Marketing Management NCERT Solutions | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: State any two advantages of branding to marketers of goods and services?Ans:
- Product Differentiation: Branding helps in differentiating a product from its competitors, allowing customers to identify the product easily.
- Customer Loyalty: Branding builds customer loyalty as a trusted brand retains its consumers over time.
Q2: How does branding help in differential pricing?
Ans: Branding allows firms to charge higher prices for their products by creating a perception of superior quality and added value.
Q3: What is the societal concept of marketing?
Ans: The societal concept of marketing focuses on meeting customer needs in a way that preserves and enhances the well-being of society, addressing long-term issues like environmental protection and ethical considerations.
Q4: Enlist the advantages of packaging of consumer products.
Ans:
- Product Protection: Protects the contents from damage during storage and transportation.
- Product Identification: Helps in identifying the product easily through labels and branding.
- Convenience: Makes it easier for customers to handle, open, and store the product.
- Promotion: Attracts attention and persuades customers through visual appeal.
Q5: List five shopping products purchased by you or your family during the last few months.
Ans: Examples include:
- Refrigerator
- Television
- Furniture
- Jewellery
- Microwave Oven.
Q6: A marketer of colour TV having 20% of the current market share of the country aims at enhancing the market share to 50 per cent in next three years. For achieving this objective, he specified an action programme. Name the function of marketing being discussed above.
Ans: The function of marketing being discussed is Marketing Planning.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. What is marketing? What functions does it perform in the process of exchange of goods and services? Explain.
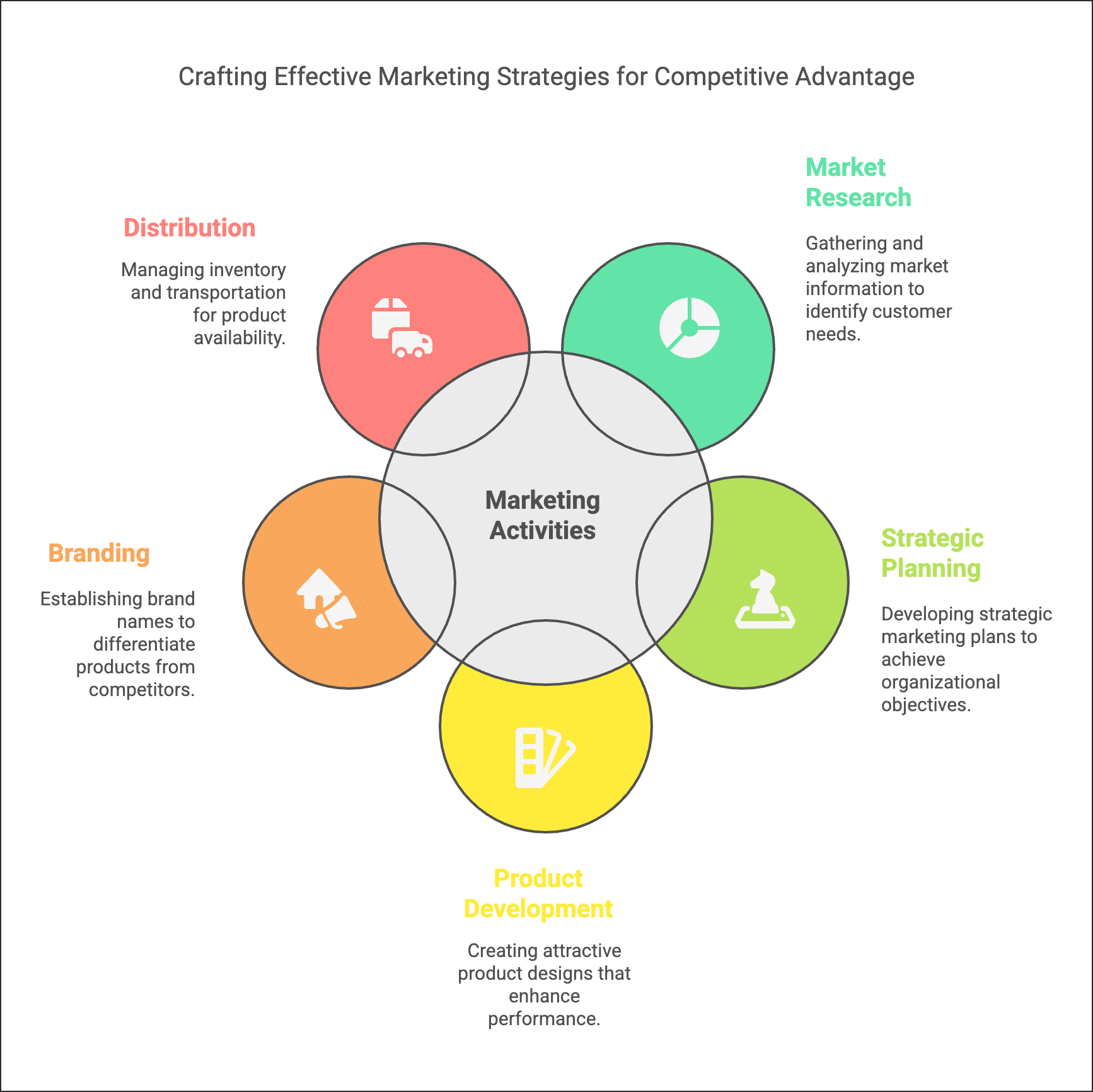
Ans: Marketing is a comprehensive system of business activities aimed at planning, pricing, promoting, and distributing goods and services that satisfy customer needs. It focuses on the exchange of products from producers to consumers and involves various key activities:
- Gathering and Analysing Market Information: This helps identify customer needs and informs decisions for effective marketing.
