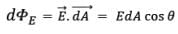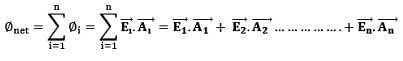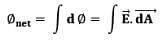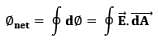Electric Flux and Electric Dipole | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Electric Flux? |

|
| Electric Dipole |

|
| Dipole in a Uniform External Field |

|
| Continuous Charge Distribution |

|
What is Electric Flux?
- Electric flux is a characteristic of an electric field, representing the number of field lines that pass through a specific area. These lines typically originate from positive charges and terminate at negative charges.
- When these lines enter a closed surface, they are seen as negative, whereas those exiting a closed surface are seen as positive.
 Electric Flux
Electric Flux
Analogy of Electric Flux with Flow of Water
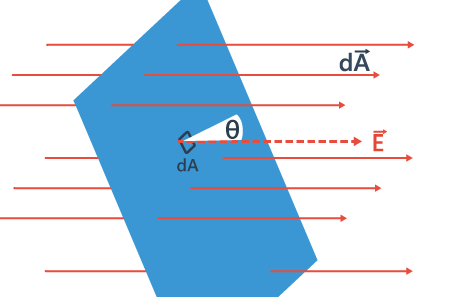
- Consider flow of a liquid with velocity v, through small flat surface dA, in a direction normal to the surface. The rate of flow of liquid is given by the volume crossing the area per unit time vdA and represents the flux of liquid flowing across the plane.
- If the normal to the surface is not parallel to the direction of flow of liquid, i.e., to v, but makes an angle θ with it, the projected area in a plane perpendicular to v is vdA cosθ. Therefore the flux going out of the surface d A is V. ñ dA.
- For the case of the electric field, we define an analogous quantity and call it electric flux.
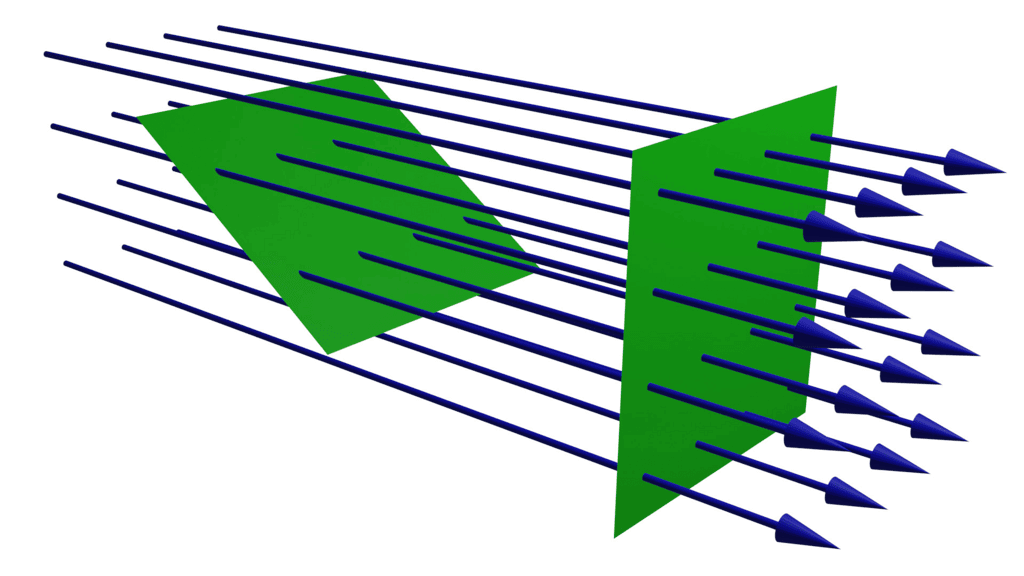
- We should however note that there is no flow of a physically observable quantity unlike the case of liquid flow. In the picture of electric field lines described above, we saw that the number of field lines crossing a unit area, placed normal to the field at a point is a measure of the strength of electric field at that point.
- This means that if we place a small planar element of area ΔA normal to E at a point, the number of field lines crossing it is proportional to E ΔA. Now suppose we tilt the area element by angle θ. Clearly, the number of field lines crossing the area element will be smaller. The projection of the area element normal to E is ΔA cos θ.
- Thus, the number of field lines crossing ΔA is proportional to E.ΔA.cosθ. When θ = 90° , field lines will be parallel to ΔA and will not cross it at all (Figure).
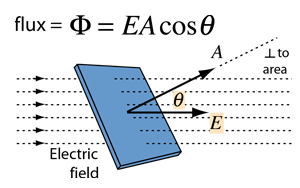
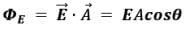
where E is the magnitude of the electric field (having units of V/m), A is the area of the surface, and θ is the angle between the electric field lines and the normal (perpendicular) to A.
Note: That that an area element should be treated as a vector. It has a magnitude and also a direction. How to specify the direction of a planar area? Clearly, the normal to the plane specifies the orientation of the plane. Thus, the direction of a planar area vector is along its normal.
But a normal can point in two directions. Which direction do we choose as the direction of the vector associated with the area element?
Conventionally, the vector associated with every area element of a closed surface is taken to be in the direction of the outward normal.
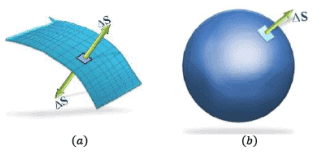
In above diagram, note that:
- Represents an open surface, thus, it is irrelevant to define ‘outward’ normal. You can choose any of the two normal at the surface.
- The surface in b is a closed one, it is important to define ‘ outward normal’ as the direction of area vector (as shown in the figure), conventionally.
- For infinitely small area element 𝑑𝐴

