Triangle and Its Properties- 2 | Mathematics for JSS 2 PDF Download
Q1.Is it possible to have a triangle with the following sides?
(i) 2 cm, 3 cm, 5 cm
(ii) 3 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm
(iii) 6 cm, 3 cm, 2 cm
Answers:
(i) 2 cm, 3 cm, 5 cm
2 + 3 > 5 No
2 + 5 > 3 Yes
3 + 5 > 2 Yes
This triangle is not possible.
(ii) 3 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm
3 + 6 > 7 Yes
6 + 7 > 3 Yes
3 + 7 > 6 Yes
This triangle is possible.
(iii) 6 cm, 3 cm, 2 cm
6 + 3 > 2 Yes
6 + 2 > 3 Yes
2 + 3 > 6 No
This triangle is not possible.
Q 2.Take any point O in the interior of a triangle PQR. Is:
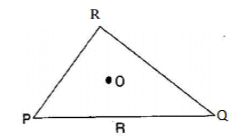
(i) OP + OQ > PQ ?
(ii) OQ + OR > QR?
(iii) OR + OP > RP ?
Answers
Join OR, OQ and OP.
(i) Is OP + OQ > PQ ?
Yes, POQ form a triangle.
(ii) Is OQ + OR > QR ?
Yes, RQO form a triangle.
(iii) Is OR + OP > RP ?
Yes, ROP form a triangle.
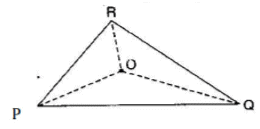
Q 3. AM is a median of a triangle ABC. Is AB + BC + CA > 2 AM? (Consider the sides of triangles ΔABM and ΔAMC.)

Since, the sum of lengths of any two sides in a triangle should be greater than the length of third side.
Ans: Therefore, In ΔABM, AB + BM > AM .. (i)
In ΔAMC, AC + MC > AM (ii)
Adding eq. (i) and (ii)
AB + BM + AC + MC > AM + AM
⇒ AB + AC + (BM + MC) > 2AM
⇒ AB + AC + BC > 2AM
Hence, it is true.
Q.4 ABCD is a quadrilateral. Is AB + BC + CD + DA > AC + BD?

Ans :Since, the sum of lengths of any two sides in a triangle should be greater than the length of third side.
Therefore, In Δ ABC, AB + BC > AC ..(i)
In Δ ADC, AD + DC > AC (ii)
In ΔDCB, DC + CB > DB (iii)
In ΔADB, AD + AB > DB (iv)
Adding equations (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get
AB + BC + AD + DC + DC + CB + AD + AB > AC + AC + DB + DB
⇒ (AB + AB) + (BC + BC) + (AD + AD) + (DC + DC) > 2AC + 2DB
⇒ 2AB + 2BC +2AD + 2DC > 2(AC+DB)
⇒ 2(AB +BC + AD +DC) > 2(AC +DB)
⇒ AB + BC + AD + DC > AC + DB
⇒ AB + BC + CD + DA > AC + DB
Hence, it is true.
Q 3.ABCD is quadrilateral. Is AB + BC + CD + DA < 2 (AC + BD)?
Ans :Since, the sum of lengths of any two sides in a triangle should be greater than the length of third side.
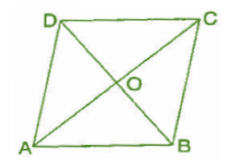
Therefore, In A AOB, AB < OA + OB .. (i)
In A BOC, BC < OB + OC (ii)
In A COD, CD<OC + OD (iii)
In AAOD, DA < OD + OA ..(iv)
Adding equations (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get
AB + BC + CD + DA < OA + OB + OB + OC + OC + OD + OD + OA
⇒ AB + BC + CD + DA < 2OA + 20B + 2OC + 2OD
⇒ AB + BC + CD + DA < 2[(AO + OC) + (DO + OB)]
⇒ AB + BC + CD + DA < 2(AC + BD)
Hence, it is proved.