- Marketing Planning: Developing strategic marketing plans to achieve organisational objectives.
- Product Designing and Development: Creating attractive product designs that enhance performance and provide a competitive edge.
- Standardisation and Grading: Ensuring uniformity in production to reduce inspection needs and classifying products based on features like quality and size.
- Packaging and Labelling: Designing product packaging for protection and promotion, while labels assist in self-service.
- Branding: Establishing brand names to differentiate products from competitors.
- Customer Support: Providing after-sales services and handling complaints to ensure customer satisfaction.
- Pricing of Products: Setting prices based on a thorough analysis of market factors affecting product success.
- Promotion: Informing customers about products and persuading them to buy through advertising, sales promotions, personal selling, and publicity.
- Physical Distribution: Managing inventory, storage, and transportation of goods to ensure availability.
- Transportation: Efficiently moving goods to target markets, considering product nature and costs.
- Storage or Warehousing: Maintaining adequate stock levels to ensure smooth market flow and meet demand contingencies.
Marketing is not just a post-production activity; it encompasses actions taken before production begins and continues after sales. By effectively managing these functions, organisations can enhance customer satisfaction and achieve their goals.
Q2. Distinguish between the product concept and production concept of marketing.
Ans: Difference between product and production concept:
Basis:
- Product concept: Focuses on creating high-quality products.
- Production concept: Emphasises large-scale production.
Focus:
- Product concept: Aims to deliver superior quality.
- Production concept: Aims for mass availability.
Means:
- Product concept: Involves continuous product improvement.
- Production concept: Ensures products are easily accessible.
Ends:
- Product concept: Seeks profit by offering better quality.
- Production concept: Seeks profit through volume production.
Q3. Product is a bundle of utilities. Explain.
Ans: A product is essentially a bundle of utilities that satisfies specific needs. Buyers choose products or services based on the benefits they offer. There are three main types of benefits that customers seek:
- Functional benefits - the practical use of the product.
- Psychological benefits - the emotional satisfaction derived from the product.
- Social benefits - the acceptance and status gained from using the product.
For example, purchasing a motorcycle provides:
- Functional utility of transportation.
- Psychological satisfaction of prestige and esteem.
- Social acceptance from peers.
These aspects are crucial when planning a product.
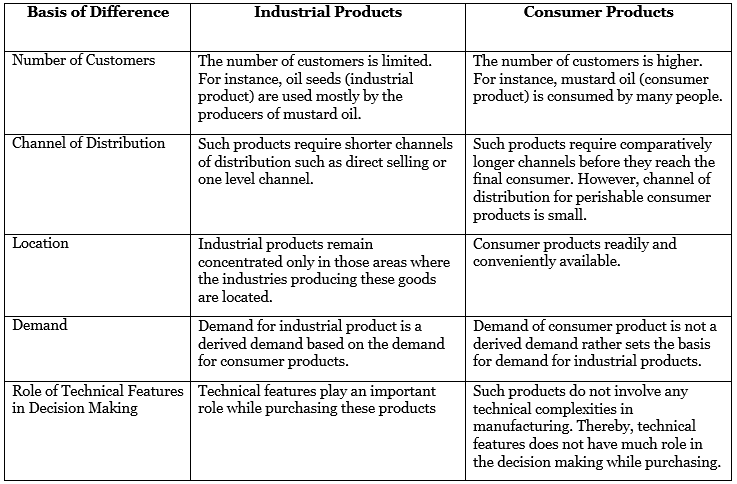
Q4. What are industrial products? How are they different from consumer products? Explain.