And if the Electric field holds different value on different points on the surface, then, we must add up the electric flux from all of them individually, - For finite number of surfaces (let’ s assume n),

- For infinite addition of infinitesimal surfaces i.e. integration,

- For closed surfaces,

Q1. An electric field of 500 V/m makes an angle of 30.00 with the surface vector. It has a magnitude of 0.500 m2. Find the electric flux that passes through the surface.
Ans. The electric flux which is passing through the surface is given by the equation as:
ΦE = E.A = EA cos θ
ΦE = (500 V/m) (0.500 m2) cos 30°
ΦE = 217 Vm
Note: That the unit of electric flux is a volt-times meter.
Q2. Consider a uniform electric field E = 3 × 103 î N/C. What is the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the yz plane?
(a) 30 Nm2/C
(b) 40 Nm2/C
(c) 50 Nm2/C
(d) 60 Nm2/C
Ans. (a)
Explanation: The flux of an electric field is given by,
ϕ = EA ⇒ ϕ = 3 × 103 × 0.1 × 0.1 ⇒ ϕ
= 30 Nm2/C
Therefore, the flux of the field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the yz plane is 30 Nm2/C
Electric Dipole
When two charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign are separated by a very small distance, then the arrangement is called electric dipole.
Total charge of the dipole is zero but electric field of the dipole is not zero as charges q and -q are separated by some distance and electric field due TO them when added is not zero.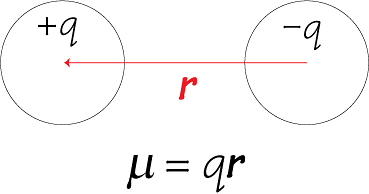
We define a quantity called Dipole Moment 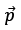 for such a system such that:
for such a system such that: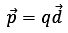
where 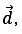 conventionally, represents the direction from –q to +q.
conventionally, represents the direction from –q to +q.
Axis of a dipole is the line joining –q to +q
- Midpoint of the axis of the dipole is called the centre of the dipole.
- All the distances in the space are measured from the centre of the dipole.
- Perpendicular bisector of the axis of the dipole is called the equatorial line of the dipole.
Q3. Why are we defining a dipole? Why can’t we treat it as simply two charge system? Why are we giving it special treatment?
Ans. Dipole is commonly occurring system in nature. We need to generalize our results in context with the dipole system to avoid repeated single point charge calculations using Coulomb’s Law. After these results we would be able to directly apply simplified results derived here to dipole systems.
The field of an Electric Dipole
1. At a point on Equatorial Plane
We now find the magnitude and direction of electric field due to dipole.
- P point in the equatorial plane of the dipole at a distance r from the centre of the dipole. Then electric field due to -q and +q are
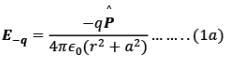
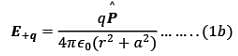
and they are equal in magnitude. Note that 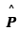 is the unit vector along the dipole axis (from -q to + q)
is the unit vector along the dipole axis (from -q to + q)
- From figure we can see the direction of

