Pressure-Volume Work & Work Done Calculations | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
EXPRESSION FOR PRESSURE – VOLUME WORK
1. Work Done in Reversible Isothermal Expansion: Consider an ideal gas enclosed in a cylinder fitted with a weightless and frictionless piston. The cylinder is not insulated.
The external pressure, Pext, is equal to pressure of the gas, Pgas Let it be P.
Pext = Pgas = P
If the external pressure is decreased by an infinitesimal amount dP, the gas will expand by an infinitesimal volume, dV.
As a result of expansion, the pressure of the gas within the cylinder falls to Pgas - dP, i.e., it becomes again equal to the external pressure and, thus, the piston comes to rest.
Such a process is repeated for a number of times, i.e., in each step the gas expands by a volume dV.
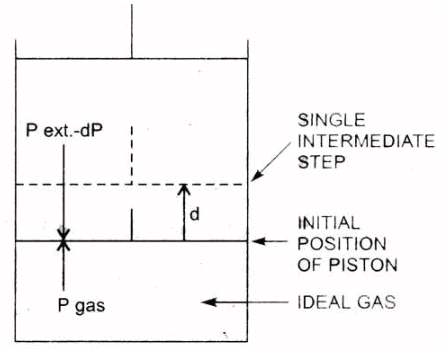
Isothernal reversible expansion work
Since, the system is in thermal equilibrium with the surroundings, the infinitesimally small cooling produced due to expansion is balanced by the absorption of heat from the surroundings and the temperature remains constant throughout the expansion.The work done by the gas in each step of expansion can be given as,
dw = -(Pext - dP)dV
= -Pext.dV
= -PdV
dP. dV, the product of two infinitesimal quantities, is neglected.
- The negative sign of this expression is required to obtain conventional sign for w, which will be positive. It indicates that in case of compression work is done on the system.
- Here (Vf – Vi ) will be negative and negative multiplied by negative will be positive. Hence the sign obtained for the work will be positive.
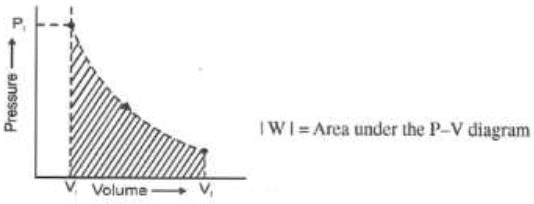
If the pressure is not constant at every stage of compression, but changes in number of finite steps, work done on the gas will be summed over all the steps and will be equal to -Σp∆V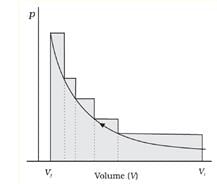 pV-plot when pressure is not constant and changes in finite steps during compression from initial volume, Vi to final volume, Vf . Work done on the gas is represented by the shaded area.
pV-plot when pressure is not constant and changes in finite steps during compression from initial volume, Vi to final volume, Vf . Work done on the gas is represented by the shaded area.
- The total amount of work done by the isothermal reversible expansion of the ideal· gas from volume V1 to volume V2 is, therefore
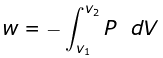
For an ideal gas, p = nRT/V
So,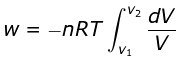
Integrating,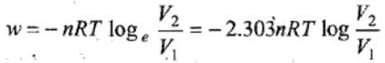
At constant temperature, according to Boyle's law,
P1V1 = P2V2
or V2/V1 = P1/P2
So,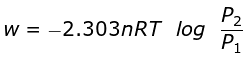
Isothermal compression work of an ideal gas may be derived similarly and it has exactly the same value with positive sign.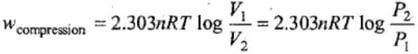
WORK DONE IN IRREVERSIBLE ISOTHERMAL EXPANSION
Two types of irreversible isothermal expansions are observed, i.e.,
(i) Free expansion and
(ii) Intermediate expansion.
- In free expansion, the external pressure is zero, i.e. , work done is zero when gas expands in vacuum.
- In intermediate expansion, the external pressure is less than gas pressure. So, the work done when volume changes from V1 to V2 is given by
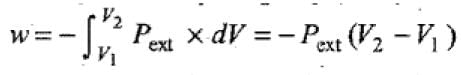 Since, Pext is less than the pressure of the gas, the work done during intermediate expansion is numerically less than the work done during reversible isothermal expansion in which Pext is almost equal to Pgas .
Since, Pext is less than the pressure of the gas, the work done during intermediate expansion is numerically less than the work done during reversible isothermal expansion in which Pext is almost equal to Pgas .
ISOTHERMAL AND FREE EXPANSION OF AN IDEAL GAS
For isothermal (T = constant) expansion of an ideal gas into vacuum ; w = 0 since pext = 0.