Ans: Industrial products are items used as inputs in the production of other goods. They are not intended for final consumption but serve as raw materials or components for manufacturers. Examples include:
- Machines
- Tools
- Engines
- Lubricants
In contrast, consumer products are goods purchased by individuals for personal use. Examples include:
- Toothpaste
- Edible oil
- Furniture
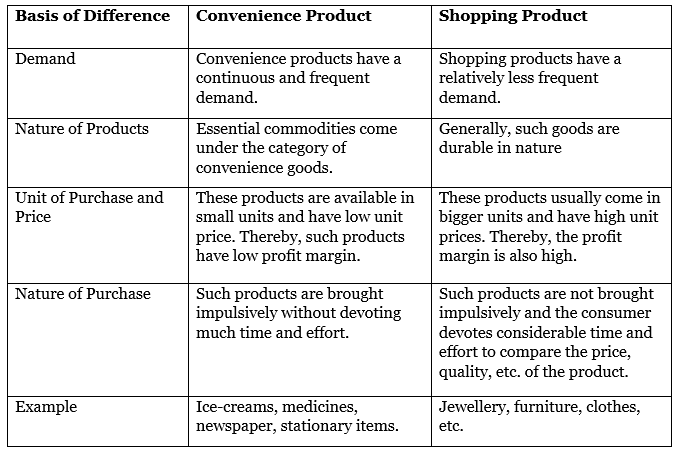
Q5. Distinguish between convenience products and shopping products.
Ans:
Q6. Describe the functions of labelling in the marketing of products.
Ans: The label on a product provides detailed information about the product, its contents, methods of use etc. The various functions performed by a label are as follows:
- Describe the Product and Specify its Contents: One of the most important functions of labels is that they describe the product, its usage, cautions in use etc and specify its contents
- Identification of the Product or Brand: A label helps in identifying the product or brand e.g., we can easily pick our favourite soap from a number of packages only because of its label.
- Grading of Products: Labels help in grading the products into different categories. Sometimes, marketers assign different grades to indicate features or quality of the product e.g., different type of tea is sold by some brands under Yellow, Red and Green label categories.
- Help in the Promotion of Products: An important function of labels is to aid in the promotion of the products. A carefully designed label can attract the customer to purchase. So, many labels provide promotional messages, some show discounts or other schemes etc
- Providing Information Required by Law: Another important function of labelling is to provide information required by law. e.g., the statutory warning on the package of cigarette or pan masala – ‘Smoking is injurious to health’ or ‘Chewing tobacco causes cancer.’
Q7. Discuss the role of intermediaries in the distribution of consumer non-durable products.
Ans: The term channels of distribution refers to facilitating the movement of goods and services and their title between the point of production and point of consumption, by performing a variety of marketing activities. Following are the functions performed by the channels of distribution
- Accumulation: It aims at holding the stock to match between the consumer demand and supply condition, warehousing helps in maintaining continuous flow of goods and services.
- Promotion: The marketing channels also help in promoting the demand for the product by displaying demonstrating and participating in various promotional activities organised by the producers.
- Negotiating: The marketing channels are the intermediaries between the producers and the consumers. They attempt to reach a final agreement on price and other terms of the offer so that the transfer of ownership is properly affected.
- Risk: Taking risk-taking is the basic responsibility of the intermediaries. It may arise out of physical deteriorations, changes in price levels, natural calamities, changes in fashion etc. These are unavoidable as they hold sufficiently large and variety of inventories till the sale of stock.
- Grading/Sorting: Grading is the process whereby they sort the products based on different sizes, qualities, moisture contents and so on. It helps us realise the time value of the product and at the same time ultimate consumer feels satisfied with the uniform quality of the product.
- Packaging: The products are packed in small tradable lots for the convenience of the consumer.
- Assembling/Assortment: Marketing channels aim at satisfying the needs of the customers. The products desired by the consumer may not be available in the market. They procure such goods from different sources and assemble or assort them as per the requirements of the consumers.
