Introduction to Grammar - Nouns | Verbal for GMAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Nouns |

|
| Classification of Nouns |

|
| Number Nouns |

|
| Noun Genders |

|
| Noun Cases |

|
| Some Solved Questions |

|
Nouns
A noun is a word that denotes a person, place, or thing, e.g. Tom, apple, laughter, Phoenix.
Example Sentence: Tom went around the world, from California to Cairo, by ship.
All underlined words are nouns.
- Tom = Name of the person
- world = place
- California = Name of the place
- Cairo = Name of the place
- ship = thing
Other Examples of Nouns:
- Name of a Person – Zuker, Max, Xavier, Joseph, etc
- Name of an Animal – Kangaroo, Dolphin, Jackal, etc.
- Name of a Place – Bostan, Australia, India, etc.
- Name of a Thing – Table, Computer, Chair, etc.
- Name of an Idea – Happiness, Superstitions, Excitement, etc.
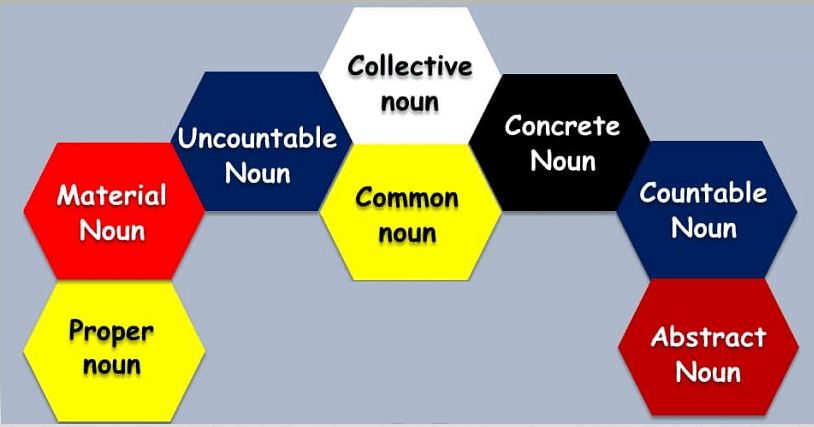
Classification of Nouns
Nouns in English are broadly classified into eight types –
1. Common Noun
The name given in common to every place, thing or person belonging to the same class or kind, like a boy, girl, teacher, doctor, country, etc.
- Nouns can be either proper or common, depending upon whether they express specific names or generic entities.
- Common Nouns are general nouns.
- In the sentence "Tom went around the world, from California to Cairo, by ship.", the nouns ‘world’ and ‘ship’ are common nouns.
- Here are some examples of Common nouns used in sentences:
(i) I did not go to school yesterday as I was sick.
(ii) Where can I find a restaurant?
(iii) The Sun is shining brightly.
(iv) Your hair looks really good.
(v) The girls took a trip to Goa.
2. Proper Noun
The name given to a particular person or a place, such as Rita, Ria, Russia, Rome, etc.
- Proper Nouns name specific persons, places, or things. They are capitalized.
- In the example sentence "Tom went around the world, from California to Cairo, by ship.", the nouns ‘Tom’, ‘California’, and ‘Cairo’ are all proper nouns since each of these nouns is the name of a person or a place.
- Here are some examples of Proper nouns used in sentences:
(i) Can you ask Mom to close the window?
(ii) Jennifer and Jackson took their dog Bailey for a walk.
(iii) Those hamsters aren’t as cute as my pet Fluffy.
(iv) I hope Mrs. Smith is my teacher next year.
(v) My favorite cartoon character is Bart Simpson.
3. Collective Nouns
A name used for a group of people, animals, or things. Example, cattle, family, herd, team, etc.
- Here are some examples of Collective nouns used in sentences:
(i) Tommy was excited to see a herd of elephants on the way to his native place.
(ii) The bench of judges gave the verdict on the case.
(iii) The kid enjoyed seeing the flock of pigeons take off all at once.
(iv) The football team was congratulated by the principal.
(v) The mob was getting crazier with time.
Anne had to face a great deal of allegations but they were all proved false.
4. Concrete Nouns
These are the names used for the things that have physical existence and we can see, such as a table, chair, mobile phones, etc.
- Nouns can be either concrete or abstract, depending upon what type of entity they denote.
- Concrete Nouns denote items that one can identify, using any of the 5 senses – sight, touch, taste, smell, & sound. For E.g. all nouns in the example sentence "Tom went around the world, from California to Cairo, by ship." are concrete nouns.
- Here are some examples of Concrete nouns used in sentences:
(i) An apple is placed on the dining table.
(ii) I can see a lot of bookcases in the library.
(iii) A baby boy is playing on the couch.
(iv) He is one of the best designers in our city.
(v) The size of an Elephant is so big compared to other animals.
5. Abstract Nouns
They are the exact opposite of concrete nouns. These are the names given to an idea, conditions, or quality.
- Basically, the name is used to refer to something that cannot be seen but is there, it does not exist physically.
- For example, truth, patriotism, sorrow, friendship, etc.
- Abstract Nouns denote items that cannot be detected by the 5 senses. E.g. love, truth, pain, skill.
- Here are some examples of Abstract nouns used in sentences:
(i) Honesty is the best policy.
(ii) There is no possibility for you to reach home by six in the evening.
(iii) This place has a really pleasant ambiance.
(iv) Pride goes before a fall.
(v) Brevity is the soul of wit.
I recognized your voice at once.
6. Material Nouns
These are the names used to refer to substances, materials or things that are made up of an alloy. Examples: Gold, Silver, Brass, Alcohol, Acid, Cloth, Air, Brick, Cement, Milk, butter, Petrol, diesel, Oil, Rubber, Salt, Sand, Clay, Coffee, Tea, Cheese, Chemical, Copper, Iron, Rain, Glass, Grass, etc.
7. Countable Nouns
That can be counted like one pen, two ladies, one chair, etc. These nouns take articles (a, an, the) with them.
A countable noun is a word that can be counted and has a plural form. For example:
The word ‘onion’ is a countable noun because:
