NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 - Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry
Exercise 7.1
1. Find the distance between the following pairs of points:
(i) (2, 3), (4, 1)
(ii) (−5, 7), (−1, 3)
(iii) (a, b), (− a, − b)
Answer
(i) Distance between the points is given by

(ii) Distance between (−5, 7) and (−1, 3) is given by

(iii) Distance between (a, b) and (− a, − b) is given by

2. Find the distance between the points (0, 0) and (36, 15). Can you now find the distance between the two towns A and B discussed in Section 7.2.
Answer
Distance between points (0, 0) and (36, 15)

Yes, Assume town A at origin point (0, 0).
Therefore, town B will be at point (36, 15) with respect to town A.
And hence, as calculated above, the distance between town A and B will be 39 km.
3. Determine if the points (1, 5), (2, 3) and (-2, -11) are collinear.
Answer
Let the points (1, 5), (2, 3), and (- 2,-11) be representing the vertices A, B, and C of the given triangle respectively.Let A = (1, 5), B = (2, 3) and C = (- 2,-11)

Since AB + BC ≠ CA
Therefore, the points (1, 5), (2, 3), and ( - 2, - 11) are not collinear.
4. Check whether (5, - 2), (6, 4) and (7, - 2) are the vertices of an isosceles triangle.
Answer
Let the points (5, - 2), (6, 4), and (7, - 2) are representing the vertices A, B, and C of the given triangle respectively.

Therefore, AB = BC
As two sides are equal in length, therefore, ABC is an isosceles triangle.
5. In a classroom, 4 friends are seated at the points A, B, C and D as shown in the following figure. Champa and Chameli walk into the class and after observing for a few minutes Champa asks Chameli, “Don't you think ABCD is a square?” Chameli disagrees.
Using distance formula, find which of them is correct.

Answer
Clearly from the figure, the coordinates of points A, B, C and D are (3, 4), (6, 7), (9, 4) and (6, 1).
By using distance formula, we get

It can be observed that all sides of this quadrilateral ABCD are of the same length and also the diagonals are of the same length.
Therefore, ABCD is a square and hence, Champa was correct
6. Name the type of quadrilateral formed, if any, by the following points, and give reasons for your answer:
(i) (- 1, - 2), (1, 0), (- 1, 2), (- 3, 0)
(ii) (- 3, 5), (3, 1), (0, 3), (- 1, - 4)
(iii) (4, 5), (7, 6), (4, 3), (1, 2)
Answer
Let the points ( - 1, - 2), (1, 0), ( - 1, 2), and ( - 3, 0) be representing the vertices A, B, C, and D of the given quadrilateral respectively.

It can be observed that all sides of this quadrilateral are of the same length and also, the diagonals are of the same length. Therefore, the given points are the vertices of a square.
(ii) Let the points ( - 3, 5), (3, 1), (0, 3), and ( - 1, - 4) be representing the vertices A, B, C, and D of the given quadrilateral respectively.

It can be observed that all sides of this quadrilateral are of different lengths. Therefore, it can be said that it is only a general quadrilateral, and not specific such as square, rectangle, etc.
(iii) Let the points (4, 5), (7, 6), (4, 3), and (1, 2) be representing the vertices A, B, C, and D of the given quadrilateral respectively.

It can be observed that opposite sides of this quadrilateral are of the same length. However, the diagonals are of different lengths. Therefore, the given points are the vertices of a parallelogram.
7. Find the point on the x-axis which is equidistant from (2, - 5) and (- 2, 9).
Answer
We have to find a point on x-axis. Therefore, its y-coordinate will be 0.
Let the point on x-axis be (x,0)
Distance between(x,0)and (2,-5) = 
Distance between(x,0)and (-2,9) = 
By the Given Condition, these distances are equal to measure.

8. Find the values of y for which the distance between the points P (2, - 3) and Q (10, y) is 10 units.
Answer
It is given that the distance between (2, - 3) and (10, y) is 10.

9. If Q (0, 1) is equidistant from P (5, - 3) and R (x, 6), find the values of x. Also find the distance QR and PR.
Answer
PQ = QR
Therefore, point R is (4, 6) or ( - 4, 6).
When point R is (4, 6),

10. Find a relation between x and y such that the point (x, y) is equidistant from the point (3, 6) and (- 3, 4).
Answer
Point (x, y) is equidistant from (3, 6) and ( - 3, 4).