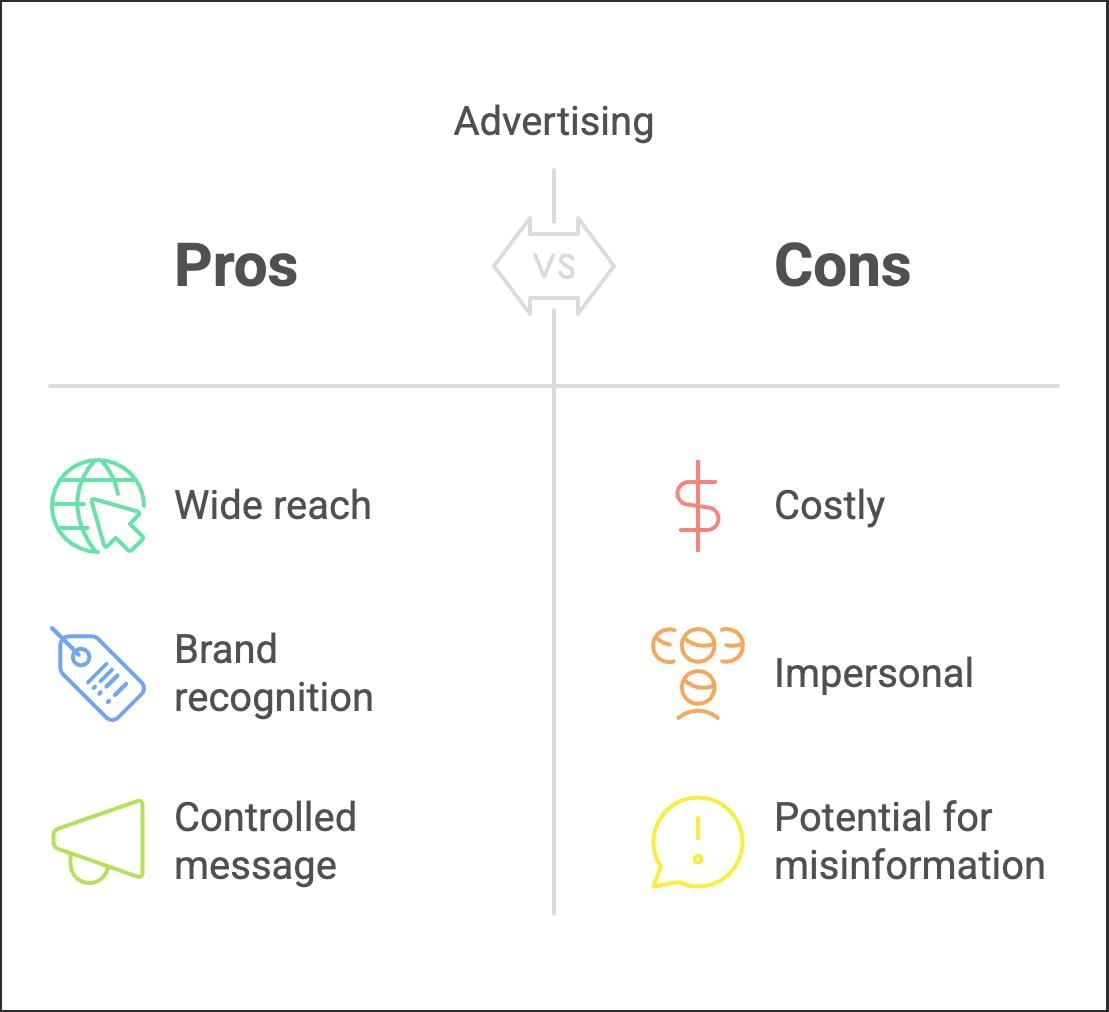
Q8. Define advertising. What are its main features? Explain.
Ans: Advertising is defined as the impersonal form of communication which is paid for by the marketer to promote some goods or services, It is commonly used as the promotional tool of the company, The important features of advertising are as follows:
- Paid Form: Advertising is a paid form of communication which means the sponsor has to bear the cost of communication with the prospects,
- Impersonality: There is no direct face-to-face contact between the prospect and advertiser, It is, therefore, referred to as the impersonal method of promotion.
- Identified Sponsor: Advertising is undertaken by some Identified individual or company, that makes the advertising efforts and also bears the cost of it.
Q9. Discuss the role of ‘sales promotion’ as an element of the promotion mix.
Ans: Sales promotion refers to short-term incentives aimed at encouraging immediate purchases of products or services. It encompasses various promotional activities beyond advertising, personal selling, and publicity, designed to boost sales. Common sales promotion activities include:
- Cash discounts and rebates
- Sales contests
- Free gifts and samples
The main objectives of sales promotion are:
- Creating demand for the product.