- It can be counted as one onion, two onions, three onions, etc.
- It has a plural form (onions).
The word ‘reason’ is a countable noun because: - It can be counted as one reason, two reasons, three reasons, etc.
- It has a plural form (reasons).
By the same reasoning as above, words such as ‘thing’, ‘job’, ‘coin’, ‘story', etc. are countable nouns.
All students in my program hope to become a rich, famous author, but statistics indicate that none of us will.
8. Uncountable Nouns
The nouns that cannot be counted. For example, Water, Soil, Sugar, Salt, etc.
- Abstract nouns and Proper nouns are always uncountable while Common and Concrete nouns can be both countable and well uncountable nouns.
- An uncountable noun is a word that cannot be counted and that *usually does not have a plural form. For example:
The word ‘garlic’ is an uncountable noun because:
• It cannot be counted as one garlic, two garlics, three garlics, etc.
• It does not have a plural form (garlics). - The word "Garlic" is written as Garlic ONLY.
The word ‘knowledge’ is an uncountable noun because:
• It cannot be counted as one knowledge, two knowledges, three knowledges, etc.
• It does not have a plural form (knowledges).
By the same reasoning as above, words such as ‘stuff’, ‘furniture’, ‘money’, ‘rice’, ‘anger’ etc. are uncountable nouns.
The noun ‘money’, which is usually an uncountable noun, has a plural form ‘moneys’, which is used in a very different context and not in the context of ‘one moneys’, ‘two moneys’, etc.
How can we determine whether a noun is countable or uncountable?
A noun is a countable noun if:
- It can be counted as 1 (noun), 2 (nouns), 3 (nouns)
- It has a plural form.
A noun is an uncountable noun if - It cannot be counted as 1 (noun), 2 (nouns), 3 (nouns)
- It does not have a plural form.
What adjectives can be used with countable and uncountable nouns?
- Quantity adjectives such as ‘few’, ‘many’, etc. can only be used with countable nouns. For example, you can say ‘few songs’ because here ‘songs’ is a countable noun, but you can’t say ‘few music’ because ‘music’ is an uncountable noun. Similarly, you can say ‘many songs’; but you can’t say ‘many music’.
- Quantity adjectives such as ‘less’, ‘amount’, etc. can only be used with uncountable nouns. For example, you can say ‘less music’ because here ‘music’ is an uncountable noun, but you can’t say ‘less songs’ because songs are countable noun, and ‘less’ cannot be used with countable nouns. Similarly the expression ‘amount of music’ is correct, while the expression ‘amount of songs’ is incorrect idiomatic usage.
Number Nouns
Nouns have a number associated with them. Since they express entities, they can either express a single entity or a plural entity. Thus, nouns can be singular or plural.
1. Singular Nouns
- When one person or a thing is denoted then it is a Singular noun, such as pen, cow, boy, chair, etc
- Singular means one. A noun in its native form is singular: e.g. – ship.
2. Plural Nouns
- When a noun denotes more than one person or a thing it is a plural noun, for example – pens, cows, boys, chairs, etc.
- Typically, most nouns can be made plural by adding –s, –es or –ies after the noun. E.g.
• ship is singular; ships is plural.
• injury is singular; injuries is plural.
Certain other nouns have distinct plural forms.
E.g.
• man is singular; men is plural.
• child is singular; children is plural.
• mouse is singular, mice are plural.
Noun Genders
1. Masculine
Nouns that refer to the male classification of a person, animal or thing example, man, lion, moon, etc
2. Feminine
Nouns denoting a female class of a person, animal or thing like nature, tigress, woman, etc.
3. Neuter
Nouns that denote a thing without life, either female or male, for example, pen, room, book, etc.
Noun Cases
Nouns classified on the basis of cases tells us the position of the noun in a sentence. There are five cases of nouns in English.
1. Possessive Case
When a noun denotes ownership or possession, for example – That is my dress. ‘My’ is in the possessive case.
2. Vocative case
A noun is in the vocative case when it is used to call (to get attention). For example, Ms. Ria, teachers are waiting for you in the staffroom. (Ms. Ria is in a vocative case).
3. Dative Case
When a noun is in the indirect object of a verb it is in the Dative case, like, Rohan brought me chocolates, (‘Me’ is in the dative case)
4. Nominative Case
If a noun is the subject of a verb it is said to be in the Nominative case. Example – Radha is an intelligent girl.
5. Objective Case
When the noun is the direct object of the verb or the preposition, they are in the objective case. Example – Please give the fruits.
Some Solved Questions
About a third of the questions that appear in the GMAT verbal section is sentence correction questions. So, Let's have a look at some solved questions.
Replace the underlined portion with the answer choice that results in a clear, precise sentence that meets the requirements of standard written English.
