such as the purchase of raw materials and payment of wages to workers. The requirement of funds for such operations is known as the working capital requirement.
Q2: List sources of raising long-term and short-term finance.
Ans: The following are some of the sources of long-term funds.
- Equity shares: These represent the ownership capital of a company. The holders of such shares enjoy a say in the management and gain higher returns when the company earns higher profits.
- Retained earnings: These are the undistributed profits of a business that are retained in the business for future use.
- Debentures: Debentures are financial instruments used by companies to raise long-term debt capital. They carry a fixed rate of return and specify a time for repayment.
The following are some of the sources of short-term funds.
- Trade credit: It is the amount of credit that is extended by the supplier to the purchaser. It facilitates the purchase of goods on credit.
- Banks: Business enterprises can also obtain short-term funds from banks.
- Commercial paper: These are credit instruments used by creditworthy firms to obtain short-term finance for their business.
Q3: What is the difference between the internal and external sources of raising funds? Explain.
Ans: Internal sources of funds are generated within a business. Examples include:
- Selling surplus inventories
- Collecting receivables
- Reinvesting profits
These funds typically meet only limited needs as the amounts raised are generally small. External sources of funds come from outside the organisation, such as:
- Suppliers
- Creditors
- Investors
- Banks and financial institutions
Funds from these sources can be significantly larger, making them suitable for financing large operations. In summary:
- Internal sources are limited and generated within the business.
- External sources can provide larger amounts and come from outside the business.
Q4: What preferential rights are enjoyed by preference shareholders? Explain.
Ans: Preference shares offer shareholders certain preferential rights regarding capital repayment and dividend payments. These shares are issued by companies to raise funds, and their repayment is governed by the terms outlined in the Companies Act, 1956. Preference shareholders enjoy the following rights:
- Fixed Dividends: Holders are entitled to receive dividends at a fixed rate before any dividends are paid to equity shareholders.
- Capital Repayment: In the event of liquidation, preference shareholders have the right to receive their invested capital before equity shareholders.
Preference shares share characteristics with both equity shares and debentures. They provide a fixed return like debentures but may not guarantee dividends, similar to equity shares. Additionally, preference shareholders typically do not have voting rights. Types of preference shares include:
- Cumulative: Unpaid dividends accumulate for future payment.
- Participating: Holders can participate in additional profits after fixed dividends are paid.
- Convertible: These can be converted into equity shares at a specified time.
Overall, preference shares are suitable for investors seeking stable income with lower risk.
Q5: Name any three special financial institutions and state their objectives.
Ans: Financial institutions refer to central or state government establishments that exist to finance business operations. These institutions provide long-term finance to firms to help them in their expansion, modernisation and reorganisation programmes.
The following are the three main financial institutions.
- Unit Trust of India (UTI): The UTI was established in 1964 under the Unit Trust of India Act, 1963, with the objective of mobilising the community’s savings and utilising the funds to finance profitable ventures.
- Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI): The ICICI was established as a public limited company in 1955. The main objective of the ICICI was to facilitate the creation, modernisation and expansion of enterprises in the private sector.
- Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI): The IFCI was established in 1948 under the Industrial Finance Corporation Act, 1948, to facilitate regional development and encourage new entrepreneurs to enter the priority sectors of the economy.
Q6: What is the difference between GDR and ADR? Explain.
Ans: Global Depository Receipts (GDRs) and American Depository Receipts (ADRs) are both financial instruments that allow investors to buy shares in foreign companies, but they differ in several key aspects:
- GDRs are issued by depository banks against shares of a company, typically to raise funds in foreign currency. They are usually denominated in US dollars and can be traded on stock exchanges outside the US.
- GDRs allow holders to convert them into shares at any time. However, they do not provide voting rights, only dividends and capital appreciation.
- Examples of Indian companies that have issued GDRs include Infosys, Reliance, and Wipro.
- ADRs are specific to companies based in the US. They are traded on US securities markets and can only be sold to US citizens.
- ADRs function similarly to GDRs but are limited to the US market, making them less accessible for international investors.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Explain trade credit and bank credit as sources of short-term finance for business enterprises.
