Overview: Acids & Bases - 1 | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Acids? |

|
| What are Bases? |

|
| What are Alkalis? |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions |

|
A wide variety of materials consists essentially of elements and compounds having different characteristics that exist around us. Some of them are sour, some are bitter, while some are salty in taste.
Example: Sour and bitter tastes of food are due to acids and bases, respectively, present in them.
Acids react with bases to produce salt whose properties are different from acid and base.
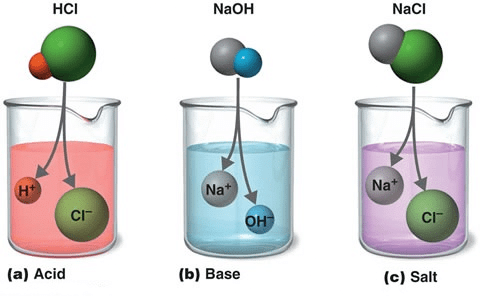
What are Acids?
The term "acid" is derived from the latin word "acidus" meaning sour to taste. Acids are defined as the one which produces hydrogen/Hydroxyl ions in water.
Example: Sulphuric Acid(H2SO4), Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) etc.
Properties of Acids:
- Acids are sour in taste.
- Acids turn blue litmus to red. This is used as a confirmation test for the presence of acid.
- Acidic solutions can conduct electricity because they dissociate into ions which conduct electricity.
- Produce hydrogen(H+)/hydroxyl(H3O+) ions in water.
- When acids react with metals, Hydrogen gas is evolved.
- Acids are corrosive in nature.
According to Arrhenius: Those substances which give hydronium ion(H3O+) or H+ ion in their aqueous solution are called acids.
Note: Due to the corrosive nature acids are stored in glass and ceramic bottles.
Chemical Properties of Acids
- The Reaction of Acid with Metal
Metal + Acid → Hydrogen gas + Salt
Mg + H2SO4 → H2 + MgSO4 - The Reaction of Acid with Metal Carbonates
Acids react with metal carbonates to form salt + water + CO2 gas↑:
Na2CO3(s) + 2 HCl (aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O (l) + CO2(g)The Reaction of Acid with Bicarbonates
Acids react with metal bicarbonates to form salt + water + CO2 gas :
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2↑The Reaction of Acids with Base (Neutralization reaction)
 Neutralisation Reaction
Neutralisation Reaction - The Reaction of Acid with Metal Oxide
Salt and water are formed as metal oxides are basic in nature: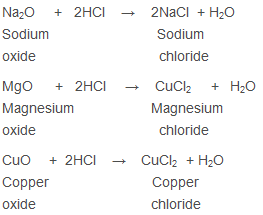
Classification of Acids
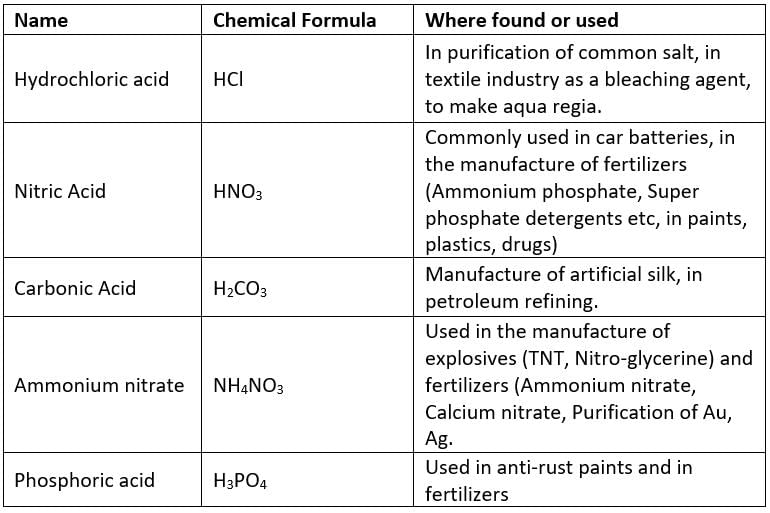
(a) Mineral Acids (Inorganic Acids)
The acids which are usually obtained from minerals are known as Inorganic acids.
Do You Know?
