Key Concepts: Manufacturing Industries | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
Importance of Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of development due to the following reasons:
- Manufacturing industries help in modernising agriculture as it provides jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
- It helps in the eradication of unemployment and poverty.
- Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
- It helps in prospering the country by giving a boost to the economy.
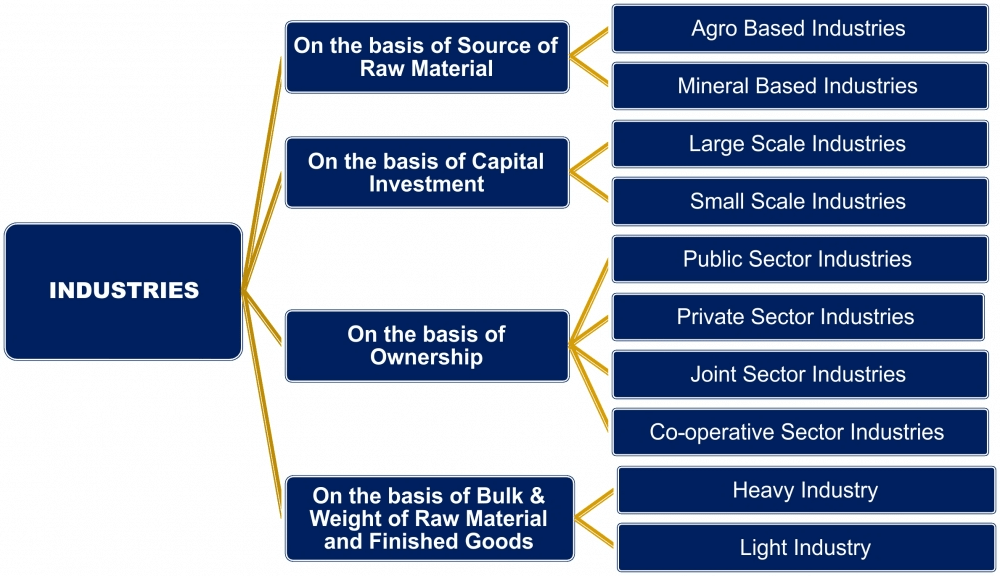
Classification of Industries
- Classification is done on the basis of their main role, capital investment, ownership, source of raw materials and the bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods.
- Large Scale Industries employ a large number of labourers.
- Small Scale Industries employ a small number of labourers.
- Heavy Industries use heavy and bulky raw materials.
- Light Industries use light raw materials.
Agro-based Industries
Industries based on agricultural raw materials. For example, cotton textiles, jute textiles, woollen textiles, silk textiles, synthetic textiles, sugar industry.
Cotton Textiles
- It occupies a unique position in the Indian economy, contributes 14% of industrial production.
- Provides employment to 35 million persons directly.
- Earlier the cotton textile industries were located in Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Today, they are spread over 80 towns and cities of India.
- Scarcity of good-quality cotton, obsolete machinery, erratic power supply, low productivity of labour and stiff competition are some of the problems faced by the cotton textiles industry.
Jute Textiles
There are about 70 jute mills in India and most of the jute is produced in West Bengal. Mainly in the Hugli basin produced in Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, Assam and Tripura.
 Jute Textiles
Jute Textiles
Sugar Industry
There are 460 sugar mills in the country. 50% of them are found in Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra. Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat are also important producers of sugar in the country.
Mineral-based Industries
Industries using minerals as their raw materials — iron and steel, cement, chemical industries, aluminium smelting, copper smelting, fertiliser industry, etc.
Iron and Steel Industry
- The iron works of Kulti, Burnpur started local production in 1870.
- The first modern steel plant was set up at Jamshedpur in 1907.
- Today there are 10 primary integrated iron and steel plants and around 200 mini steel plants in the country.
- Raw materials used in this industry are iron ore, coal, limestone and manganese ore.
- The location of this industry is decided by the availability of raw materials. All the important iron and steel plants are located in the north-eastern and southern parts of the Indian Peninsula.
- Only Visakhapatnam has a coastal location.
- These plants are managed by the Steel Authority of India Ltd. (SAIL)
- India produces about 32.8 million tonnes of steel and ranks ninth among the world crude steel producers.