Also, Joule determined experimentally that q = 0; therefore, ∆U = 0
∆U = q + w can be expressed for isothermal irreversible and reversible changes as follows:
1. For isothermal irreversible change
q = – w = Pext (Vf – Vi )
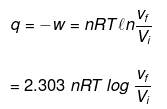
3. For adiabatic change, q = 0,
∆U = wad
REVERSIBLE ISOTHERMAL COMPRESSION OF AN IDEAL GAS
This can be achieved by placing particles of sand one by one at a very slow take in the assembly which keeps the temperature of gas constant in this case the expression of work done will be exactly similar to as obtained in case of reversible expansion of gas
W= -nRT ln (Vf /Vi)
This will automatically come out to be +ve as Vf < Vi
Example 1. 10 gm of Helium at 127°C is expanded isothermally from 100 atm to 1 atm Calculate the work done when the expansion is carried out
(i) In single step
(ii) In three steps the intermediate pressure being 60 and 30 atm respectively and
(iii) Reversibly.
Solution.
(i) Work done = V.ΔP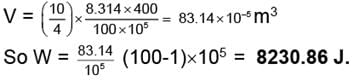
(ii) In three steps
VI = 83.14 × 10-5 m3
WI = (83.14 × 10-5) × (100 - 60) × 105
= 3325.6 Jules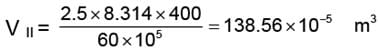
WII = V. DP
WII = 138.56 × 10-5 (60 - 30) × 105
= 4156.99 ≈ 4157 J.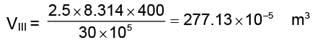
WIII = 277.13 × 10-5 (30 - 1) × 105
WIII = 8036.86 J.
W total = WI + WII + WIII
= 3325.6 + 4156.909 + 8036.86 = 15519.45 J.
(iii) For reversible process
Example 2. Calculate the amount of work done by 2 mole of an ideal gas at 298 K in reversible isothermal expansion from 10 litre to 20 litre.
Solution. Amount of work, done in reversible isothermal expansion,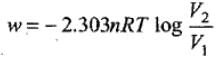
Given, n = 2, R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1, T = 298 K, V2 = 20 L and V1 = 10 L.
Substituting the values in above equation,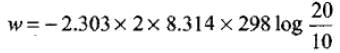
= -2.303 × 8.314 × 298 × 0.3010 = -3434.9 J
i.e., work is done by the system.
Example 3. 5 moles of an ideal gas expand isothermally and reversibly film a pressure of 10 atm to 2atm at 300K. What is the largest mass which can be lifted through a height of l metre in this expansion?
Solution. Work done by the system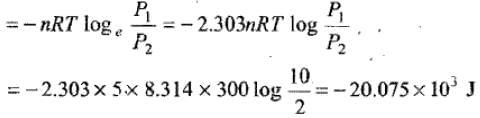
Let M be the mas which can be lifted through a height of 1 m.
Work done in lifting the mass = Mgh = M × 9.8 × 11
So, M × 9.8 = 20.075 × 103 M
= 2048.469 kg
WORKDONE CALCULATION
(1) Isochoric process:
V = constant 
dV = 0
| W = 0 |
dU = dqV
ΔU = qV = nCVΔT
| ΔH = nCpΔT |
(2) Isobaric process:
W = - Pext (V2-V1)
Reversible & isobaric process
W = - P (V2-V1)
= - nR (T2-T1)
Irreversible & isobaric process
P1 = P2 = Pext
For reversible & irreversible isobaric or isochoric process, workdone is same.
(3) Isothermal process.
(a) Reversible Expansion or compression
W = -P∫ dv
= -∫Pgas dV
In Expansion W = - ve
ΔE = 0
| q = -W |
(b) Single stage irreversible expansion
W = - Pext(V2 - V1)
|Wrev| > |Wirr| (in case of expansion)
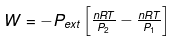
(c) Two Stage irreversible Expansion:
Stage I. Pext = 3 atm, Pi = 5 atm
Stage II. P"ext = 2 atm , Pf = 2 atm
Workdone in 2nd stage > Workdone in Ist stage
(d) n- stage expansion
Compression - (One stage Compression )
| Wirr | = Pext DV
P1 = 1 atm , P2 = 5 atm , Pext = 5 atm
| Wirr | > | Wrev | For compression
Example 1. 2 moles of an ideal gas initially present in a piston fitted cylinder at 300 K, and 10 atm are allowed to expand against 1 atm but the piston was stopped before it stablished the mechanical equilibrium. If temperature were maintained constant through out the change and system delivers 748.26 J of work, determine the final gas pressure and describe the process on PV diagram.
Solution.
Wirrv = - 748.26
Wirr = - Pext [1/P2- 1/P1]nRT
P2 = 4atm
Example 2. 1150 Kcal heat is released when following reaction is carried out at constant volume.
C7H16(l) 11O2(g) → 7CO2(g) 8H2O(l)
Find the heat change at constant pressure.