Their components normal (perpendicular) to dipole cancel away and components along the dipole add up. - Dipole moment vector points from negative charge to positive charge so in vector form.
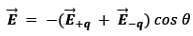
Substituting the values of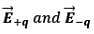 calculated above also, by geometry,
calculated above also, by geometry,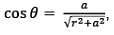
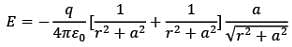
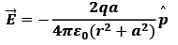
Now, very frequently we measure electric field at large distances from the dipole ie. r>>a
Therefore, by approximation,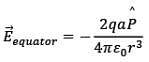
We know that, by definition,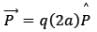
Hence,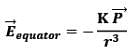
Observe, the - sign, it represents that electric field at the equator is in the opposite direction to the dipole moment of the electric dipole i.e. +q to –q.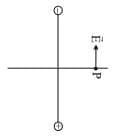 2. At a Point on the Axial Line
2. At a Point on the Axial Line
- Let P be the point at a distance r from the centre of the dipole on side of charge +q as shown in the figure
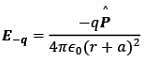
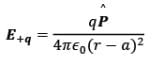
Where 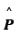 is the unit vector along the dipole axis (from -q to + q)
is the unit vector along the dipole axis (from -q to + q)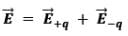
Thus,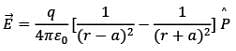
or
for r >> a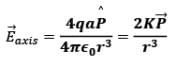
As we know that, by definition of dipole moment,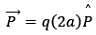
- Unit of dipole moment is Coulomb meter (Cm).
- Thus, in a nutshell, in terms of electric dipole moment, electric field due to a dipole at large distances (r >> a)
(i) At point on equatorial plane ( r >> a)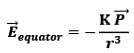
(ii) At point on dipole axis (r>>a)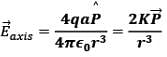
Note: Dipole field at large distances falls off as 1/r3.
Now, we can generalize the calculation of electric field at any general point in space due to the dipole using the above results.
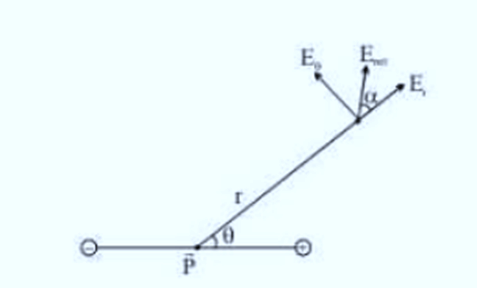
Any general point in space, can be located using the polar coordinates r and 𝜃, where the origin can be placed at the center of the dipole, as shown in the above figure.
Now, for any general point P in space located at distance r from centre and inclined at an angle 𝜃 with the axis of the dipole, we can imagine components of the original dipole with dipole moment  such that the P lies on the equator of one component and on the axis of the other component.
such that the P lies on the equator of one component and on the axis of the other component.
Now, Lets express our dipole moment 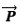 as,
as,
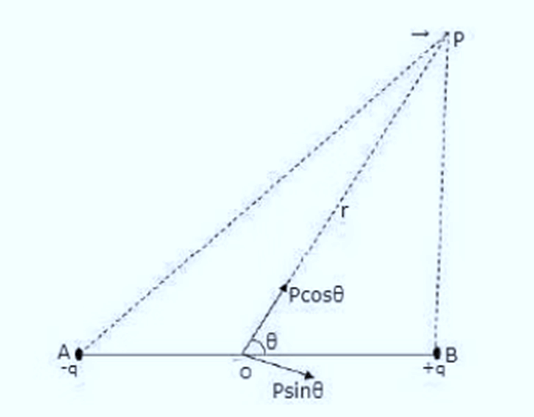
Where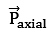 is the component of the original dipole moment, such that point P is located on the axis of this dipole, i.e.
is the component of the original dipole moment, such that point P is located on the axis of this dipole, i.e.
Now, at P,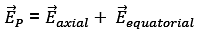
We know that,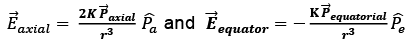
Thus,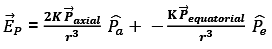
Therefore,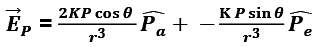
