Supercharging, Engine Testing & Emissions | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) PDF Download
SUPERCHARGING, ENGINE TESTING AND EMISSIONS
- To increase the power output of the engine, following can be done
- Increase the air inducted per unit time to burn more fuel
- Improve the degree of utilization of air
- Improve the thermal efficiency
- To increase the air input per unit time, either speed of the engine or density of air should be increased.
- Increasing the density of air to increase the power output of the engine is called super charging
- In addition to increase the power output of an engine, supercharging compensate for low density at high attitude.
- Supercharging increases detonation tendency in SI engine so detonation limits the super charging and hence power output of SI engine
- In SI engine supercharging is used only in aircraft and racing car engines
- In CI engine, supercharging reduces detonation tendency. So it is always useful for CI engine i.e. more power, more economy and less detonation. The limit of supercharging is governed by thermal loading due to very high temperature
EFFECT OF SUPERCHARGING ON ENGINE PERFORMANCE
- Increased power output from the same engine
- Slight improvement in mechanical efficiency
- Better scavenging and reduced exhaust gas temperature
- Low specific fuel consumption
- At part loads, fuel consumption after supercharging is more than natural aspirated engines.
Superchargers
- Supercharger can be run in a number of ways. It may be run by the engine through gearing.
- Sometimes an exhaust driven turbine is used to run the compressor, this is called turbocharging.
- A special form is a free piston engine in which the engine supplies total power to the compressor and the exhaust gasses from the engine drive a turbine to give the power output.
Turbochargers
- These are the centrifugal compressors driven by exhaust gas turbine.
- These are extensively used for the supercharging of CI engines.
- By utilizing the exhaust energy, it recovers a major part of energy which would otherwise go waste. Thus it does not use the engine power.
BASIC PERFORMANCE PARAMETERS OF IC ENGINE
- Power output
- Mechanical efficiency
- Brake mean effective pressure
- Specific power output
- Volumetric efficiency
- Fuel-air ratio
- Specific fuel consumption
- Thermal efficiency
- Heat balance
- Exhaust emission
- Higher the mean effective pressure, higher will be the power developed by the engine for a given displacement so mean effective pressure is the true indication of the relative performance of different engines.
Specific power output = 
- Volumetric efficiency of an engine is an indication of the measure of the degree of
utilization of swept volume of the engine.
- For supercharged engine, volumetric efficiency has no meaning as it is more
than unity.
- Specific power output =

- Brake specific fuel consumption (bsfc) =

- Indicated specific fuel consumption (isfc) =

- Brake thermal efficiency
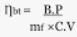

Measurement of Engine Parameters
| Parameter | Method of measurement |
| Speed | Tacho meter |
| Air consumption | Air boxmethod |
| Exhaust emission | Flameionisation det ector (for hydrocarbon) spectroscope analysis |
| Brakepower | dynamometer |
| Friction power | Morse test,motoring test, Willan ' s linemethod |
- The break up of the total energy input and output into different heads is called heat balance. It includes
- Heat equivalent to the effective work of the engine
- Heat rejected to the cooling medium
- Heat carried away with the exhaust gases.
- Unaccounted heat loss which includes radiation losses, heat loss due to incomplete combustion.
- Friction loss is included in heat rejected to the cooling medium.
Emissions
- Air pollution can be defined as addition to our atmosphere of any material with will have a deleterious effect on life upon earth.
- The main pollutants contributed by automobiles are
- Carbon mono oxide (CO)
- Unburned hydro carbon (HBHC)
- Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx)
- Perfect combustion gives carbon dioxides (CO2) and water vapour in exhaust.
Pollutant from Petrol Engine
| Source | Quantity |
| Evaporative loss from tank & carburetor | 15%-25%of HC |
| Crankcase blow by fumes | 20%-35%of HC |
| Exhaust emission | 50%-60%of HC and completely unburnt CO and NO |
- Ketones and aldehydes in exhaust from smog in the presence of sunlight.
Carbon Monoxides (CO)
- Percentage of CO decreases with speed.
- CO emission are high during idling and maximum during declaration.
- They are lowest during acceleration and steady speed.
Hydrocarbon
- The HC emission is higher during deceleration, idling and low speed operation.
- Lower surface to volume (S/V) ratio lowers HC emission. S/V can be reduced by lower compression ratio, high stroke to bore ratio, larger displacement of piston etc.
Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx)
- High temperature and availability of oxygen are main reason for NOx emission.
- For lean and rich air fuel mixture the NOx concentration is low.
- Increasing the spark advance will result in high NOx concentration in exhaust.
- At near stoichiometric fuel-air mixture both HC and CO emission are higher and lean mixture emit low HC/CO.
- The combination of HC and NOx in the presence of sunlight produce photo chemical smog.
Control of Air Pollution by Petrol Engine
- By using leaner air-fuel ratio
- Retarding ignition timing
- Reducing quenching area in combustion chamber
- Lower compression ratio
- Reduced valve overlap
- After burning of exhaust by oxygen
- Recirculation crankcase blow by gases to intake air cleaner
Total Emission Control Package
- Thermal reactor package
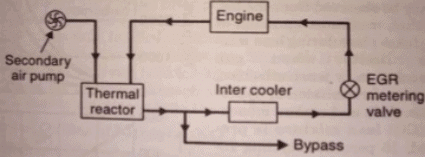
- It consists of two enlarged exhaust manifold which allow greater residence time for complete burning of HC and CO with oxygen in the pumped in air. Also about 10% - 15% exhaust gas is recirculated to air cleaner via inter cooler. This re-circulation reduces the temperature of the combustion gases and provides for the control of NOx.
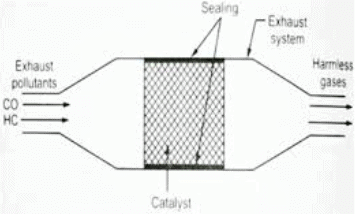
Catalytic Converter Package
- Converters for HC, CO and NOx are arranged as in the diagram, NOx catalyst is the first element in the path. There is no heat release. Then comes HC/CO catalyst which cause heat release. Exhaust gas is also recirculated for NOx control.
- Catalytic converter uses non leaded fuel because lead affects performance of the catalyst.
- The power output is 30% less and fuel consumption 10% more for this system.
Diesel Emission
- Exhaust in turbocharged engine is low in HC and high in NOx.
- During idle mode, HC, NOx are lowest.
- Acceleration mode has more smoke level
- Maximum emission at full load.
- NOx is high at acceleration mode and full load.
- A precombustion chamber design produces less NOx.
Causes of Smoke
- Incomplete combustion
- Incorrect A/F ratio
- Improper mixing
- Improper atomization excessive duration of injection.
Emission Control
- Emission from SI engines can be controlled by the following measures:
Engine Design Modification
1. Leans A/F ratio: They reduce CO and HC emissions.
2. Reducing the CR: It reduces the peak temperature which reduces NOx emissions.
3. Reducing valve overlap: This would reduce the amount of UBHC from escaping along e exhaust gases.
4. Combustion chamber modification: By suitable design of combustion chamber quench areas can be eliminated. This would result in proper combustion and reduce CO and HC.
5. Retarding the spark: This reduce the peak temperature and reduces NOx.
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Supercharging, Engine Testing & Emissions - Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical)
| 1. What is supercharging and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the benefits of supercharging an engine? |  |
| 3. How are engines tested for performance and efficiency? |  |
| 4. What are emissions in the context of engine testing? |  |
| 5. How do mechanical engineers contribute to supercharging and engine testing? |  |
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|

















