Tissues & The Tissue System | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Tissue? |

|
| The Tissue System |

|
| 1. Epidermal Tissue System |

|
| 2. Ground Tissue System |

|
| 3. Vascular/ Conducting Tissue System |

|
What is Tissue?
Tissue is like a group of cells, which can be the same or different but doing a specific job in the body of a plant or animal.
Types of Plant Tissues
(i) Meristematic Tissue
(ii) Permanent Tissue

Meristematic Tissue
Meristematic tissue consists of cells capable of dividing. These meristems are found in specialized regions of plants and are responsible for their growth.
 Types of Merismatic Tissue
Types of Merismatic Tissue
Permanent Tissue
Permanent tissues develop from meristematic tissue and consist of cells that no longer have the ability to divide.
 Types of Permanent Tissue
Types of Permanent Tissue
As we know, different types of tissues are based on the types of cells they consist of. However, tissues in plants also exhibit variation based on their location within the plant body, which in turn affects their structure and function.
In this document, we will delve into the concept of tissue systems in plants, specifically focusing on the three main types: the epidermal tissue system, the ground or fundamental tissue system, and the vascular or conducting tissue system.

The Tissue System
In higher plants, several tissues work together in form of a unit to perform a particular function. These tissues have the same origin. Such tissues form a system which is called tissue system. On the basis of the division of labour, position & morphology tissue is categorized by Sachs (German scientist) into three types of tissue systems. Each system usually consist of an association of tissues which perform specific function.
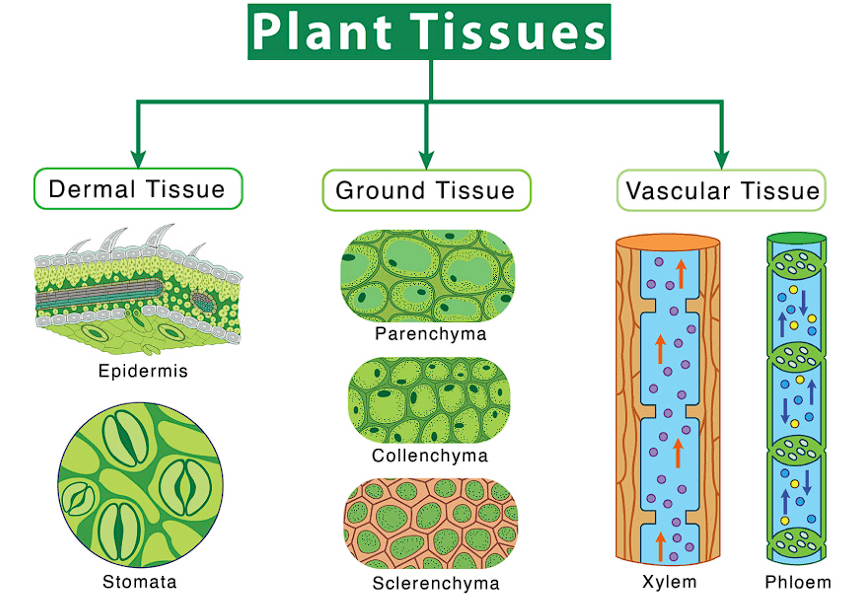
1. Epidermal Tissue System
(a) Structure of Epidermis
- Forms the outermost covering of the plant body.
- Comprises of epidermal cells, stomata, and epidermal appendages such as trichomes and hairs.
- Epidermis is the outermost layer of the primary plant body.
- Made up of elongated, compactly arranged cells that form a continuous layer.
- Usually single-layered.
- Epidermal cells are parenchymatous with a small amount of cytoplasm lining the cell wall and a large vacuole.
(b) Role of Cuticle
- The outside of the epidermis is often covered with a waxy thick layer called the cuticle.
- Cuticle prevents the loss of water by reducing water loss through the epidermis.
- Cuticle is absent in roots.
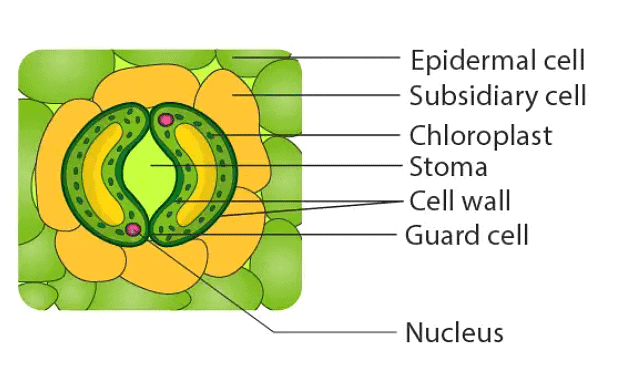
(c) Stomata and their Function
- Stomata are structures present in the epidermis of leaves.
- Stomata regulate the process of transpiration and gaseous exchange.
- Each stoma is composed of two bean-shaped cells known as guard cells which enclose stomatal pore.
- In grasses, the guard cells are dumb-bell shaped.
- The outer walls of guard cells (away from the stomatal pore) are thin, and the inner walls (towards the stomatal pore) are highly thickened.
- Guard cells possess chloroplasts and regulate the opening and closing of stomata.
- Subsidiary cells: Some epidermal cells near the guard cells become specialized in shape and size and are known as subsidiary cells.
- The stomatal aperture, guard cells, and subsidiary cells together are called the stomatal apparatus.
(d) Epidermal Hairs
- Root hairs: Unicellular elongations of epidermal cells in roots that help absorb water and minerals from the soil.
- Stem hairs (Trichomes): Epidermal hairs on stems that are usually multicellular.
- Types of trichomes: Branched or unbranched, soft or stiff, and may even be secretory.
- Function of trichomes: Help in preventing water loss due to transpiration in shoot system.