Aqua regia is also known as royal water because it can dissolve less reactive metals into it.Example: Gold(Au) and Platinum(Pt)
(b) Organic Acids: Acids which are derived from plants and animals are known as Organic Acids.
Example: Citric Acid from fruit
Table: Organic Acids
➢ On the Basis of their Basicity
The basicity of an acid is the number of replaceable hydrogen atoms present in a molecule that can be produced by the complete ionisation of one molecule of that acid in an aqueous solution.
OR
The basicity of an acid is determined by the number of hydronium ions (H3O+/H+(aq) produced per molecule of acid on ionisation.
(a) Monobasic Acids
The acid on complete ionisation produces one hydronium ion in aqueous solution.
Example:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Nitric acid (HNO3)
Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Formic acid (HCOOH)
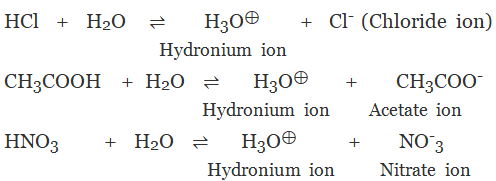
The acid on complete ionization produces two hydronium ions per molecule of acid in aqueous solution.
Example:
- Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
- Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
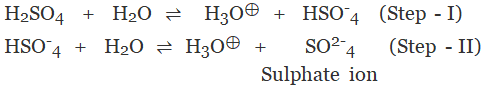
(c) Tribasic Acid
The acid on complete ionisation produces three hydronium ions per molecule of acid in aqueous solution.
Example:
- Phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
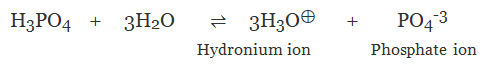
➢ Classification on the Basis of their Strength
(a) Strong Acid
The acid which undergoes complete ionisation in an aqueous solution is known as strong acids.
Example:
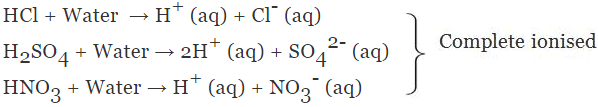
 (b) Weak Acid
(b) Weak Acid
The acid which undergoes partial or incomplete ionization in aqueous solution is known as weak acids.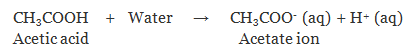 Example:
Example:
- Formic acid (HCOOH)
- Oxalic acid (COOH)2
- Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
- Phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
➢ Classification on the Basis of Concentration of the Acid
(a) Concentrated Acid
The acids which contain a very small amount of water is called a concentrated acid.
(b) Dilute Acid
- The acid which contains more amount of water is called a dilute acid. "Strength of an acid does not depend upon the concentration of an acid."
Important Fact
Aqua - Regia - Aqua regia is a mixture of (3 part HCl & 1 part HNO3) which dissolves even noble metals like Au(Gold), Pt(Platinum).
- Strength of an Acid ∝ Concentration of hydronium ion
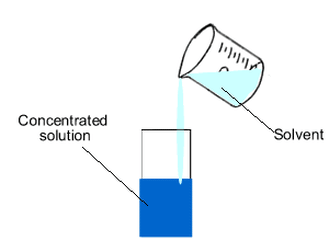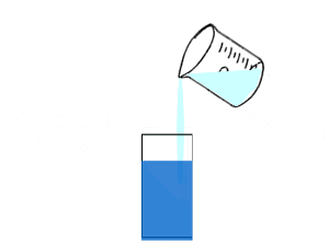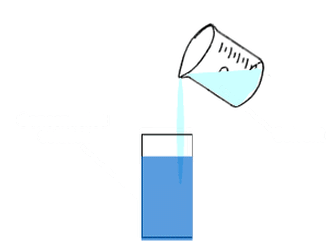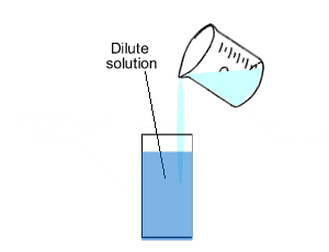
Dilution
 Process of Dilution
Process of Dilution
- Dilution is the process of reducing the concentration of a solution by adding more solvent (usually water) to it.
- It is a highly exothermic process.