Exercise 7.2
1. Find the coordinates of the point which divides the join of (- 1, 7) and (4, - 3) in the ratio 2:3.
Answer
Let P(x, y) be the required point. Using the section formula, we get

2. Find the coordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining (4, -1) and (-2, -3).

Let P (x1, y1) and Q (x2, y2) are the points of trisection of the line segment joining the given points i.e., AP = PQ = QB
Therefore, point P divides AB internally in the ratio 1:2.


3. To conduct Sports Day activities, in your rectangular shaped school ground ABCD, lines have been drawn with chalk powder at a distance of 1 m each. 100 flower pots have been placed at a distance of 1 m from each other along AD, as shown in the following figure. Niharika runs 1/4th the distance AD on the 2nd line and posts a green flag. Preet runs 1/5th the distance AD on the eighth line and posts a red flag. What is the distance between both the flags? If Rashmi has to post a blue flagexactly halfway between the line segment joining the two flags, where should she post her flag?

Answer
It can be observed that Niharika posted the green flag at 1/4th of the distance AD i.e., (1×100/4)m = 25m from the starting point of 2nd line. Therefore, the coordinates of this point G is (2, 25).
Similarly, Preet posted red flag at 1/5 of the distance AD i.e., (1×100/5) m = 20m from the starting point of 8th line. Therefore, the coordinates of this point R are (8, 20).
Distance between these flags by using distance formula = GR

4. Find the ratio in which the line segment joining the points (-3, 10) and (6, - 8) is divided by (-1, 6).
Answer
Let the ratio in which the line segment joining ( -3, 10) and (6, -8) is divided by point ( -1, 6) be k : 1.Therefore, -1 = 6k-3/k+1
-k - 1 = 6k -3
7k = 2
k = 2/7
Therefore, the required ratio is 2:7.
5. Find the ratio in which the line segment joining A (1, - 5) and B (- 4, 5) is divided by the x-axis. Also find the coordinates of the point of division.
Answer
Let the ratio in which the line segment joining A (1, - 5) and B ( - 4, 5) is divided by x-axisbe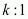 .
.
Therefore, the coordinates of the point of division is (-4k+1/k+1, 5k-5/k+1).
We know that y-coordinate of any point on x-axis is 0.
∴ 5k-5/k+1 = 0
Therefore, x-axis divides it in the ratio 1:1.

6. If (1, 2), (4, y), (x, 6) and (3, 5) are the vertices of a parallelogram taken in order, find x and y.
Answer


Since the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, the mid point of AC and BD are same.
∴ x+1/2 = 7/2 and 4 = 5+y/2
⇒ x + 1 = 7 and 5 + y = 8
⇒ x = 6 and y = 3
7. Find the coordinates of a point A, where AB is the diameter of circle whose centre is (2, - 3) and B is (1, 4).
Answer
Let the coordinates of point A be (x, y).
Mid-point of AB is (2, - 3), which is the center of the circle.

8. If A and B are (–2, –2) and (2, –4), respectively, find the coordinates of P such that AP = 3/7 AB and P lies on the line segment AB.
Answer

The coordinates of point A and B are (-2,-2) and (2,-4) respectively.
Since AP = 3/7 AB
Therefore, AP:PB = 3:4
Point P divides the line segment AB in the ratio 3:4.

9. Find the coordinates of the points which divide the line segment joining A (- 2, 2) and B (2, 8) into four equal parts.

From the figure, it can be observed that points X, Y, Z are dividing the line segment in a ratio 1:3, 1:1, 3:1 respectively.

10. Find the area of a rhombus if its vertices are (3, 0), (4, 5), (-1, 4) and (-2,-1) taken in order. [Hint: Area of a rhombus = 1/2(product of its diagonals)]

