Kohlrausch's Law | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Kohlrausch's Law of Independent Migration of Ions:
Kohlrausch determine ^0 values of pairs of some strong electrolytes containing same cation say KF and KCl, NaF and NaCl etc., and found that the difference in ^0 value in each case remains the same
^0m (KCl) - ^0m (KF) = ^0m (NaCl) - ^0m (NaF)
He also determined ^0 values of pairs of strong electrolytes containing same anion say KF and NaF, KCl and NaCl etc. and found that the difference in ^0 values is each case remains the same.
^0m (KF) - ^0m (NaF) = ^0m (KCl) - ^0m (NaCl)
This experimental data led him to formulate the following law called Kohlrausch's law of independent migration of ions.
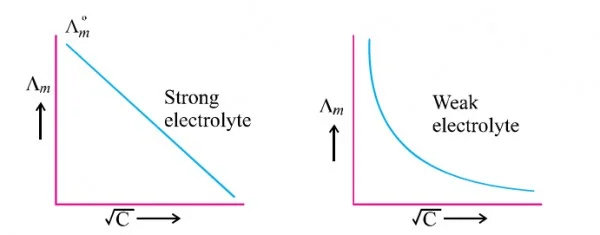 Variation with Strong and Weak electrolytes
Variation with Strong and Weak electrolytes
At infinite dilution when dissociation is complete, every ion makes some definite contribution towards molar conductance of the electrolyte irrespective of the nature of the other ion which with it is associated and that the molar conductance at infinite dilution for any electrolyte is given by the sum of the contribution of the two ions. Thus,
^0m =λ+o + λ-o
Where λ0 is the contribution of the cation is the contribution of the anion towards the molar conductance at infinite dilution. These contributions are called molar ionic conductances at infinite dilution. Thus, λ0 is the molar ionic conductance of cation and λ-o is the molar ionic conductance of anion, at infinite dilution. The above equation is, however, correct only for binary electrolyte like NaCl, MgSO4 etc.
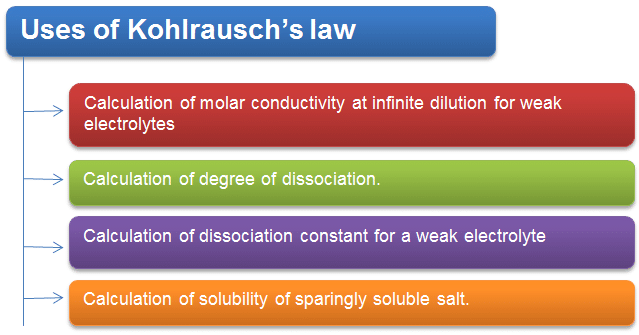
Application of Kohlrausch's law:
(1) Determination of ^0m of a weak electrolyte: In order to calculate ^0m of a weak electrolyte say CH3COOH, we determine experimentally ^0m values of the following three strong electrolytes:
(a) A strong electrolyte containing same cation as in the test electrolyte, say HCl
(b) A strong electrolyte containing same anion as in the test electrolyte, say CH3COONa
(c) A strong electrolyte containing same anion of (a) and cation of (b) i.e. NaCl.
^0m of CH3COOH is the given as:
^0m (CH3COOH) = ^0m (HCl) + ^0m (CH3COONa) - ^0m (NaCl)
Proof :
^0m (HCl) =  +
+  ..................(i)
..................(i)
^0m (CH3COONa) =  +
+  ..................(ii)
..................(ii)
^0m (NaCl) =  +
+  ..................(iii)
..................(iii)
Adding equation (i) and equation (ii) and subtracting (iii) from them:
^0m (HCl) + 
(2) Determination of degree of dissociation (α) :
α = 
(3) Determination of solubility of sparingly soluble salt:
The specific conductivity of a saturated solution of the est electrolyte (sparingly soluble) made in conductivity water is determined by the method as described above. From this the specific conductivity of conductivity water is deducted.
The molar conductance of the saturated solution is taken to be equal to ^0m as the saturated solution of a sparingly soluble salt is extremely dilute. Hence from equation (4).
^0m = 
Where C is the molarity of solution and hence the solubility.
ATLAS


|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on Kohlrausch's Law - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is Kohlrausch's Law? |  |
| 2. How is Kohlrausch's Law applied in practice? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of Kohlrausch's Law in chemical analysis? |  |
| 4. How does temperature affect Kohlrausch's Law? |  |
| 5. Can Kohlrausch's Law be applied to non-aqueous solutions? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