Q 4.The lengths of two sides of a triangle are 12 cm and 15 cm. Between what two measures should the length of the third side fall?
Ans :Since, the sum of lengths of any two sides in a triangle should be greater than the length of third side.
It is given that two sides of triangle are 12 cm and 15 cm.
Therefore, the third side should be less than 12 + 15 = 27 cm.
And also the third side cannot be less than the difference of the two sides.
Therefore, the third side has to be more than 15 – 12 = 3 cm. Hence, the third side could be the length more than 3 cm and less than 27 c
Q 5.PQR is a triangle, right angled at P. If PQ = 10 cm and PR = 24 cm, find QR.
Ans:
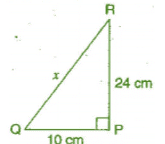
Given: PQ = 10 cm, PR = 24 cm
Let QR be x cm.
In right angled triangle QPR,
[Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Perpendicular)2 [By Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (QR)2 = (PQ)2 + (PR]2
⇒ x2 = (10)2 +(24)2
⇒ x2 = 100 + 576 = 676
⇒ 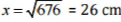
Thus, the length of QR is 26 cm.
Q 6.ABC is a triangle, right angled at C. If AB = 25 cm and AC = 7 cm, find BC.
Ans:
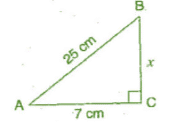
Let BC be x cm.
In right angled triangle ACB,
(Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Perpendicular)2 [By Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (AB)2 = (AC)2 + (BC)2
⇒ (25)2 = (7)2+x2
⇒ 625 = 49 + x2
⇒ x2 = 625 - 49 = 576
⇒
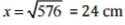
Thus, the length of BC is 24 cm.
Q 7. A 15 m long ladder reached a window 12 m high from the ground on placing it against a wall at a distance a. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the wall.

Ans:
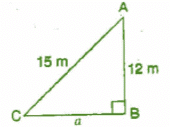
Let AC be the ladder and A be the window.
Given: AC = 15 m, AB = 12 m, CB = a m
In right angled triangle ACB,
(Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Perpendicular)2 [By Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (AC)2 = (CB)2 + (AB)2
⇒ (15)2 + (a)2 = (12)2
⇒ 225 = a2 + 144
⇒ a2 = 225 - 144 = 81
⇒ 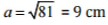
Thus, the distance of the foot of the ladder from the wall is 9 m.
Q 8.Which of the following can be the sides of a right triangle?
(i) 2.5 cm, 6.5 cm, 6 cm
(ii) 2 cm, 2 cm, 5 cm
(iii) 1.5 cm, 2 cm, 2.5 cm
In the case of right angled triangles, identify the right angles.
ANSWERS:
Let us consider, the larger side be the hypotenuse and also using Pythagoras theorem,
(Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Perpendicular)2
(i) 2.5 cm, 6.5 cm, 6 cm
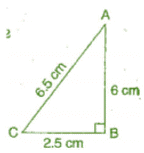
In tri ABC, (AC)2 = (AB)2 + (BC)2
L.H.S. = (6.5)2 = 42.25 cm
R.H.S. = (6)2 + (2.5)2 = 36 + 6.25 = 42.25 cm
Since, L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Therefore, the given sides are of the right angled triangle.
Right angle lies on the opposite to the greater side 6.5 cm, i.e., at B.
(ii) 2 cm, 2 cm, 5 cm
In the given triangle, (5)2 = (2)2 + (2)2
L.H.S. = (5)2 = 25
R.H.S. = (2)2 + (2)2 = 4 + 4 = 8
Since, L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
Therefore, the given sides are not of the right angled triangle.
(iii) 1.5 cm, 2 cm, 2.5 cm
In ΔPQR, (PR)2 = (PQ)3 + (RQ)2
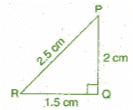
L.H.S. = (2 5)2 = 6.25 cm
R.H.S. = (1.5)2 + (2)2 = 2.25 + 4 = 6.25 cm
Since, L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Therefore, the given sides are of the right angled triangle.