Let (3, 0), (4, 5), ( - 1, 4) and ( - 2, - 1) are the vertices A, B, C, D of a rhombus ABCD.
Exercises 7.3
1. Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are:
(i) (2, 3), (-1, 0), (2, -4)
(ii) (-5, -1), (3, -5), (5, 2)
Answer
(i) Area of a triangle is given by
Area of triangle = 1/2 {x1 (y2 - y3)+ x2 (y3 - y1)+ x3 (y1 - y2)}
Area of the given triangle = 1/2 [2 { 0- (-4)} + (-1) {(-4) - (3)} + 2 (3 - 0)] = 1/2 {8 + 7 + 6} = 21/2 square units.
(ii) Area of the given triangle = 1/2 [-5 { (-5)- (4)} + 3(2-(-1)) + 5{-1 - (-5)}] = 1/2{35 + 9 + 20} = 32 square units
2. In each of the following find the value of 'k', for which the points are collinear.
(i) (7, -2), (5, 1), (3, -k)
(ii) (8, 1), (k, -4), (2, -5)
Answer
(i) For collinear points, area of triangle formed by them is zero.
Therefore, for points (7, -2) (5, 1), and (3, k), area = 0
1/2 [7 { 1- k} + 5(k-(-2)) + 3{(-2) + 1}] = 0
7 - 7k + 5k +10 -9 = 0
-2k + 8 = 0
k = 4
(ii) For collinear points, area of triangle formed by them is zero.
Therefore, for points (8, 1), (k, - 4), and (2, - 5), area = 0
1/2 [8 { -4- (-5)} + k{(-5)-(1)} + 2{1 -(-4)}] = 0
8 - 6k + 10 = 0
6k = 18
k = 3
3. Find the area of the triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the sides of the triangle whose vertices are (0, -1), (2, 1) and (0, 3). Find the ratio of this area to the area of the given triangle.
Answer
Let the vertices of the triangle be A (0, -1), B (2, 1), C (0, 3).
Let D, E, F be the mid-points of the sides of this triangle. Coordinates of D, E, and F are given by
D = (0+2/2 , -1+1/2) = (1,0)
E = (0+0/2 , -3-1/2) = (0,1)
F = (2+0/2 , 1+3/2) = (1,2)
Area of a triangle = 1/2 {x1 (y2 - y3) + x2 (y3 - y1) + x3 (y1 - y2)}
Area of ΔDEF = 1/2 {1(2-1) + 1(1-0) + 0(0-2)} = 1/2 (1+1) = 1 square units
Area of ΔABC = 1/2 [0(1-3) + 2{3-(-1)} + 0(-1-1)] = 1/2 {8} = 4 square units
Therefore, the required ratio is 1:4.
4. Find the area of the quadrilateral whose vertices, taken in order, are (-4, -2), (-3, -5), (3, -2) and (2, 3).
Answer

Let the vertices of the quadrilateral be A ( - 4, - 2), B ( - 3, - 5), C (3, - 2), and D (2, 3). Join AC to form two triangles ΔABC and ΔACD.
Area of a triangle = 1/2 {x1 (y2 - y3) + x2 (y3 - y1) + x3 (y1 - y2)}
Area of ΔABC = 1/2 [(-4) {(-5) - (-2)} + (-3) {(-2) - (-2)} + 3 {(-2) - (-5)}] = 1/2 (12+0+9) = 21/2 square units
Area of ΔACD = 1/2 [(-4) {(-2) - (3)} + 3{(3) - (-2)} + 2 {(-2) - (-2)}] = 1/2 (20+15+0) = 35/2 square units
Area of ☐ABCD = Area of ΔABC + Area of ΔACD = (21/2 + 35/2) square units = 28 square units
5. You have studied in Class IX that a median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of equal areas. Verify this result for ΔABC whose vertices are A (4, - 6), B (3, - 2) and C (5, 2).
Answer

Let the vertices of the triangle be A (4, -6), B (3, -2), and C (5, 2).
Let D be the mid-point of side BC of ΔABC. Therefore, AD is the median in ΔABC.
Coordinates of point D = (3+5/2, -2+2/2) = (4,0)
Area of a triangle = 1/2 {x1 (y2 - y3) + x2 (y3 - y1) + x3 (y1 - y2)}
Area of ΔABD = 1/2 [(4) {(-2) - (0)} + 3{(0) - (-6)} + (4) {(-6) - (-2)}] = 1/2 (-8+18-16) = -3 square units
However, area cannot be negative. Therefore, area of ΔABD is 3 square units.
Area of ΔABD = 1/2 [(4) {0 - (2)} + 4{(2) - (-6)} + (5) {(-6) - (0)}] = 1/2 (-8+32-30) = -3 square units
However, area cannot be negative. Therefore, area of ΔABD is 3 square units.
The area of both sides is same. Thus, median AD has divided ΔABC in two triangles of equal areas.
|
5 videos|292 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 - Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry
| 1. What is coordinate geometry? |  |
| 2. How is the coordinate system used in coordinate geometry? |  |
| 3. How do we find the distance between two points in coordinate geometry? |  |
| 4. How do we find the midpoint of a line segment in coordinate geometry? |  |
| 5. How do we determine whether three points are collinear in coordinate geometry? |  |
|
5 videos|292 docs|59 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|


