- Educating consumers about new products or uses of existing products.
- Building brand loyalty.
Sales promotion also complements other promotional efforts, enhancing overall effectiveness. However, frequent reliance on sales promotions can negatively impact a product's image, suggesting poor quality or pricing issues.
Q10. As the marketing manager of a big hotel located at an important tourist destination, what societal concerns would be faced by you and what steps would you plan to take care of these concerns? Discuss.
Ans: As a marketing manager of a large hotel in a key tourist destination, several societal concerns may arise:
- Environmental Impact: Hotel operations can affect the environment through energy use, water consumption, waste generation, and emissions. It's essential to preserve natural resources and ecosystems.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Tourism can lead to the commodification or misrepresentation of local cultures. Respecting and preserving the cultural heritage of local communities is crucial.
- Community Integration and Empowerment: The tourism industry may contribute to social and economic disparities within local communities. Ensuring equitable distribution of benefits and supporting community development is vital.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Challenges may arise in making tourism facilities and experiences accessible to everyone, including people with disabilities and marginalised groups.
To address these concerns, the following steps can be implemented:
- Sustainable Practices: Adopt energy-efficient measures, water conservation initiatives, and waste reduction programmes. Pursuing green certifications shows our commitment to environmental responsibility.
- Cultural Sensitivity Training: Train staff to promote respectful interactions with guests from diverse backgrounds. Collaborate with local cultural experts to offer authentic experiences and avoid cultural appropriation.
- Community Engagement: Partner with local businesses and organisations to support economic empowerment and community development. Offer job training programmes, educational scholarships, and infrastructure improvements to benefit the local population.
- Accessibility Measures: Conduct assessments of hotel facilities to identify and address barriers. Implement modifications such as wheelchair ramps, accessible rooms, and inclusive activities to ensure all guests feel welcome.
By taking these proactive steps, our hotel can enhance its reputation as a responsible tourism destination, attract socially conscious travellers, and positively contribute to the well-being of the local community and environment.
Q11. What information is generally placed on the package of a food product? Design a label for one of the food products of your choice.
Ans: Information typically placed on the package of a food product includes:
Product Name: Clearly stating the name of the food product for easy identification.
Ingredients: Listing all the ingredients used in the product, usually in descending order of predominance by weight.
Nutritional Information: Providing details about the nutritional content per serving, including calories, macronutrients (such as fat, carbohydrates, and protein), and micronutrients (such as vitamins and minerals).
Allergen Information: Highlighting any common allergens present in the product, such as gluten, dairy, nuts, or soy.
Net Weight: Displaying the weight of the product contents.
Manufacturer Information: Including the name and address of the manufacturer, packer, or distributor responsible for the product.
Batch/Lot Number: Indicating the batch or lot number for traceability purposes.
Expiration Date: Providing the date by which the product should be consumed for optimal quality and safety.
Storage Instructions: Advising on the proper storage conditions to maintain product freshness and safety.
Country of Origin: Specifying the country where the product was produced or manufactured.
Certifications: Displaying any relevant certifications or seals of approval, such as organic, non-GMO, or halal.
Here's a label design for a box of breakfast cereal:
Breakfast Cereal- NutriOats
Ingredients:
- Whole grain oats, sugar, salt, vitamins, minerals, natural flavor
Nutritional Information:
- Serving Size: 1 cup
- Calories: 120
- Total Fat: 2g
- Carbohydrates: 25g
- Protein: 4g
- Fiber: 3g
Allergen Information:
- Contains wheat
- Net Weight: 400g
Manufacturer: ABC Inc.
123 Main Street, Anytown, USA
Batch/Lot Number: 123456
Expiration Date: 12/2023
Store in a cool, dry place
Q12. For buyers of consumer durable products, what ‘customer care services’ would you plan as a manager of a firm marketing new brand of motorcycle. Discuss.
Ans: As a manager of a firm marketing a new brand of motorcycles, I would focus on the following customer care services:
- Pre-Sale Support: Provide detailed information about motorcycle features, offer test rides, and assist customers in making informed purchase decisions.
- Purchase Assistance: Guide customers through financing options, simplify the purchasing process, and ensure clear pricing.
- Delivery and Installation: Ensure prompt delivery, proper assembly, and support with setup and familiarisation.
- After-Sales Service: Establish authorised service centres for maintenance and repairs, offer flexible service plans, and supply genuine spare parts.