Ans: Trade Credit: Trade credit is the credit provided by suppliers to purchasers of goods or services. It allows buyers to acquire products without immediate cash payment, which can help manage cash flow effectively. Trade credit is typically extended to customers deemed creditworthy by the supplier.
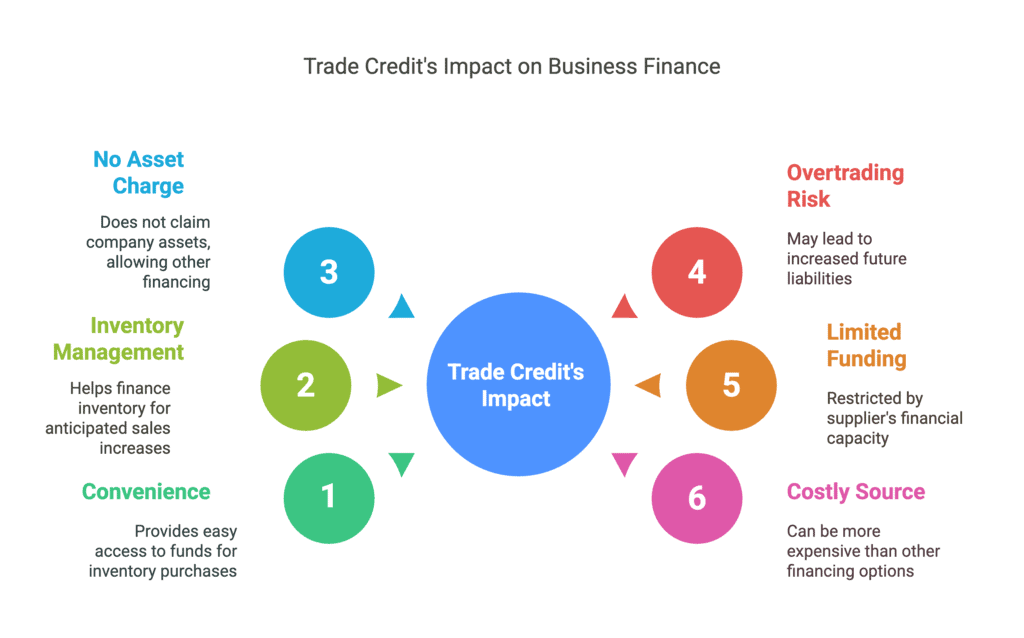
Merits of Trade Credit:
- Convenience: It serves as a continuous source of funds, making it easy for businesses to purchase inventory.
- Inventory Management: Businesses can finance inventory accumulation to meet anticipated sales increases.
- No Asset Charge: Trade credit does not create claims on the company's assets, allowing for other financing options.
Demerits of Trade Credit:
- Overtrading Risk: Easy access to trade credit may lead to overtrading, increasing future liabilities.
- Limited Funding: The amount available through trade credit is restricted by the supplier's financial capacity.
- Costly Source: Trade credit can be more expensive compared to other financing options.
Bank Credit: Bank credit refers to loans provided by banks to businesses. The interest rate is typically influenced by the prevailing economic conditions. To secure a loan, borrowers often need to mortgage assets.
Merits of Bank Credit:
- Confidentiality: Banks maintain confidentiality regarding customer information.
- Flexibility: Borrowers can adjust the loan amount based on their business needs.
Demerits of Bank Credit:
- Loan Increase Difficulty: It can be challenging to increase the loan amount once established.
- Restrictive Terms: Banks may impose strict conditions, such as limiting the sale of mortgaged goods.
Q2: Discuss the sources from which a large industrial enterprise can raise capital for financing modernisation and expansion.
Ans: The following are some of the sources of long-term funds.
- Equity shares: These shares represent the ownership capital of a company. The holders of such shares are known as equity shareholders and enjoy a say in the management and gain higher returns when the profits are higher. They are also called the owners of the company, or residual owners, since payments to them are made only after paying the external debts or claims.
- Retained earnings: Firms generally keep a certain fraction or part of their profits before distributing dividends to their shareholders. These undistributed profits are known as retained earnings because the funds are kept for future use.
- Preference shares: These types of shares provide the shareholders a preferential right regarding the repayment of capital and payment of earnings after a certain specified period of time. Such repayment to the preference shareholders is made in accordance with the terms specified in Section 80 of the Companies Act, 1956.
