Tracing Evolutionary Relationships, Fossils & Evolution | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
Fossils
1. Fossils: Fossil is an organic relic of a long dead life form.
Or
Fossils are the petrified remains and for impressions of the hard parts of the extinct organism preserved in the sedimentary rock or other media.
Palaeontology: Study of fossils is known as palaeontology.
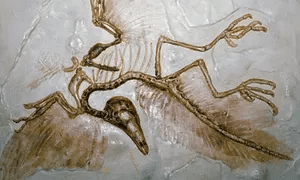 Fossil of Archaeopteryx
Fossil of Archaeopteryx

How do fossils form layer by layer?

Let us start 100 million years ago. Some invertebrates on the seabed die, and are buried in the sand. More sand accumulates, and sandstone forms under pressure.
Millions of years later, dinosaurs living in the area die, and their bodies too were buried in mud. This mud is also compressed into rock, above the rock containing the earlier invertebrate fossils.


Again millions of years later, the bodies of horse-like creatures dying in the area are fossilized in rocks above these earlier rocks.

Much later, erosion by, sun, water flow, wears away some of the rocks and exposes the horse-like fossils. As we dig deeper, we will find older and older fossils.

Living fossils : The animals which underwent little changes during long geological periods.
IMPORTANT LIVING FOSSILS
1. Peripatus, Limulus (Arthropoda)
2. Nautilus, Neopilina (Mollusca)
3. Lingula (Brachiopoda)
4. Latimeria (Coelacanth fish)
5. Spenodon (Reptilia)
Determination of the age of fossil: There are three ways of determining age of the fossils.
1. Relative method: If we dig into the earth and starts finding fossils it is reasonable to suppose that the fossils we find closer to the surface are more recent than the fossils we find in deeper layer.
2. Using Radioactive Elements: The age of a fossil is determined with the help of certain radioactive elements such as uranium present in the rock.
3. Carbon dating: Carbon dioxide of air contains a small proportion of radioactive carbon (C14). CO2 is used during photosynthesis and there is equal proportion of C14 among carbon atoms of all organisms.
The radioactivity of C14 is lost at a precise rate. Half life of C14 is about 5,600 years.
If a fossil shows radioactivity one fourth of that found in the living organisms the organisms died about 11,200 years ago. (Two half lives.)
Evolution by Stages
Evolutionary changes are fundamental characteristics of living organisms. Such changes may be convergent, it means that the similar looking structures may have different ancestral designs. This can be explained by example of eye.
Eye: Eyes of insects, octopus and vertebrates have similar looks but different structures and must have separate evolutionary origin or different ancestral designs.
Rudimentary eye can be useful to some extent.


Feathers: The function of feathers was insulation in cold weather later this feature might have proved to be useful for the purpose of flight.
Dinosaurs is an example depicting presence of feathers in them but these were not used for flying. Later birds seem to have adaptation of flying using feathers. This shows close relationship of birds to reptiles and proves that characters appearing as a variation can be useful later to perform different functions.
Cabbage: Humans have developed different types of vegetables from the wild cabbage by artificial selection.
| S.No. | Vegetable evolved | Edible part |
| 1. | Cabbage | Selection for fleshy terminal buds and short distance between the leaves. |
| 2. | Brussels sprouts | Selection for fleshy lateral buds. |
| 3. | Kohl rabi | Selection for fleshy stem. |
| 4. | Kale | Selection for large sized leaves so it is a leafy vegetable. |
| 5. | Broccoli | Selection for leafy sized and arrested flower development. |
| 6. | Cauliflower | Selection for fleshy sterile flower. |

More to Know
Molecular Phylogeny
Ancestors of different organism including humans can be traced by studying the change in their DNA.
A change in DNA means a change in its protein sequences. The ancestry or phylogeny determined by comparative study of DNA sequences is called molecular phylogeny.
Studies in molecular phylogeny help in the classification of organisms.
Haeckel propounded 'The theory of recapitulation or 'Biogenetic law',which states that an individual organism in its development (ontogeny) tends to repeat the stages passed through by its ancestors (phylogeny means ontogeny repeats phylogeny.
Evolution should not be Equated with Progress
Though organic evolution involves descent with modification in which there is a progressive trend of emergence of more or more complex body designs from earlier similar body designs by gradual changes but evolution should not be equated with progress because of following reasons:
1. In evolution older species are not eliminated during formation of new species and most of older and simple species still survive.
eg : Earliest organisms like bacteria are found even in many hospitable habitats like hot springs, deep-sea, thermal vents, Antarctic ice. etc.
2. The evolved species are not always better than the parental species. Evolution depends upon natural selection and genetic drift which is together resulting in population which is reproductively isolated from the parental species.
Human Evolution
Evolutionary history of man has been built from the palaeontology (fossil studies) and molecular biology (especially DNA changes).
Example: It is not true that human beings have evolved from chimpanzees. Rather both human beings and chimpanzees have common ancestors a long time ago. That common ancestors is likely to have been neither human or chimpanzee. The two resultant species have probably evolved in their separate ways to give rise to the current forms.
Anthropology: The scientific study of tracing the human evolution is called anthropology. Scientists involved in studying human evolution are called anthropologists.
Studies have revealed that human evolution started in Africa and earliest human type was Austalopithecus Africans. African ape man fossil was discovered by Prof. Raymond Dart. (Fossil of skull of 5-6 years old baby from old Pliocene rock of Tuang region (S.Africa)). He named it Tuang baby. It had many ape like characters but had a bipedal locomotion like man. The cradle of human evolution is East Africa where genetic foot prints of earliest members of human species Homosapiens can be traced. A couple of hundred thousand years ago, some of own ancestors left across the planet from Africa.

The first human types evolved into modern man, Homosapiens through a number of intermediate human types.

Homo erectus erectus → Jawa man

Homo erectus pekinesis → Peking man

Homo sapiens neaderthalensis → Neanderthal man

Homo sapiens fossils → Cro-magnon man
In the course of their evolution, these migrant human types went forward and backwards and moved in and out of South Africa. Modern man evolved from Cro-Magnon man about 25000 years ago and spread all over the world about 10,000 years.
Modern man is divided into four ethnic groups:
Negroid: African Pygmies and bushman
Caucasian: Italian English
Eastern: Chinese Japanese Eskimos
Mangolid: These ethnic group differ from one another in their skin colouration, lips and hair pattern but all of these belong to same species because these are not reproductively isolated from one another. All human races have same chromosomes number and similar grass morphology of chromosomes.

Man of future:
Homo sapiens futuralis.
(A prediction by American anthropologist Dr. Sapiro.)
|
110 videos|93 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Tracing Evolutionary Relationships, Fossils & Evolution - Biology for Grade 10
| 1. What are fossils and how do they provide evidence for evolution? |  |
| 2. How do scientists trace evolutionary relationships using fossils? |  |
| 3. Why should evolution not be equated with progress? |  |
| 4. What does the term "evolution by stages" mean? |  |
| 5. How do fossils contribute to our understanding of evolution? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Grade 10 exam
|

|