Q.1. Favouring handmade suits and buying Italian leather shoes, the young man’s ability to spend on fashion items was unparalleled among his friends.
Possible Answers:
a) Favoring handmade suits and buying Italian leather shoes
b) Favored handmade suits and buying Italian leather shoes
c) Favoring handmade suits, buying Italian leather shoes
d) Favoring handmade suits and Italian leather shoes
e) Favoring handmade suits and bought Italian leather shoes
Answer: Favoring handmade suits and Italian leather shoes
Explanation: The use of both "favouring" and "buying" in the opening phrase is awkward and ruins the parallelism between the suits and the shoes. Tying the two items to the same verb streamlines the phrase and makes the sentence more grammatically correct. " Favoring handmade suits and Italian leather shoes" is the only answer choice that makes the appropriate correction to the sentence.
Q.2. Both of Tim's triplets were developing quite nicely. No error
Select the underlined word or phrase that needs to be changed to make the sentence correct. Some sentences contain no error at all.
Possible Answers:
a) No error
b) Both
c) triplets
d) were
e) Tim's
Answer: Both
Explanation: In this question, the nouns "both" and "triplets" disagree. Triplets would suggest three things, while "both" only applies to differentiating between two options. Therefore "both" should be replaced, perhaps with a word like "all."
Q.3. Replace the underlined portion with the answer choice that results in a sentence that is clear, precise, and meets the requirements of standard written English. One of the answer choices reproduces the underlined portion as it is written in the sentence.
After months of organizing the gala, several of the party planners are beginning to wish they worked as a waiter or bartender instead.
Possible Answers:
a) several of the party planners is beginning to wish they worked as waiters or bartenders instead.
b) several of the party planners are beginning to wish they worked as waiter or bartender instead.
c) several of the party planners are beginning to wish they worked as a waiter or bartender instead.
d) several of the party planners are beginning to wish they worked as waiters or bartenders instead.
e) several of the party planners is beginning to wish they worked as a waiter or as a bartender instead.
Answer: several of the party planners are beginning to wish they worked as waiters or bartenders instead.
Explanation: Because there are several party planners longing for different jobs, the jobs themselves must be plural; three or four people can’t work as a single waiter or bartender. And because “party planners” is plural, the correct verb conjugation is “are.”
Q.4. Replace the underlined portion with the answer choice that results in a sentence that is clear, precise, and meets the requirements of standard written English. One of the answer choices reproduces the underlined portion as it is written in the sentence.
Trying to convince me to go with them, my friends described the concert as once-in-a-lifetime experiences.
Possible Answers:
a) my friends described the concert as once-in-a-lifetime experiences.
b) my friends described the concert as a once-in-a-lifetime experience.
c) my friends described the concert as a once-in-a-lifetime experiences.
d) my friends described the concert as experienced once-in-a-lifetime.
e) my friends described the concert as an experience once-in-a-lifetime.
Answer: my friends described the concert as a once-in-a-lifetime experience.
Explanation: Because a "concert" is a singular noun, it can only be one experience and not many. “Trying to convince me to go with them, my friends described the concert as a once-in-a-lifetime experience” is the least awkward option.
Q.5. Replace the underlined portion with the answer choice that results in a sentence that is clear, precise, and meets the requirements of standard written English. One of the answer choices reproduces the underlined portion as it is written in the sentence.
Dani drove her car into the parking garage, turned off the engine, and made sure to lock her cars doors securely as she left.
Possible Answers:
a) to lock her car doors securely
b) to lock her cars doors securely
c) to locking her cars doors securely
d) to lock her cars doors securely
e) to locked her cars' doors securely
Answer: to lock her car doors securely
Explanation: There is a disagreement between the nouns "cars" and "doors" in the sentence; we are told earlier in the sentence via its use of "her car" that Dani only drove one car into the parking garage. Therefore, the correct answer choice is "to lock her car doors."
|
52 videos|55 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Grammar - Nouns - Verbal for GMAT
| 1. What are nouns in grammar? |  |
| 2. What is the classification of nouns? |  |
| 3. What are number nouns? |  |
| 4. What are noun genders? |  |
| 5. What are noun cases? |  |

|
Explore Courses for GMAT exam
|

|


















