NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Indian Economic Development
Q1: Why are regional and economic groupings formed?
Ans: With the objective of understanding various means and strategies to strengthen the economies, different nations of the world are motivated to form regional and global economic groups like SAARC, European Union, ASEAN, etc. The formation of such regional and economic groups helps the member countries to know the development strategies and measures adopted by other member countries. This enables them to analyse their strength and weakness and, thereby, formulate policies to accelerate social progress and cultural development among its member countries. Secondly, another important purpose behind setting up of these groups is maintenance of peace and stability of the member countries. In addition to this, these groups provide a common platform to raise their voice in a unified manner on common issues to safeguard their common interests.
Q2: What are the various means by which countries are trying to strengthen their own domestic economies?
Ans: The following are the various means through which the nations are trying to strengthen their own domestic economies:
- Nations are forming various regional and economic groupings like SAARC, European Union, G-8, G-20, ASEAN etc. in order to strengthen their economies. These groups provide a common platform to the member countries to raise their voice in a unified manner on common issues to safeguard their common interests.
- Further, they are also interested in knowing the developmental process adopted by their neighbouring nations, so as to analyse their strengths and weaknesses. Accordingly, they formulate policies to accelerate social progress and cultural development among the member countries.
- Moreover, nations also resort to liberalising their economies. This minimises the government interference in economic activities. The economy is governed by market forces, i.e. demand and supply forces.
- Nations also resort to the process of globalisation to open up their economies to provide wide international market to their domestic producers.
Q3: What similar developmental strategies have India and Pakistan followed for their respective developmental paths?
Ans: India and Pakistan both have followed a similar developmental strategy. The main similarities between the developmental strategies can be summed up as:
- India and Pakistan both have started their developmental programmes based on economic planning soon after their independence in 1947.
- Both the countries relied on the public sector for initiating the process of growth and development.
- Both of them have followed the path of mixed economic structure involving the participation of both the state as well as the private sector.
- Both of them introduced economic reforms at the same time to strengthen their economies.
Q4: Explain the Great Leap Forward campaign of China as initiated in 1958.
Ans: The Great Leap Forward (GLF) was a campaign initiated in 1958 in China. The aims of this campaign are as follows:
- The aim of the campaign was to initiate large scale industrialisation in the country concentrating not only in the urban areas but also in the rural ones.
- The people in the urban areas were motivated to set up industries in their backyards.
- In the rural areas, Commune System was implemented. Under this system, people were engaged in collective farming.
Q5: China's rapid industrial growth can be traced back to its reforms in 1978. Do you agree? Elucidate.
Ans: Yes, it cannot be denied that China's rapid industrial growth is an aggregate outcome of the various economic reforms that were introduced in phases since 1978. In the initial phase, reforms were initiated in agriculture, foreign trade and investment sectors. The system of collective farming known as Commune System was implemented. Under this system, land was divided into small plots that were allocated to the individual households. These households were allowed to keep the remaining income from land after paying the taxes to the government. In the later phase, reforms were initiated in the industrial sector. During this phase, the private firms and village and township enterprises were allowed to produce goods and services and to compete with the State Owned Enterprises. The reforms also included dual pricing. The dual pricing implies that the farmers and the industrial units were required to buy and sell a fixed quantity of inputs and output at the price fixed by the government and the remaining quantities were traded at the market price. Gradually, with the rapid increase in the aggregate production in the later years, the quantities traded in the market increased by many folds. The reforms also included setting up of Special Economic Zones to attract foreign investors. Therefore, China's rapid industrial growth is attributable to the success of different phases of its economic reforms.
Q6: Describe the path of developmental initiatives taken by Pakistan for its economic development.
Ans:
- With the aim of economic development, Pakistan adopted the pattern of mixed economy where both private and public sectors coexist
- Pakistan introduced a variety of regulated policy framework for import substitution, industrialisation during 1950s and 1960s. This implies producing goods domestically to substitute imports, thereby, discouraging imports and simultaneously encouraging and developing domestic industries.
- In order to protect domestic industries producing consumer goods, policy measure was initiated to create t tariff barriers.
- The introduction of Green Revolution mechanised agriculture leading to the increase in the production of food grains.