- 24/7 Helpline and Online Support: Provide round-the-clock customer support through various channels for quick assistance.
- Technical Assistance and Training: Offer resources for troubleshooting, basic maintenance, and enhancing riding skills.
- Feedback and Improvement: Collect customer feedback to identify areas for product and service enhancement.
These services aim to create a seamless and positive experience for motorcycle buyers, fostering loyalty and advocacy for the brand.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. What is marketing concept? How does it help in the effective marketing of goods and services.
Ans: The marketing concept centres on meeting customer needs and wants while achieving business goals. It focuses on understanding the target market, creating value, and fostering long-term relationships.
How It Helps in Effective Marketing:
- Customer Orientation: Promotes understanding of customer preferences, leading to improved product offerings.
- Value Creation: Ensures products and services align with customer expectations.
- Improved Decision-Making: Provides insights into market demands, facilitating better strategies.
- Increased Loyalty: Cultivates strong customer relationships, resulting in repeat business and referrals.
Q2. What is marketing mix? What are its main elements? Explain.
Ans: Marketing mix refers to the combination of four main elements known as the four P’s: Product, Price, Promotion, and Place.
Product Mix: This aspect covers the features of a product, which include:
- Range: Variety of products offered.
- Quality: Standard of the product.
- Size: Dimensions of the product.
- Labelling: Information provided on the product.
- Packaging: How the product is wrapped or contained.
- Branding: Identity of the product.
All products should meet consumer needs and expectations, offering good quality at fair prices.
Price Mix: This involves making decisions about:
- Price determination: Setting the product's price.
- Discounts and allowances: Reductions in price offered to customers.
- Credit terms: Conditions under which credit is extended.
It also includes pricing objectives and policies. The price should cover production costs and selling expenses while ensuring a reasonable profit margin. The pricing strategy should consider costs, customer demand, and competition.
Place Mix: This connects sellers and buyers through distribution channels. Key considerations include:
- Channels of distribution: Routes through which products reach customers.
- Transportation: Methods of moving goods.
Factors influencing channel choice include the timing and location of delivery, the nature of the goods, destination, costs, and availability.
Promotion Mix: This encompasses all marketing activities aimed at boosting product sales, including:
- Advertising: Paid promotions to reach potential customers.
- Personal selling: Direct interaction with customers to persuade them to buy.
- Publicity: Generating public awareness about the product.
- Sales promotion: Short-term incentives to encourage purchases.
The goal is to inform and convince potential buyers to choose a specific product.
Q3. How does branding help in creating product differentiation? Does it help in marketing of goods and services? Explain.
Ans: Branding helps a firm distinguish its products from that of its competitors.
- This helps the firm to secure and control the market for its products.
- If products were sold by generic names, it would be very difficult for marketers to distinguish their products from its competitors.
- Thus, most marketers give a name to their product, which helps in identifying and distinguishing their products from their competitors' products.
- This process of giving a name or a sign or a symbol etc to a product is called branding.
Q4. What are the factors affecting the determination of the price of a product or service? Explain.
Ans: There are several factors which affect the fixation of the price of a product. Some of the important factors in this regard are discussed below:
(i) Product Cost The cost sets the minimum level or the floor price at which the product may be sold. There are broadly three types of cost - fixed costs, variable costs and semi-variable costs. The total cost is the sum of all these three. Generally, all firms try to cover all their costs, at least in the long run. In addition, they aim to earn a margin of profit over and above the costs.
(ii) The Utility and Demand The utility provided by the product and the intensity of demand of the buyer sets the upper limit of price, which a buyer would be prepared to pay. The price must reflect the interest of both the parties to the transaction – the buyer and the seller. The buyer may be ready to pay up to the point, where the utility of the product is at least equal to the sacrifice made in terms of the price paid. The seller would, however, try to cover the costs. According to the law of demand, consumers generally purchase more units at a low price than at a high price.
(iii) The Extent of Competition in the Market The price is also affected by the nature and degree of competition. The price will tend to reach the upper limit in case there is less degree of competition while under free competition, the price will tend to be set at the lowest level.
(iv) Government and Legal Regulations To protect the interest of the public against unfair practices in the field of price fixing, the Government can intervene and regulate the price of commodities. The government can declare a product as an essential product and regulate its price.
(v) Pricing Objectives Pricing objectives are another important factor affecting the fixation of the price of a product or a service. Apart from price maximization, the pricing objectives of a firm may include:
- Obtaining Market Share Leadership If a firm's objective is to obtain a larger share of the market, it will keep the price of its products at a lower level, so that a greater number of people are attracted to purchase the products.