The pressure of liquid is a linear function of volume (P = a + bV) and the internal energy of the liquid is U = 34 + 3PV find a, b, w, ΔE & ΔH for change in state from 100 Pa, 3m3 to 400 Pa, 6m3
Solution. 100 = a + bV
⇒ 100 = a + 3b
Also, 400 = a + 6b
⇒ a = -200, b = 100
ΔU = 34 + 3(P2V2 - P1V1)
= 6300 J
ΔH = ΔU + P2V2 - P1V1
= 6300 + 2100 = 8400 J
P is a linear function
Pext = (400 + 100)/2 = 250
W = - Pext(dV)
= - 250(6 - 3) = - 750 J
Example 3. 4 moles of an ideal gas (Cv = 15 J) is subjected to the following process represented on P - T graph. From the given data find out whether the process is isochoric or not ? also calculate q, w, ΔU, ΔH,
Solution. PV = nRT
4V = 4R × 400
V = 400 R ........(1)
3V = 4R × 300
⇒ V = 400 R ........(2)
i.e., V is constant
w = 0
ΔU = nCV + ΔT ⇒ 4 ×15 ×100 = 6000 J
ΔH = nCP + ΔT ⇒ n (CV + R ) ΔT
⇒ 4 ×(15 8.3)×100
⇒ 9320 J
| q = ΔU = 6kj |
Example 4. 2 mole of a gas at 1 bar and 300 K are compressed at constant temperature by use of a constant pressure of 5 bar. How much work is done on the gas ?
Solution. 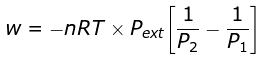
= 19953.6 J
Example 5. 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas (CV = 5/2 R) at 300 K, 5 atm expanded irreversibly and adiabatically to a final pressure of 2 atm against a constant pressure of 1 atm.
(1) Calculate final temperature q, w, ΔH & ΔU
(2) Calculate corresponding values if the above process is carried out reversibly.
Solution.
w = CV (T2 - T1)
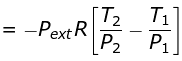
Given T2 = 270K
Pext = 1,P2 = 2,P1 = 5
q = 0
w = ΔU = nCVΔT
= -1247.1 J
ΔH = nCPΔT
= 1745.94 J
If process is reversible Pvγ = Constant
P1- γTγ = Constant
| T = 231 K |
ADIABATIC IDEAL GAS EXPANSION AND COMPRESSION
dq = 0
dU = dW
| Δ U = W |
| W = nCV ΔT = nCV T2 - T1) |
For an ideal gas CP - CV = R
REVERSIBLE ADIABATIC EXPANSION OR COMPRESSION
nCVdT = - Pext dV
Pint = dP = Pext
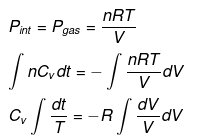
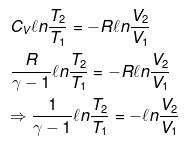
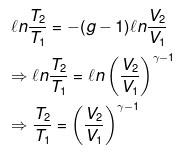
⇒ T2(V2)γ - 1 = V1γ - 1T1
TVγ - 1 = Constant
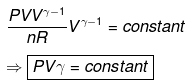
IRREVERSIBLE ADIABATIC EXPANSION OR COMPRESSION
dU = dW
⇒ nCV(T2 - T1) = - Pext dV
= - Pext [V2 - V1]
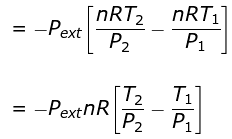
COMPARISON OF REVERSIBLE ISOTHERMAL AND REVERSIBLE ADIABATIC IDEAL GAS EXPANSION
(i) If final volumes are same
Isothermal process.
P1v1 = Piso V2
⇒
Adiabatic process.
P1v1γ = Padia V2γ
⇒ Piso > Padia |
(ii) If final pressures are same
Isothermal process.
P1V1 = P2 Viso
.......(1)
P1V1γ = P2Vγ adia
In ideal gas expansion,
| Wiso | > | Wadia |
Hence
⇒ Viso > Vadia |
Compression
(i) If final volumes are same
For isothermal process
P1V1 = PisoV2
..........(1)
Adiabatic process.
P1V1γ = PadiaV2γ
..........(2)
Padia > Piso |
(ii) If final pressures are same
P1V1 = P2 Viso ..........(1)
P1V1γ = P2 Vγ adia ..........(2)
⇒
⇒
⇒ Vadia > Viso |
|
117 videos|226 docs|237 tests
|
FAQs on Pressure-Volume Work & Work Done Calculations - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What is pressure-volume work? |  |
| 2. How is the work done calculated in pressure-volume work? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of pressure-volume work in everyday life? |  |
| 4. How does pressure affect the amount of work done in pressure-volume work? |  |
| 5. Can pressure-volume work be negative? |  |
















