NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography - Our Country - India
Q1. Answer the following questions briefly.
(a) Name the major physical divisions of India.
Ans: The major physical divisions of India are:
- The Himalayas
- The Northern Indian Plains
- The Great Indian Desert
- The Peninsular Plateau
- The Coastal Plains
- The Islands

(b) India shares its land boundaries with seven countries. Name them.
Ans: The countries that share land boundaries with India are:
- Afghanistan
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- China
- Pakistan
- Nepal
- Myanmar
(c) Which two major rivers fall into the Arabian Sea?
Ans: Narmada and Tapti are the two major rivers that fall into the Arabian Sea.
(d) Name the delta formed by the Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
Ans: Sunderbans delta is formed by the Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
(e) How many States and Union Territories are there in India? Which states have a common capital?
Ans: There are 28 states and 8 Union Territories. Haryana and Punjab have the same capital.
(f) Why do a large number of people live in the Northern Plains?
Ans: Northern plains are formed by the alluvial deposits laid down by the rivers- the Indus, the Ganga, the Brahmaputra and their tributaries. These river plains provide fertile land for cultivation. Therefore, a large number of people live in the Northern plains.
(g) Why is Lakshadweep known as a coral island?
Ans: Lakshadweep island is known as coral island because it has been made up of coral, which are skeletons of tiny marine animals called polyps. When the living polyps die, other polyps grow on top of their hard skeletons. They grow higher and higher and thus form coral islands.
 Q2. Tick the correct answers.
Q2. Tick the correct answers.
(a) The southernmost Himalayas are known as
(i) Shiwaliks
(ii) Himadri
(iii) Himachal
Ans: (i) Shiwaliks
The Shiwaliks are the outermost range of the Himalayas, located closest to the plains.
(b) Sahyadris is also known as
(i) Aravali
(ii) Western Ghats
(iii) Himadri
Ans: (ii) Western Ghats
The Western Ghats, also called the Sahyadris, run parallel to the western coast of India.
(c) The Palk Strait lies between the countries
(i) Sri Lanka and Maldives
(ii) India and Sri Lanka
(iii) India and Maldives
Ans: (ii) India and Sri Lanka
It separates the southeastern coast of India from the northeastern coast of Sri Lanka.
(d) The Indian islands in the Arabian Sea are known as
(i) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(ii) Lakshadweep Islands
(iii) Maldives
Ans: (ii) Lakshadweep Islands
The Lakshadweep islands are located off the southwestern coast of India in the Arabian Sea.
(e) The oldest mountain range in India is the
(i) Aravali hills
(ii) Western ghats
(iii) Himalayas
Ans: (i) Aravali hills
The Aravali Hills are considered the oldest mountain range in India, dating back more than 2.5 billion years.
Q3. Fill in the blanks.
(a) India has an area of about ___________.
Ans: 3.28 million sq. kms.
(b) The Greater Himalayas are also known as ___________.
Ans: Himadri
(c) The largest state in India in terms of area is ___________.
Ans: Rajasthan
(d) The river Narmada falls into the ___________ sea.
Ans: Arabian
(e) The latitude that runs almost halfway through India is ___________.
Ans: Tropic of Cancer
Map skills
Q1. On an outline map of India, mark the following.
(a) Tropic of Cancer
(b) Standard Meridian of India
(c) State in which you live
(d) Andaman Islands and Lakshadweep Islands
(e) Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Ans: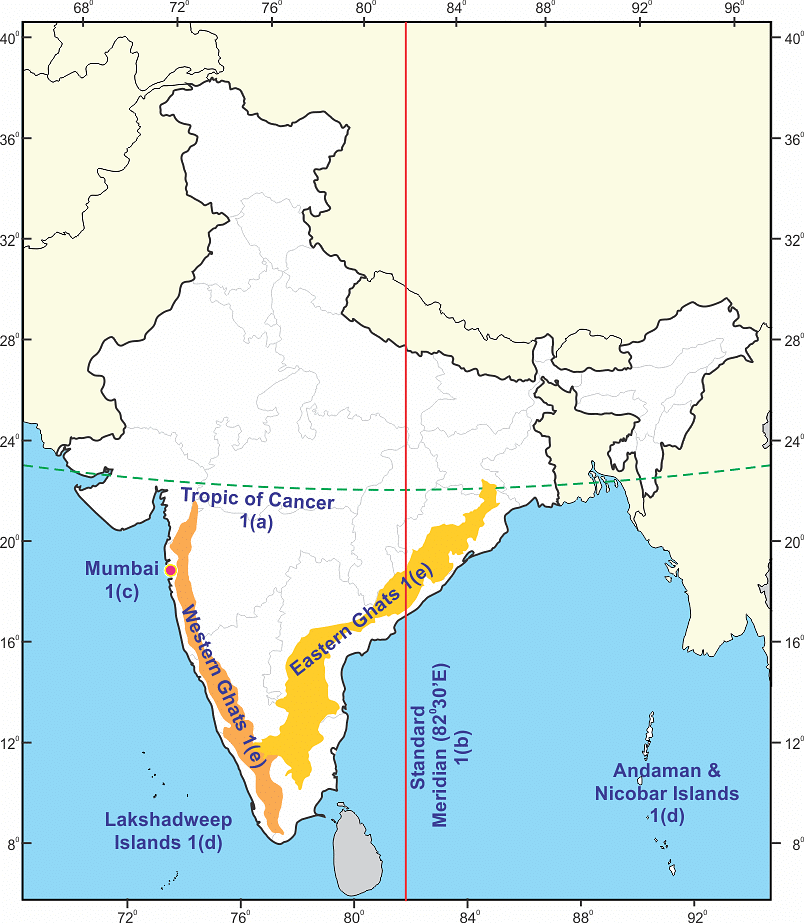
|
297 videos|1066 docs|204 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography - Our Country - India
| 1. What are the major geographical features of India? |  |
| 2. How does India's culture reflect its diversity? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. What are the main economic activities in India? |  |
| 5. How does India’s history influence its present? |  |

