- Surviving in a Competitive Market If a firm is facing difficulties surviving in the market because of intense competition or the introduction of a more efficient substitute by a competitor.
- Attaining Product Quality Leadership Higher prices are charged to cover high quality and high costs of R&D (Research and Development).
(vi) Marketing Methods Used: Price fixation is also affected by other elements of marketing such as distribution system, quality of salesmen employed, quality and amount of advertising, sales promotion efforts, the type of packaging, product differentiation, credit facility and customer service provided.
Q5. Explain the major activities involved in the physical distribution of products.
Ans: Physical distribution encompasses all activities required to move products from manufacturers to customers. The key activities involved in this process include:
- Order Processing: This is the initial step in the buyer-seller relationship. When a customer places an order, it triggers the flow of products from manufacturers to customers. An efficient order processing system ensures orders are handled accurately and quickly, preventing delays and errors that could lead to customer dissatisfaction.
- Transportation: This involves the methods used to move goods from production sites to sales locations. Effective transportation is crucial for ensuring that products are available when customers want to purchase them.
- Warehousing: This refers to storing and organising products until they are needed. Proper warehousing creates time utility, allowing goods to be stored until required. The location and efficiency of warehouses significantly affect how well a business serves its customers.
Inventory Control: Managing inventory levels is vital. Higher inventory can enhance customer service but also increase carrying costs. Key factors influencing inventory decisions include:
- The company’s customer service policy: Higher service levels typically require larger inventories.
- The accuracy of sales forecasts: More precise forecasts can reduce the need for high inventory levels.
- The responsiveness of the distribution system: Effective communication between inventory needs and production facilities is essential.
- Costs associated with inventory, including holding costs and capital tied up in stock.
Q6. ‘Expenditure on advertising is a social waste.’ Do you agree? Discuss.
Ans: The opponents of advertising say that the expenditure on advertising is a social waste as it adds to the cost, multiplies the needs of the people and undermines social values. The proponents, however, argue that advertising is very useful as it increases the reach, brings the per unit cost of production down and adds to the growth of the economy.
The following are the points of criticism:
- Adds to Cost: The opponents of advertising argue that advertising unnecessarily adds to the cost of the product, which is ultimately passed on to the buyers in the form of high prices. It is a line that advertisement of a product costs lots of money but it helps to increase the demand for the product as a large number of potential buyers come to know about the availability of the products, its features etc and are persuaded to buy it. This increases the demand and therefore the production. As a result, the per unit cost of production comes down as the total cost is divided by a larger number of units.
- Undermines Social Values: Advertising undermines social values and promotes materialism. It breeds discontent among people as they come to know about new products and feel dissatisfied with their present state of affairs. This criticism is not entirely time. Advertisement in fact helps buyers by informing them about the new products which may be Improvement over the existing products.
- Confuses the Buyers: Another criticism against advertisements is that so many products are being advertised which makes similar claims that the buyer gets confused as to which one is true and which should be relied upon. e.g., there are so many brands of soaps, shampoos, cars, TVs, cell phones etc which are advertised. The supporters of advertisement, however, argued that we are all rational human beings who make our decisions for purchase of products on factors, such as price, style, size, etc. Thus the buyers can clear their confusion by analysing the information provided in the advertisements and other sources before taking a decision to purchase a product.
- Encourages Sale of Inferior Products: Advertising does not distinguish between superior and inferior products and persuades people to purchase even inferior products. The desired level of quality will depend on the economic status and preferences of the target customers. Advertisements sell products of a given quality and the buyers will buy if it suits their requirements.
- Some Advertisements are in Bad Taste: Another criticism against advertising is that some advertisements are in bad taste. They show something which is not approved by some people. Some advertisements spoil the relationship between employer and employee, husband and wife etc.
From the above discussion, we have learnt that although advertisements are criticised still they have their own advantages. It is not a social waste, rather it adds value to the social cause by giving a boost to production and generating employment.