- The mechanisation of agriculture was followed by the nationalisation of capital goods industries in 1970s.
- In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Pakistan shifted its policy orientation by denationalising the thrust areas, thereby, encouraging the private sector.
- All these above measures created an environment conducive to initiate the economic reforms that were ultimately initiated in 1988.
Q7: What is the important implication of the one child norm in China?
Ans: The important implication of the one-child norm in China is the low population growth. This measure also led to the fall in the sex ratio in China, i.e. the proportion of females per thousand males. However, the country believes that in the coming decades there will be more elderly people in proportion to the young people. This will oblige the country to provide social security measures with fewer workers.
Q8: Mention the salient demographic indicators of China, Pakistan and India.
Ans: The important demographic indicators of Indian, China and Pakistan are tabulated as below.
The important demographic indicators are as follows:
- Total Population: China is the largest populated country in the world followed by India. The above table depicts that China’s population in 2000-01 was approximately 1303.7 million and that of India and Pakistan was 1103.6 million and 162.4 million respectively.
- Annual Growth Rate of Population: Although China is the largest populated country but a strong positive point for China is that, its annual growth rate of population is just 1% per annum while that of India and Pakistan is 1.7% and 2.5% per annum. With such a high growth rate it would not be wrong to expect that in the forthcoming decades India will surpass the total population of China.
- Density of Population: In spite of the fact that China is highly populated and geographically occupying the largest area among the three nations, its density of population is the lowest. It is as low as 138 persons per square kilometer of area compared to 358 and 193 persons in India and Pakistan respectively. Lower the degree of density of population the lower is the pressure on the country’s natural resources and higher is the probability of sustainable development.
- Sex Ratio: This ratio counts the number of females per 1000 males. The sex ratios in all the three countries are almost same with China having a marginally higher sex ratio of 937 females per 1000 males. This depicts the low economic and social status of women in India and Pakistan.
- Fertility Rate: This rate refers to the number of children a woman gives birth to during her lifetime. China enjoys an upper hand in this case. The fertility rate of Chinese woman is only 1.8 whereas those of India and Pakistan are 3.0 and 5.1. This implies that in India and Pakistan a woman usually gives birth to approximately 3 and 5 children. This is the most important concern for both India and Pakistan, as with such a high fertility rate, population in the coming decades will surpass that of China.
- Urbanisation: Lastly, China is comparatively more urbanised than India and Pakistan. The rate of urbanisation in China is 36.1% while that in India and Pakistan is 27.8% and 33.4% respectively. The degree of urbanisation depicts the standard and quality of living of people of a particular country. Also, this confirms the shift in the economic structure of an economy. Higher degree of urbanisation reveals higher industrialisation and development of tertiary sector in the economy.
Thus to sum up, although China is the largest populated country but its other demographic indicators are stronger than those of both India and Pakistan. It would not be wrong to expect a decline in China’s population in the coming decades due to implementation of various policy measures and also due to low annual growth rate of population.
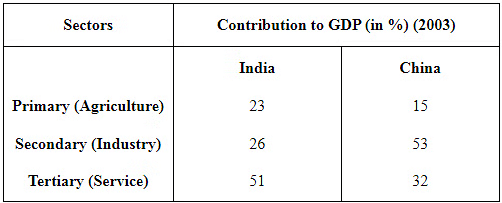
Q9: Compare and contrast India and China's sectoral contribution towards GDP in 2003. What does it indicate?
Ans: The comparison of India’s and China’s sectoral contribution towards their respective GDP can be done with the help of the data tabulated below:
 Contribution of Primary Sector to GDP: The data above reveals that the contribution of the primary sector to India’s GDP is 23% compared to 15% of China’s GDP. This confirms the agrarian nature of Indian economy.
Contribution of Primary Sector to GDP: The data above reveals that the contribution of the primary sector to India’s GDP is 23% compared to 15% of China’s GDP. This confirms the agrarian nature of Indian economy.- Contribution of Secondary Sector to GDP: The data also reveals that China has comparatively a strong industrial base as compared to India. The contribution of secondary sector to China’s GDP is 53% against the contribution of mere 26% to India’s GDP. From this, we can infer that India’s industrial sector is far behind that of China.