- Debentures: Debentures are financial instruments used by companies to raise long-term debt capital. They imply that a company has borrowed a certain sum of money, which it will repay later to the debenture holders. Just like loans, they carry a fixed rate of return and specify in advance the time for repayment of the debts.
- Loans from banks and other financial institutions: Business enterprises can borrow funds for a fixed period of time from banks and financial institutions in return for a fixed periodic payment called interest. The time for repayment of such a loan is fixed and is stated in advance at the time of granting the loan.
Q3: What advantages does the issue of debentures provide over the issue of equity shares?
Ans: Debentures are financial instruments used by companies to raise long-term debt capital. They imply that the company has borrowed a certain sum of money, which it will repay later to the debenture holders. They are considered fixed-income securities as they carry a fixed rate of return and are repayable on a certain pre-specified date in the future. The following are the advantages of issuing debentures over issuing equity shares.
- No dilution of ownership: The issue of equity shares denotes the dilution of ownership of a firm. This is because the equity shareholders own specified shares of the company and have voting rights. In contrast, debenture holders do not have any rights in the company. That is, they do not enjoy voting rights or any kind of ownership in the firm. Rather, they are only entitled to a fixed amount as payment. Thus, debentures do not result in any kind of dilution of ownership of the firm. Thus, issuing debentures is more advantageous for a firm than issuing equity shares.
- Lower costs: In order to issue shares, a company has to incur huge costs. Besides, it has to pay dividends to its shareholders, which are not tax deductible. On the other hand, a company receives tax deductions on the interest paid to its debenture holders. Hence, issuing debentures is advantageous for a firm in terms of low costs.
- Fixed returns: Debentures carry a fixed rate of return. This implies that irrespective of the profit earned, the company has to pay only a fixed interest to its debenture holders. On the other hand, a company that issues shares has to pay dividends to the shareholders, which varies with the profit—i.e., the higher the profit, the higher the dividends. Thus, companies prefer to issue debentures if they expect to earn higher profits in a year.
Q4: State the merits and demerits of public deposits and retained earnings as methods of business finance.
Ans: Public deposits: Organisations raise public deposits directly from the public to finance their short-term as well as medium-term financial requirements. The rate of return on such deposits is generally higher than the return paid on bank deposits. In case a person is interested in investing in a business (by depositing money), then he or she can submit a prescribed form along with the deposit. In return for this sum borrowed, the organisation issues a deposit receipt as a token of acknowledgment of the debt.
Merits of Public Deposits:
- Raising money by accepting public deposits is a very simple process with few regulations involved.
- The cost of raising funds by accepting public deposits is generally lower than the cost involved in borrowing loans from commercial banks.
- The depositors do not have any voting or management rights. Thus, the acceptance of public deposits does not result in any dilution of ownership of the business.
Demerits of Public Deposits:
- The amount of money that can be raised from public deposits is limited as it depends on the availability of funds and the willingness of people to invest in the company concerned.
- Generally, it is difficult for new companies to raise capital through public deposits as people lack faith in them.
- When a firm has huge capital requirements, it may face difficulty in borrowing funds through the issue of public deposits.
Retained Earnings: Firms usually keep a certain part of the profits earned before distributing dividends to their shareholders. These undistributed profits are retained in the business for future use and are known as retained earnings.