Right angle lies on the opposite to the greater side 2.5 cm, i.e., at Q.
Q 9.A tree is broken at a height of 5 m from the ground and its top touches the ground at a distance of 12 m from the base of the tree. Find the original height of the tree.
Ans: Let A'CB represents the tree before it broken at the point C and let the top A’ touches the ground at A after it broke. Then ΔABC is a right angled triangle, right angled at B.
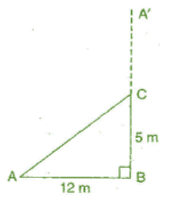
AB = 12 m and BC = 5 m
Using Pythagoras theorem, In ΔABC
(AC)2 =(AB)2 + (BC)2
⇒ (AC)2 = (12)2 + (5)2
⇒ (AC)2 = 144 + 25
⇒ (AC)2 = 169
⇒ AC = 13 m
Hence, the total height o f the tree = AC + CB 13 + 5
Q 10.Angles Q and R of a ΔPQR are 25° and 65°
Write which of the following is true:
(i) PQ2 + QR2 = RP2
(ii) PQ2 + RP2 = QR2
(iii) RP2 + QR2 = PQ2
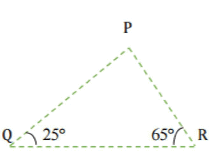
Ans: In ΔPQR, ∠PQR + ∠QRP + ∠RPQ = 180° [By Angle sum property of a Δ]
⇒ 25° + 65° + ∠RPQ = 180°
⇒ 90° + ∠RPQ = 180°
⇒ ∠RPQ = 180°- 90° = 90°
Thus, ΔPQR is a right angled triangle, right angled at P.
∴ (Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Perpendicular)2 [By Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (QR)2 = (PR)2 + (QP)2
Hence, Option (ii) is correct
Q 11.Find the perimeter of the rectangle whose length is 40 cm and a diagonal is 41 cm.
Ans: Given diagonal (PR) = 41 cm, length (PQ) = 40 cm
Let breadth (QR) be x cm.
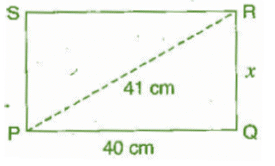
Now, in right angled triangle PQR,
(PR)2 = (RQ)2 +(PQ)2 [By Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (41)2 = x2 + (40)2
⇒ 1681 = x2 + 1600
⇒ x2 = 1681 - 1600
⇒ x2 = 81
⇒ 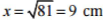
Therefore the breadth of the rectangle is 9 cm,
Perimeter of rectangle - 2(length + breadth)
= 2 [9 + 49)
= 2 x 49 = 98 cm
Hence, the perimeter of the rectangle is 98 cm
Q 12.The diagonals of a rhombus measure 16 cm and 30 cm. Find its perimeter.
Ans: Given: Diagonals AC = 30 cm and DB = 16 cm.
Since the diagonals of the rhombus bisect at right angle to each other.
Therefore, 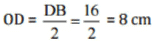
And 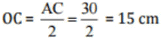
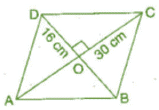
Now , In right angle triangle DOC,
(DC)2 =(OD)2 + (OC)2 [By Pythagoras dieorem]
⇒ (DC)2 = (8)2+(15)2
⇒ (DC)2 = 64 + 225 = 289
⇒ 
Perimeter of rhombus = 4 x side = 4 x 17 = 68 cm
Thus, die perimeter of rhombus is 68 cm.
|
83 videos|156 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Triangle and Its Properties- 2 - Mathematics for JSS 2
| 1. What is a triangle and what are its properties? |  |
| 2. What is the Pythagorean theorem and how is it used in triangles? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between an acute triangle and an obtuse triangle? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between the sides and angles of an equilateral triangle? |  |
| 5. How can the area of a triangle be calculated? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JSS 2 exam
|

|


