- Contribution of Tertiary Sector to GDP: We can also analyze that although India’s industrial sector is not as strong as that of China yet the contribution of India’s service sector is much stronger to its than that of China.
Thus, analysing the above data helps us to conclude that a significant portion of India’s GDP is contributed by tertiary sector followed by its agriculture sector. On the contrary, the major contributor to China’s GDP is the secondary sector followed by its tertiary sector.The process of economic growth has led to a tremendous shift in the sectoral share of output and employment. The percentage share of the primary sector in total output and employment tends to decrease while that of the secondary and tertiary sector tends to increase. The following facts explain the sectoral share in output and employment of Indiaand China. Both India and China have shown a noticeable structural transformation from the primary sector to other two sectors. The primary sector in both the countries is no longer the important contributor to the nation’s GDP. While India is relying more on its tertiary sector China is relying more on its secondary sector in terms of the sectoral contribution to their GDP. The experience of China is similar to that of the other developed countries in the world. The experience of the developed countries shows that secondary sector followed by the tertiary sector emerge as the leading sectors of the economy. Compared to China, India showed a direct shift from the primary sector to tertiary sector. This is due to the fast integration of these two economies with the other market economies of the world.
Q10: Mention the various indicators of human development.
Ans: The indicators of human development are:
- Life Expectancy.
- Adult Literacy Rate.
- Infant Mortality Rate.
- Percentage of the population below poverty line.
- GDP per capita
- Percentage of the population having access to improved sanitation
- Percentage of the population having access to improved water sources.
Q11: Define liberty indicator. Give some examples of liberty indicators.
Ans: Liberty Indicator may be defined as the measure of the extent of demographic participation in the social and political decision making. In other words, it is an index used to measure the participation of the people in taking decisions. Some examples of liberty
indicators are the measures of the extent of the Constitutional Protection Rights given to the citizens and the extent of the Constitutional Protection of the independence of the Judiciary and Rule of Law.
Q12: Evaluate the various factors that led to the rapid growth in economic development in China.
Ans: China's rapid economic development is an aggregate outcome of the introduction of the reforms in phases since 1978. The following are the various factors that led to the rapid growth in the economic development in China:
- In the initial phase, reforms were initiated in agriculture, foreign trade and investment sectors. The system of collective farming known as Commune System was implemented. Under this system, land was divided into small plots that were allocated to the individual households. These households were allowed to keep the remaining income from land after paying the taxes to the government.
- In the later phase, reforms were initiated in the industrial sector. During this phase, the private firms, village and township enterprises were allowed to produce goods and services and to compete with the State Owned Enterprises.
- The dual pricing were implemented. This implies that the farmers and the industrial units were required to buy and sell a fixed quantity of inputs and output at the price fixed by the government and the remaining quantities were traded at the market price. Gradually, with rapid increase in aggregate production in the later years, the quantities traded in the market increased by many folds.
- The reforms also included setting up of Special Economic Zones to attract foreign investors and to encourage its exports.
Therefore, the aggregate focus of all these economic reforms resulted in rapid industrial growth and economic development in China.
Q13: Group the following features pertaining to the economies of India, China and Pakistan under three heads
- One-child norm
- Low fertility rate
- High degree of urbanisation
- Mixed economy
- Very high fertility rate
- Large population
- High density of population
- Growth due to manufacturing sector
- Growth due to service sector
Ans:
Q14: Give reasons for the slow growth and re-emergence of poverty in Pakistan.
Ans: The following are the main reasons for the slow growth and re-emergence of poverty in Pakistan:
- Greater Dependency on the Public Sector Enterprises: The main cause behind the slow economic growth in Pakistan is the greater dependence on Public Sector Enterprises. Pakistan relied largely on the policy of protection by assigning central role to the Public Sector
Enterprises. The operational inefficiencies of Public Sector Enterprises along with the misallocation of scarce resources resulted in dormant economic growth rate. - Traditional Agricultural Practices: The agricultural practices in Pakistan relied heavily on traditional methods and the vagaries of climatic conditions resulting in low productivity. Consequently, the agricultural sector was not able to flourish to the extent it was thought of.