- To dilute acid, the acid must be added to water and not the other way round.
What are Bases?
Substances with a bitter taste and give a soapy touch are known as bases.
Example:
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
- Zinc oxide (ZnO)
- Copper oxide (CuO)
- Calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2]
- Magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2]
- Aluminium hydroxide [Al(OH)3]
Properties of Bases:
- Bases produce hydroxide ions [OH–] in H2O.
- Water-soluble bases are called alkalies.
- Bases are bitter in taste.
- Bases turn Red Litmus blue.
- Bases act as electrolytes in Solution.
- Bases neutralize solutions containing H+ ions.
- Bases have a slippery, ‘soapy’ feel.
- Bases dissolve fatty material.
- Strong bases are corrosive in nature.
Example: NaOH, KOH
According to Arrhenius
"Those substances which give hydroxide or hydroxyl ion (OH-) in their aqueous solution" are called bases.NaOH(aq.) → Na+(aq) + OH-(aq)
KOH(aq.) → K+(aq) + OH-(aq)
- The compounds which are either metallic oxides or metallic hydroxides combine with acids to form salts and water only:
CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
Base Acid Salt Water
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Base Acid Salt Water
Mg (OH)2 + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + 2H2O
Base Acid Salt Water
What are Alkalis?
Bases that completely dissolve in water are called alkalis.
Examples: KOH, NaOH, Ca(OH)2
All the alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis.
Examples: [Fe(OH)3] ferric hydroxide and cupric hydroxide [Cu(OH)2] are base, but not an alkali.
Chemical Properties of Bases
1. Reaction with Metals
Base reacts with active metals and produce hydrogen gas.
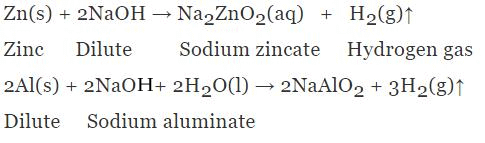
2. Reaction with Acids (Neutralization Reaction)
- Base reacts with acids to form salts and water.
Example: KOH + HCl → KCl + H2O
3. Reaction with Non-metallic Oxides
- Base reacts with non-metallic oxides to form salts and water.
- Base + Non metallic → salt + water
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
NaOH + CO2 → Na2CO3 + H2O
Mg(OH)2 + CO2 → MgCO3 + H2O
Classification of Bases
➢ Classification on the basis of their Strength
(a) Strong alkalis or bases
- The alkalis or bases which undergo almost complete ionisation in aqueous solution are known as strong alkalis or bases.
Example: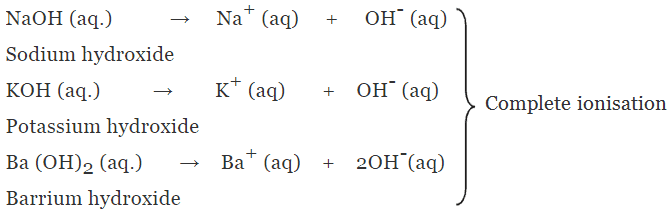
(b) Weak alkalis or bases
- The alkalis or bases which undergo only partial ionisation in aqueous solution are known as weak alkalis or Bases.
Example: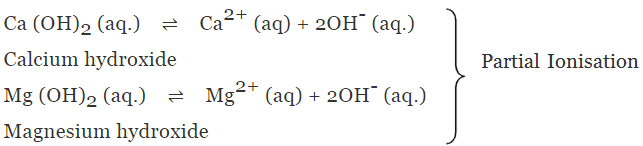
➢ Classification on the basis of their Concentration
(a) Concentrated Base or Alkali
- The bases or alkalis which contain a very small amount of water is called concentrated bases or alkalis.
(b) Dilute Base
- The bases or alkali which contain more amount of water is called a dilute bases or alkalis
- The acidity of a base is determined by the number of hydroxyl (OH-) ions produced per molecule of a Base or Alkali on complete dissociation in water.
- The "number of hydrogen ions of an acid with which a molecule of that alkali or base react to produce salt and water is known as the acidity of an alkali or Base".
(a) Mono Acidic Bases or Alkali
- The base or alkali on complete ionisation produces one hydroxyl (OH_) ion per molecule of the base in an aqueous solution.
