Characteristics & Classification of Solids | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Solid? |

|
| Types of Solids: |

|
| Classification of Crystalline SolidsMolecular Solids |

|
| Ionic Solids |

|
| Metallic Solids: |

|
| Covalent Solids or Networked Solids |

|
What is a Solid?
A matter is said to be solid when its constituent particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) are closely packed.
 Solid State
Solid State
A solid is also defined as that form of matter which possesses rigidity and hence possesses a definite shape and a definite volume. Unlike gases and liquids, whose fluidity is determined by the relative free motion of their molecules, in solids, on the contrary, molecules or atoms or ions are not free to move but can oscillate around their fixed positions due to strong intermolecular or inter-atomic, or inter-ionic forces. This confers rigidity and long-range order in solids.
We shall find that the explanation of these macroscopic properties in terms of the atomic theory involves the idea of lattice: a permanent ordered arrangement of atoms held together by forces of considerable magnitude.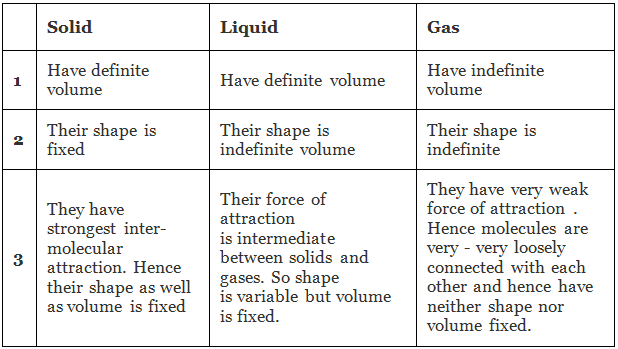 Differentiation between Solid, Liquid and Gas
Differentiation between Solid, Liquid and Gas
Thus the extremes of molecular behaviour occur in gases and solids. In the former, we have molecular chaos and vanishing inter-molecular forces, and in the latter, we have an ordered arrangement in which the interatomic forces are large.
Types of Solids:
a) Crystalline solids: In a single crystal the regularity of arrangement of the pattern extends throughout the solid and all points are completely equivalent.b) Amorphous solids: An amorphous solid differs from a crystalline substance in being without any shape of its own and has completely random particle arrangement, i.e. no regular arrangement.
Example: Glass, Plastic
 Types of Solids
Types of Solids
Distinction Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solids

Classification of Crystalline Solids
Molecular Solids

Classification of Crystalline Solids
Those solids which consists of small molecules are called molecular solids.
Non - polar molecular solids:
electronegativity sequence
(F > O > N ≈ Cl > Br > S > C-H)
The solids which have zero dipole moment are called non-polar molecular solids. The molecules are held together by weak Van Der Waals forces . Hence they are either gas or liquids at room temperature.
They are poor conductor of electricity due to their non-polar nature.Polar molecular solids:
Those solids which have non-zero dipole moments are called polar molecular solids.
Polar molecular solids have dipole - dipole interaction, which is slightly stronger than Van Der Waals force and hence they have larger melting and boiling points than the non - polar molecular solids.
Example: Solid CO2 , Solid NH3
They are generally liquids or gases at room temperature.Hydrogen bonded molecular solids:
Those molecular solids which are bonded with each other by hydrogen bonds are called hydrogen bonded molecular solids.
Example: Ice
They are non-conductor of electricity.
Generally they are liquid at room temperature or soft solids.
Ionic Solids
All those solids whose constituent particles are ions are called ionic solids,
Example: NaCl, CsBr, AgBr, CsCl
Metallic Solids:
- All those solids which are bonded by metallic bonds are called metallic solids.
- Inner core electrons are immobile.
- Metallic solids show a great electrical conductivity due to availability of large number of free electrons whose movements constitute electric current.
- Metallic solids are malleable and ductile.
- Metallic solids have luster.
- Metallic solids have good thermal conductivity.
What are metallic solids?
In these solids, the constituent particles in metallic solids are metal atoms which have valence electrons to be given/lost, therefore ending up being positively charged. The sea of electrons available is spread all through the crystal and can easily move about. The attractive force between positively charged ions and the sea of electrons is the cause for metallic bond formation. This is the force holding the metal ions together. Metallic solids have a regular structure with high melting and boiling points. Because of the sea of electrons, they have high thermal and metallic conductivity. All metals and alloys are metallic solids.Covalent Solids or Networked Solids
Whenever an electric field is applied, electrons move between the layers.
- Graphite is a good conductor of electricity due to the availability of free electrons.
- Networked solids are hard and brittle.
Carbon-Carbon bond has got partial double bond character in graphite.
- Two layers in graphite are attached to each other by weak Van Der Waals force.
- Graphite can be used as a lubricant at high temperatures.
Diamonds
The structure of diamond is shown at the right in a "ball-and-stick" format. The balls represent the carbon atoms and the sticks represent a covalent bond. Be aware that in the "ball-and-stick" representation the size of the balls does not accurately represent the size of carbon atoms. In addition, a single stick is drawn to represent a covalent bond irrespective of whether the bond is a single, double, or triple bond or requires resonance structures to represent. In the diamond structure, all bonds are single covalent bonds ( σ bonds). The "space-filling" format is an alternate representation that displays atoms as spheres with a radius equal to the van der Waals radius, thus providing a better sense of the size of the atoms.

Notice that diamond is a network solid. The entire solid is an "endless" repetition of carbon atoms bonded to each other by covalent bonds. (In the display at the right, the structure is truncated to fit in the display area.)
Graphite
The most stable form of carbon is graphite. Graphite consists of sheets of carbon atoms covalently bonded together. These sheets are then stacked to form graphite. The figure shows a ball-and-stick representation of graphite with sheets that extended "indefinitely" in the xy plane, but the structure has been truncated for display purposes. Graphite may also be regarded as a network solid, even though there is no bonding in the z-direction. Each layer, however, is an "endless" bonded network of carbon atoms.
 Rotating Graphite Structure.
Rotating Graphite Structure.
Fullerenes
Until the mid-1980s, pure carbon was thought to exist in two forms: graphite and diamond. The discovery of C6O molecules in interstellar dust in 1985 added a third form to this list. The existence of C6O, which resembles a soccer ball, had been hypothesized by theoreticians for many years. In the late 1980s, synthetic methods were developed for the synthesis of C6O, and the ready availability of this form of carbon led to extensive research into its properties.
 Examples of Fullerene: A Buckyball and an Extended Bucktube.
Examples of Fullerene: A Buckyball and an Extended Bucktube.
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on Characteristics & Classification of Solids - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is a solid? |  |
| 2. What are the types of solids? |  |
| 3. What are molecular solids? |  |
| 4. What are metallic solids? |  |
| 5. What are covalent or networked solids? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|