- Undeveloped Manufacturing Sector: The major portion of the foreign exchange earnings of Pakistan was in the form of remittances from Pakistani workers in the Middle-east and exports of highly volatile agricultural products. This can be regarded as one of the reasons for the slow economic growth. This is because the inflow of foreign exchange in the form of remittances substituted the need for development of manufacturing sector to earn foreign exchange by exporting manufactured goods.
- Increasing Dependence on Foreign Loans: There was an increasing dependence on foreign loans for meeting t foreign exchange requirements. Pakistan faced increasing difficulty in repaying these loans along with the mounting interest obligations in the years of agricultural failure. The increasing burden of huge foreign loans impeded the economic growth prospects of Pakistan.
- Lack of Political Stability: The lack of political stability demanded huge public expenditure for maintaining law and order in the country. This huge public expenditure acted as a drain on the country's economic resources.
- Insufficient Foreign Investment: Pakistan also failed to attract sufficient foreign investment due to lack of political stability, low degree of international credibility and lack of well developed infrastructure.
Q15: Compare and contrast the development of India, China and Pakistan with respect to some salient human development indicators.
Ans: The following are the indicators of human development:
- Life Expectancy
- Adult Literacy Rate
- Infant Mortality Rate
- Percentage of the population below poverty line
- GDP per capita
- Percentage of the population having access to improved sanitation
- Percentage of the population having access to improved water sources.
On the basis of individual indices of these parameters, a Human Development Index (HDI) was constructed. The higher the value of HDI, higher will be the level of growth and development of a country. The rankings are accorded to the countries as per their HDI. China ranked 81, India 128th and Pakistan 136th. High ranking of China is due to the higher GDP per capita. Moreover, the one-child norm led to sustained rise in the GDP, consequently, China was ranked higher than India and Pakistan in HDI.
Q16: Comment on the growth rate trends witnessed in China and India in the last two decades.
Ans: India, with democratic institutions, performed moderately, but the majority of its people still depend on agriculture. Infrastructure is lacking in many parts of the country. It is yet to raise the Standard of living of more than one-fourth of its population that lives below the poverty line.
On the other hand, the lack of political freedom and its implications in China are the major concern in the last two decades. The country used the market system without losing political commitment and succeeded in raising the level of growth along with poverty alleviation. China used the market mechanism to create additional social and economic opportunities. The country has also ensured social security in the rural areas by retaining collective farming known as Commune System. Public intervention in social infrastructure prior to the introduction of the economic reforms has brought positive results in the human development indicators of China.
Q17: (i) First Five Year Plan of ________________ commenced in the year 1956. (Pakistan/China)
(ii) Maternal mortality rate is high in _____________. (China/Pakistan)
(iii) Proportion of people below poverty line is more in __________.(India/Pakistan)
(iv) Reforms in ______________ were introduced in 1978. (China/Pakistan)
Ans: (i) First Five Year Plan of Pakistan commenced in the year 1956.
(ii) Maternal mortality rate is high in Pakistan.
(iii) Proportion of people below poverty line is more in India.
(iv) Reforms in China were introduced in 1978.
|
58 videos|216 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Indian Economic Development
| 1. What are the main objectives of the Indian Economic Development chapter in NCERT? |  |
| 2. How does the Indian Economic Development chapter in NCERT explain the concept of poverty and unemployment in India? |  |
| 3. What role does agriculture play in the Indian economy as discussed in the Indian Economic Development chapter in NCERT? |  |
| 4. How does the Indian Economic Development chapter in NCERT analyze the role of industrial sector in India's economic growth? |  |
| 5. What are the key policy measures discussed in the Indian Economic Development chapter in NCERT to promote sustainable development in India? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
 Contribution of Primary Sector to GDP: The data above reveals that the contribution of the primary sector to India’s GDP is 23% compared to 15% of China’s GDP. This confirms the agrarian nature of Indian economy.
Contribution of Primary Sector to GDP: The data above reveals that the contribution of the primary sector to India’s GDP is 23% compared to 15% of China’s GDP. This confirms the agrarian nature of Indian economy.

