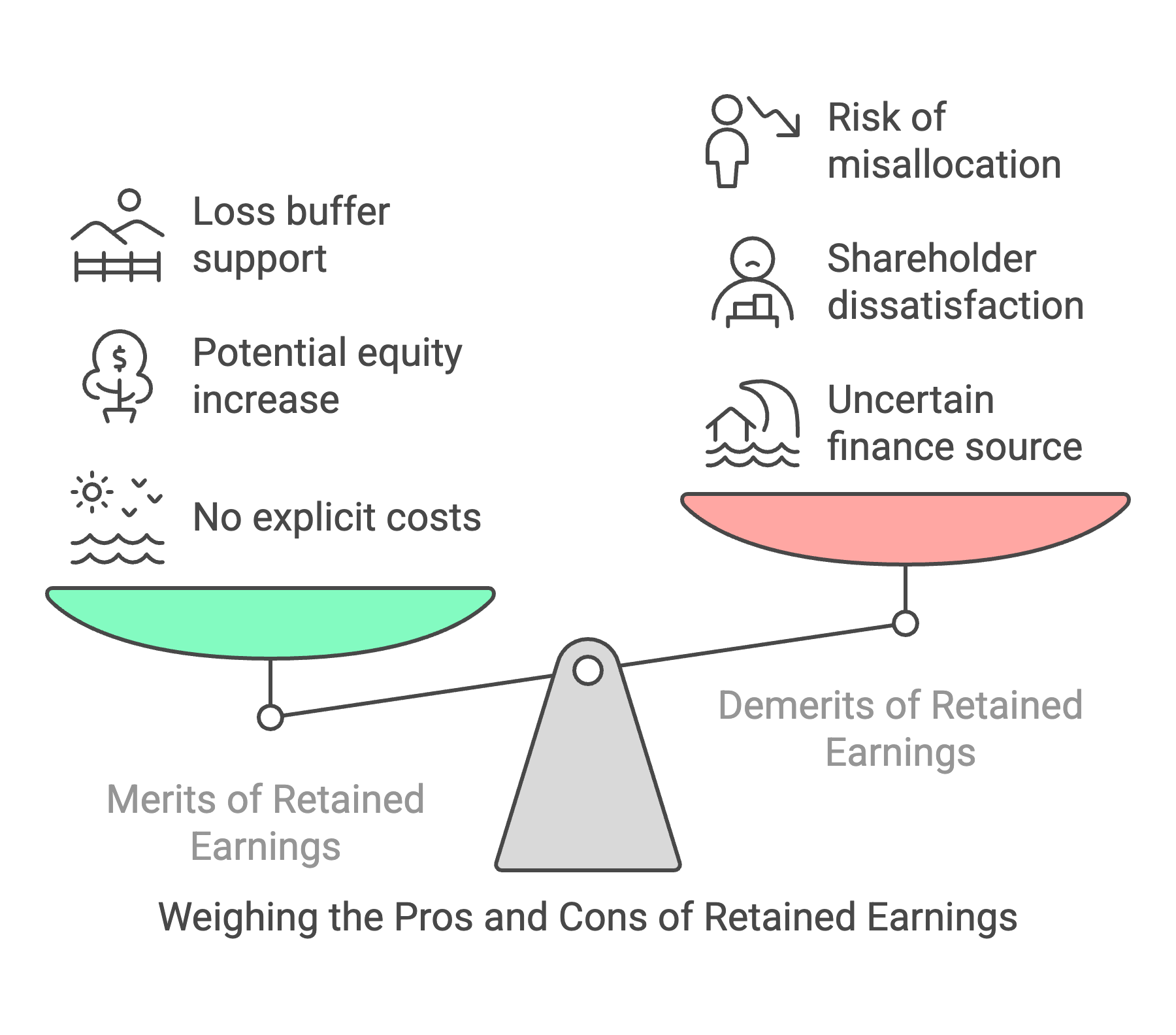
Merits of Retained Earnings:
- As these funds are raised internally, they do not involve any kind of explicit costs, such as floatation cost and interest.
- High amounts of retained earnings can lead to an increase in the price of equity shares.(c) Since these are surplus profits retained in the business, they help in reducing the burden of unexpected losses.
Demerits of Retained Earnings:
- Retained earnings are an uncertain source of finance as the business profits keep fluctuating from time to time.
- In case a firm reinvests a large portion of profits in the business, then very few funds are left for payments to the shareholders, and this creates dissatisfaction among them.
- Firms often fail to recognise the opportunity cost of the earnings retained in the business. As a result, these funds are often misused or sub-optimally used.
|
38 videos|180 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Sources of Business Finance NCERT Solutions - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the different sources of business finance? |  |
| 2. How can a company raise funds through equity shares? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of raising funds through debentures? |  |
| 4. How can a company obtain loans from financial institutions? |  |
| 5. What is trade credit and how does it serve as a source of business finance? |  |






