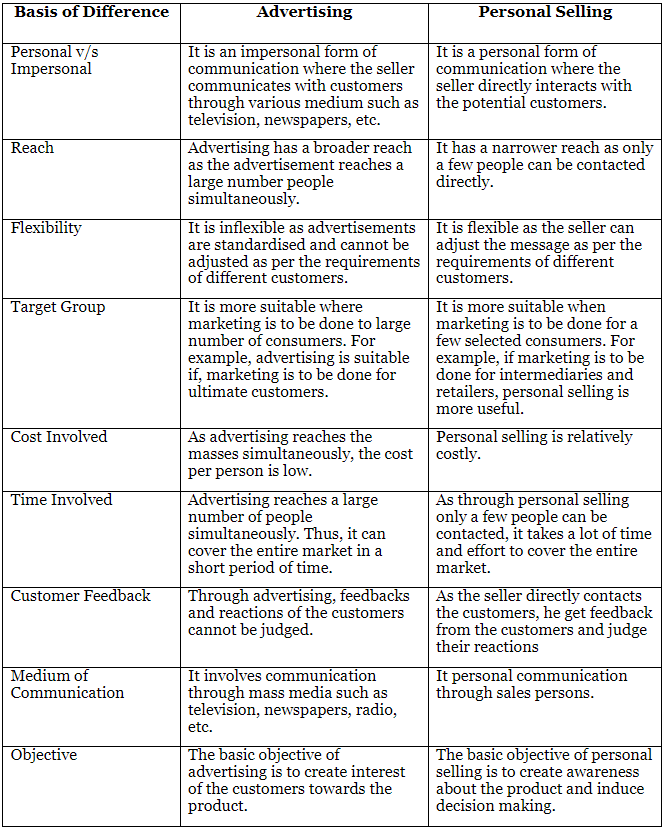
Q7. Distinguish between advertising and personal selling.
Ans:
Advertising is a form of communication that is typically paid and less personal. It is used by marketers to promote products and services.
- In contrast, personal selling involves direct communication between the seller and potential customers. This means that it includes face-to-face interactions aimed at selling a product.
- The key difference between advertising and personal selling lies in their approach: advertising is more about reaching a large audience, while personal selling focuses on one-on-one contact.
- Marketers use advertising to create awareness and interest in their offerings without direct engagement with each individual.
- On the other hand, personal selling allows sellers to address the specific needs and questions of customers directly, which can lead to a more personalized experience.
- Overall, advertising is about broadcasting a message broadly, while personal selling is about building relationships and understanding customer needs
Q8. Explain the factors determining the choice of channel of distribution.
Ans: The choice of channel of distribution, or distribution channel, is influenced by several factors:
- Nature of the Product: The characteristics of the product, such as its perishability, size, weight, and value, determine the most suitable distribution channel. For example, perishable goods may require direct and fast distribution channels, while durable goods may be distributed through intermediaries.
- Target Market Characteristics: Understanding the preferences, behaviours, and locations of the target market is crucial. Factors such as geographic dispersion, demographics, and purchasing habits influence the choice of distribution channels. For instance, urban markets may have different distribution needs compared to rural areas.
- Competitive Environment: The distribution strategies of competitors can impact channel selection. Analyzing competitors' distribution channels, strengths, and weaknesses can help in identifying gaps or opportunities for differentiation.
- Company Resources and Capabilities: The financial resources, infrastructure, and logistical capabilities of the company play a significant role. Companies with limited resources may opt for simpler distribution channels, while those with extensive resources may choose more complex channels.
- Market Coverage Objectives: Companies need to decide whether they aim for intensive, selective, or exclusive distribution. Intensive distribution aims to make the product available in as many outlets as possible, selective distribution focuses on specific outlets that match the product image, and exclusive distribution involves limited outlets to maintain exclusivity.
- Channel Member Capabilities: Assessing the capabilities and effectiveness of potential channel members, such as wholesalers, retailers, and distributors, is crucial. Companies need to ensure that channel members can effectively deliver the product to the end consumer and represent the brand appropriately.
- Legal and Regulatory Factors: Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, such as licensing, permits, and trade restrictions, may dictate the choice of distribution channels, especially in international markets.
- Market Trends and Technology: Keeping abreast of market trends and technological advancements is essential. Changes in consumer behaviour, such as the growing preference for online shopping, may necessitate adjustments to distribution channels to stay competitive.
By considering these factors comprehensively, companies can make informed decisions about the most suitable distribution channels to reach their target markets effectively and efficiently.
|
51 videos|230 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Marketing Management NCERT Solutions - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the significance of marketing management in a business? |  |
| 2. What are the key components of a marketing management strategy? |  |
| 3. How does market research influence marketing management? |  |
| 4. What is the role of digital marketing in marketing management? |  |
| 5. How can a company measure the effectiveness of its marketing management efforts? |  |

