2. Ground Tissue System
Ground tissue is a type of plant tissue that makes up the bulk of the plant body, excluding the epidermis and vascular bundles. Ground tissue is composed of simple tissues, including parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
Main function of Ground Tissue System:
Manufacture and storage of food material.
Mechanical support (additional work)
Types of Ground Tissue
(a) Parenchyma
- Parenchyma is a type of ground tissue that consists of loosely packed, living cells with thin cell walls.
- Parenchyma cells are usually present in the cortex, pericycle, pith, and medullary rays of primary stems and roots.
- Parenchyma cells are involved in various functions such as photosynthesis, storage, and secretion.
(b) Collenchyma
- Collenchyma is a type of ground tissue that consists of elongated cells with irregularly thickened cell walls.
- Collenchyma cells provide mechanical support to young plant organs, such as stems and leaves, as they have the ability to stretch and elongate.
(c) Sclerenchyma
- Sclerenchyma is a type of ground tissue that consists of thick-walled, dead cells with lignified cell walls.
- Sclerenchyma cells provide mechanical support to mature plant organs, such as stems, roots, and vascular bundles, as they are rigid and non-stretchable.
Ground Tissue in Leaves
- In leaves, the ground tissue is referred to as mesophyll.
- Mesophyll consists of thin-walled cells that contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis.
- Mesophyll cells play a crucial role in capturing sunlight and converting it into energy through the process of photosynthesis.
3. Vascular/ Conducting Tissue System
The vascular system in plants is composed of complex tissues called phloem and xylem. Phloem and xylem together constitute vascular bundles, which are responsible for the transport of water, minerals, and nutrients throughout the plant.
(a) Vascular Bundles in Dicotyledonous Stems
- In dicotyledonous stems, cambium is present between the phloem and xylem in the vascular bundles.
- Cambium is a meristematic tissue that has the ability to form secondary xylem and phloem tissues, allowing for secondary growth in the stem.
- Vascular bundles with cambium are called open vascular bundles, as they possess the ability to form secondary tissues.
(b) Vascular Bundles in Monocotyledons
- In monocotyledonous plants, the vascular bundles do not have cambium present in them.
- As a result, they do not have the ability to form secondary tissues, and hence are referred to as closed vascular bundles.
(c) Radial Vascular Bundles
- Radial vascular bundles refer to the arrangement of xylem and phloem within a vascular bundle in an alternate manner along different radii.
- This type of arrangement is commonly found in roots, where xylem and phloem are arranged radially, allowing for efficient transport of water and nutrients.
(d) Conjoint Vascular Bundles
- Conjoint vascular bundles refer to the arrangement of xylem and phloem along the same radius of the vascular bundle.
- This type of arrangement is commonly found in stems and leaves of plants.
- In conjoint vascular bundles, phloem is usually located only on the outer side of xylem.
|
181 videos|362 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Tissues & The Tissue System - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main types of tissue in plants? |  |
| 2. What is the function of the Epidermal Tissue System? |  |
| 3. How does the Ground Tissue System contribute to plant structure? |  |
| 4. What role does the Vascular/Conducting Tissue System play in plants? |  |
| 5. How do the different tissue systems interact within a plant? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