Aluminium Smelting
- Aluminium is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
- It is used as a substitute for steel, copper, zinc and lead.
- In the production of one tonne of aluminium, 6 tonnes of bauxite and 18,600 kWh of electricity is required.
- The availability of electricity and bauxite decides the location of this industry.
- The 8 aluminium plants in the country are located in Orissa, West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
- India produces over 600 million tonnes of aluminium per annum.
Chemical Industry
- Heavy inorganic chemicals include sulphuric acid, nitric acid, alkalis, caustic soda and soda ash. They are widely spread around the country.
- Sulphuric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilisers, synthetic fibres, plastics, paints and dyes.
- Soda ash is used in the manufacture of glass, paper, soap and detergents.
- Heavy organic chemicals include petrochemicals which are used in the manufacture of synthetic fibres, synthetic rubber, plastics, dye stuffs, drugs and pharmaceuticals. These chemical plants are located near oil refineries and petrochemical plants.
- The chemical industries contribute 14% of the production of the entire manufacturing sector.
Fertiliser Industry
- The first plant was set up at Ranipet in Tamil Nadu.
- With the setting up of a plant at Sindri by the Fertiliser Corporation of India (FCI) in 1951, the production of fertilisers increased.
- With the onset of the Green Revolution, this industry was set up in Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab and Kerala.
- Other important producers are Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, Rajasthan, Bihar, Maharashtra, Assam, West Bengal, Goa, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka.
- There are 57 fertiliser units manufacturing nitrogenous fertilisers, 29 for urea and 9 for ammonium sulphate as a by-product, 68 other small units produce single super phosphate
Cement Industry
 Cement Industry
Cement Industry
- Cement is used for the construction of buildings, houses, factories, roads and dams.
- The raw materials used are limestone, silica, alumina and gypsum, coal and electric power are also used.
- The first cement plant was set up at Chennai in 1904. At present, there are 119 large and over 300 mini cement plants in India.
- Indian cement is in great demand in South and East Asia, Middle East and Africa because of its superior quality.
Automobiles
- Commercial vehicles like trucks, passenger buses, cars, motor cycles, scooters, etc., are manufactured in large numbers.
- India is the second largest producer of three wheelers.
- The industries producing bicycles, scooters and bicycles are distributed around Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Indore, Hyderabad, Jamshedpur and Bengaluru.
Electronic Industry
- Bengaluru has emerged as the electronic capital of India. Other major electronic goods producing centres are Hyderabad, Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Kanpur, Pune, Lucknow and Coimbatore.
- Many Software Technology Parks have also developed.
Industrial Pollution and Environmental Degradation
Industries create four types of pollution, namely air, water, land and noise.
- Air pollution is caused by the presence of a high proportion of undesirable gases, such as sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide. Smoke is emitted by chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries and smelting plants, and burning of fossil fuels leads to air pollution. It adversely affects human health, animals, plants, buildings and the atmosphere as a whole.
- Water pollution is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and effluents discharged into rivers. The industries which are mainly responsible for water pollution are paper, pulp, chemical, textile and dyeing, petroleum refineries, tanneries and electroplating industries.
- Thermal pollution of water occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling.
- Noise pollution is the propagation of noise with harmful impact on the activity of human or animal life. It results in irritation, anger, cause hearing impairment, increased heart rate and blood pressure.
Measures to Control Environmental Degradation

- Proper fuel selection and utilisation.
- Use of oil instead of coal in the industries.
- Treatment of liquids in three phases:
- Primary treatment by a mechanical process.
- Secondary treatment by biological process.
- Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes.
- Pollution of land and soil can be controlled by three activities:
- Collection of wastes from different places.
- Dumping and disposing of the waste by landfilling.
- Recycling of wastes for further use.
|
63 videos|445 docs|87 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts: Manufacturing Industries - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What are the key differences between agro-based and mineral-based industries? |  |
| 2. How does industrial pollution impact the environment? |  |
| 3. What measures can be taken to control environmental degradation caused by industries? |  |
| 4. Why is manufacturing important for economic development? |  |
| 5. What are the main causes of environmental degradation in industrial sectors? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|


