Example:
NaOH (aq.) → Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq)Hydroxyl ion
KOH(aq.) → K+ (aq) + OH- (aq)Hydroxyl ion
(b) Diacidic Bases (or alkalis)
- The base or alkali on complete ionization produces two hydroxyl ion (OH-) per molecule of the base in an aqueous solution.
Example:
(i) Diacidic Bases
Ca(OH)2(aq.) → Ca2+(aq.) + 2OH-(aq.)
Mg(OH)2(aq.) → Mg2+(aq.) + 2OH-(aq.)
(ii) Ferrous hydroxide [Fe(OH)2] and copper hydroxide [Cu(OH)2]
Fe(OH)2(aq.) → Fe2+ + 2OH-(aq.)
Fe+2(OH)2- + 2H+Cl-(aq.) → FeCl2 + 2H2O
(c) Tri Acidic Bases
- The base or alkali on complete ionization produces three hydroxyl ion (OH)- per molecule of the base in aqueous solution.
Example: Aluminium hydroxide [Al(OH)3], Ferric hydroxide [Fe(OH)3]
Al(OH)3(aq.) → Al3+(aq.) + 3OH-(aq.)
Al3+(OH)3- + 3HCl(aq.) → AlCl3 + 3H2O
Table: Uses of Bases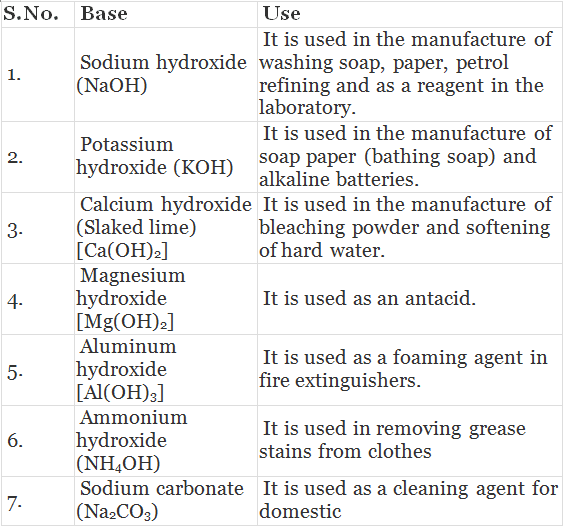
Table: Comparison Between Properties of Acids & Bases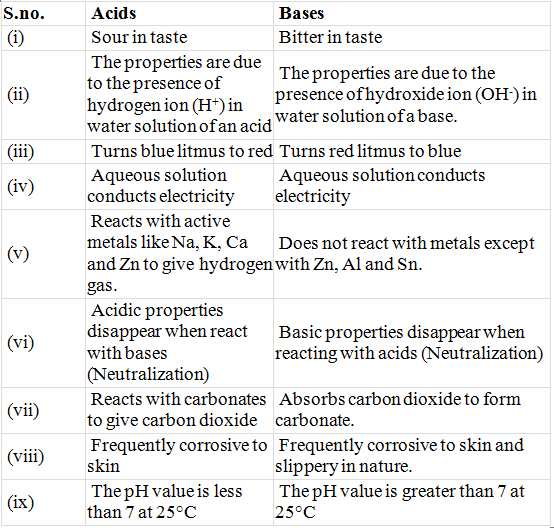

Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. What types of ions are formed:
(a) When an acid is dissolved in water.
(b) When a base is dissolved in water?
When an acid is dissolved in water, it forms hydrogen or H+ ions whereas when a base is dissolved in water, it forms hydroxide or OH- ions.
Q 2. Name the acid along with its chemical formula present in ant sting.
The acid present in ant sting is methanoic acid (formic acid). The chemical formula is HCOOH.
Explanation: When an ant stings, it leaves formic acid (Methanoic acid) which causes pain and irritation. To get relief from the sting, a mild base like baking soda on the stung area gives relief.
|
365 videos|700 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Acids & Bases - 1 - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What are acids? |  |
| 2. How do acids and bases differ? |  |
| 3. What are bases? |  |
| 4. How do bases and alkalis relate to each other? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between bases and alkalis? |  |
















