NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 5 - Judiciary
Q1. You read that one of the main functions of the judiciary is 'upholding the law and Enforcing Fundamental Rights'. Why do you think an independent judiciary is necessary to carry out this important function?
Ans: The independence of the judiciary is essential for the courts to effectively uphold the law and enforce Fundamental Rights. This independence ensures:
- Protection against misuse of power by the legislature and executive.
- Citizens can approach the courts if they believe their rights have been violated.
- Judgments cannot be altered by politicians or those with social influence.
Q2. Re-read the list of Fundamental Rights provided in chapter 1. How do you think the Right to Constitutional Remedies connects to the idea of judicial review?
Ans: The Right to Constitutional Remedies enables Indian citizens to seek legal recourse if they believe their Fundamental Rights have been violated by the State. This right is closely linked to the concept of judicial review, which allows the judiciary to examine and potentially invalidate laws passed by Parliament that contravene the Constitution's fundamental principles.
- Citizens can approach the courts for justice if their rights are infringed.
- The judiciary serves as the ultimate interpreter of the Constitution.
- Judicial review ensures that laws align with the Constitution's basic structure.
- This connection safeguards the protection of Fundamental Rights.
Q3. In the Following illustration, fill in each tier with the judgments given by the various courts in the Sudha Goel case. Check your responses with others in class.
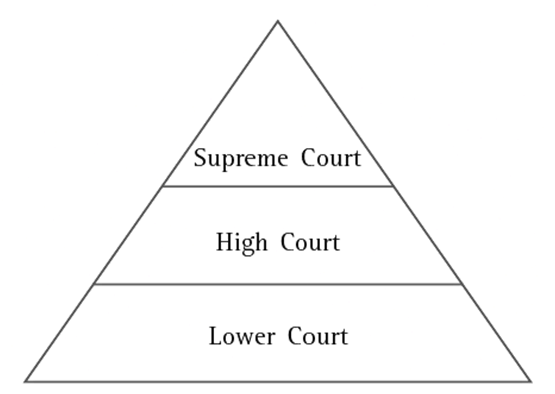
Ans: Lower Court (Trial Court): Laxman, his mother Shakuntala, and his brother-in-law Subhash Chandra were sentenced to death.
High Court: Laxman, Shakuntala, and Subhash Chandra were acquitted.
Supreme Court: Laxman and Shakuntala received life imprisonment, while Subhash Chandra was acquitted due to a lack of sufficient evidence.
Q4. Keeping the Sudha Goel case in mind, tick the sentences that are true and correct the ones that are false.
(a) The accused took the case to the High Court because they were unhappy with the decision of the Trial Court.
(b) They went to the High Court after the supreme Court had given its decision.
(c) If they do not like the Supreme Court verdict, the accused can go back again to the Trial Court.
Ans: (a) True
(b) False. The accused took the case to the High Court because they were unhappy with the Trial Court's decision.
(c) False. If they disagree with the Supreme Court's verdict, the accused cannot return to the Trial Court, as the Supreme Court is the highest court in the judicial hierarchy.
Q5. Why do you think the introduction of Public interest Litigation (PIL) in the 1980s is a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all?
Ans: In the early 1980s, the Supreme Court introduced Public Interest Litigation (PIL) to enhance access to justice for all. This allowed:
- Any individual or organisation to file a PIL in the High Court or Supreme Court on behalf of those whose rights were violated.
- The legal process to be simplified; even a letter or telegram could be treated as a PIL.
PILs addressed numerous issues, including:
- Rescuing bonded labourers from inhumane conditions.
- Releasing prisoners in Bihar who had served their sentences.
This initiative marked a significant step towards ensuring justice for all citizens, making the courts more accessible to those in need.
Q6. Re-read excerpts from the judgment on the Olga Tellis vs Bombay Municipal Corporation case. Now write in your own words what the judges meant when they said that the Right to Livelihood was part of the Right to Life.
Ans: In the Olga Tellis vs. Bombay Municipal Corporation case, the judges stated that the Right to Livelihood is an essential part of the Right to Life. They explained that:
- The concept of life extends beyond mere survival; it includes the ability to earn a living.
- For slum dwellers, eviction would result in losing their jobs and, consequently, their means of survival.
- The court linked the Right to Life with basic needs such as food, clothing, and shelter.
The judges emphasised that:
- The Right to Life, as defined by Article 21, is broad and significant.
- Life encompasses more than just existence; it involves having the means to live.
- Evicting individuals from their homes leads to the loss of their livelihood, which is a violation of their right to life.
Q7. Write a story around the theme, ‘Justice delayed is justice denied’.
Ans: Mr. Shankar was a government employee who returned to his forefather's house after retirement. He asked the tenant to vacate the property, but the tenant refused, stating that Mr. Shankar should seek justice through the courts.
As a result, Mr. Shankar had to live in a rented house. He initiated legal action against the tenant, which led to a lengthy court battle:
- The case lasted for five years before the trial court ruled in Mr. Shankar's favour.
- The tenant appealed the decision, causing further delays.
- It took an additional ten years for the case to be resolved.
Ultimately, Mr. Shankar felt that the prolonged wait for justice was itself a form of injustice. He realised that justice delayed is indeed justice denied.
Q8. Make sentences with each of the glossary words given?
Ans: Acquit: After a lengthy trial, Mohan was acquitted of the murder charge against his friend.
To Appeal: I will appeal to a higher court regarding the lower court's decision that I find unsatisfactory.
Compensation: Ruchi received 5 lakh as compensation for her husband's accidental death.
Eviction: The court is currently handling eviction proceedings initiated by the Rent Commissioner.
Violation: Breaking the untouchability act is a violation punishable under the Constitution.
Q9. The following is a poster made by the Right to Food campaign.
- Read this poster and list the duties of the government to uphold the Right to Food.
- How does the phrase “Hungry stomachs, overflowing godowns! We will not accept it!!” used in the poster relate to the photo essay on the Right to Food

Ans: The duties of the government to uphold the Right to Food include:
- Ensuring that everyone has access to sufficient food.
- Making sure no one goes to sleep hungry.
- Providing special support to vulnerable groups, such as the elderly, disabled, and widows.
- Preventing deaths due to malnutrition or hunger.
The phrase “Hungry stomachs, overflowing godowns! We will not accept it!!” highlights the injustice of food scarcity during a crisis, even when government storage facilities are full. This connects to the photo essay on the Right to Food, which shows that despite droughts in Rajasthan and Orissa leading to severe food shortages, government godowns were stocked with grain.
The People’s Union of Civil Liberties filed a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) claiming that the Right to Food is part of the Right to Life under Article 21. The Supreme Court responded by directing the government to:
- Distribute food at lower prices through ration shops.
- Ensure mid-day meals for children.
|
65 videos|424 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 5 - Judiciary
| 1. What is the role of the judiciary in India? |  |
| 2. How is the Indian judiciary structured? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Supreme Court in the Indian judiciary? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of cases handled by the judiciary? |  |
| 5. How does the judiciary protect the rights of citizens? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|


