One of the component will be along the axial component of electric dipole i.e.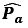 and the other component will be along the equatorial component of electric dipole i.e.
and the other component will be along the equatorial component of electric dipole i.e. 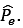
Physical Significance of Dipoles
In most molecules, the centers of positive charges and of negative charges lie at the same place, hence their dipole moment is zero, e.g., CH4. However, they develop a dipole moment when an electric field is applied. But some molecules have permanent dipole moment, e.g., H2O, which are called polar molecules. If the center of mass of positive charges coincides with the center of mass of negative charges, the molecule behaves as a non-polar molecule.
Electric Field Intensity Due To A Dipole
The electric field due to a pair of equal and opposite charges at any test point can be calculated using the Coulomb’s law and the superposition principle. Let the test point P be at a distance r from the center of the dipole. The distance between +q and -q is d.
We have shown the situation in the diagram below.If
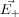 and
and  be the electric field at point P due to the positive and the negative charges separately then the total electric field
be the electric field at point P due to the positive and the negative charges separately then the total electric field  at Point P can be calculated by using the superposition principle.
at Point P can be calculated by using the superposition principle.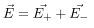
Please note that the directions of 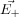 and
and  are along
are along  and
and  respectively. This is the most general form of the electric field due to a dipole. However, we will express this vector in terms of radial and inclination vectors as shown in the diagram below.
respectively. This is the most general form of the electric field due to a dipole. However, we will express this vector in terms of radial and inclination vectors as shown in the diagram below.In order to calculate the electric field in the polar coordinate, we will use the expression of the electric potential due to an electric dipole which we have calculated earlier.
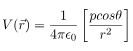
Here p is the magnitude of the dipole moment and is given by qd
We can easily derive the electric field due to this dipole by calculating the negative gradient of this electric potential. In polar coordinate electric field will be independent of azimuthal (ϕ) coordinate.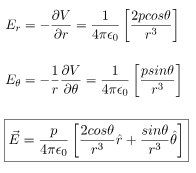
The resultant electric field at point P is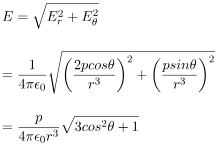
As shown in the diagram, the resultant electric field makes an angle \alpha with the radial vector. Then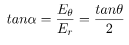
Electric Field Intensity At Any Point On The Axis Of Uniformly Charged Ring
The electric field intensity at any point Q on the axis is given by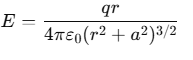
where, q= total charge, a= radius of the ring and r= distance of the point Q from the centre of the ring.
Note - The direction of E is along QX, the axis of the loop.
Dipole in a Uniform External Field
Torque on an Electric Dipole in a Uniform Electric Field
Consider an electric dipole consisting of two charges −q and +q placed in a uniform external electric field of intensity E.
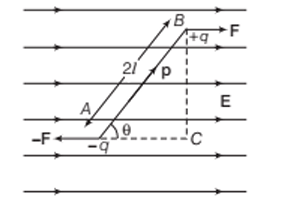
The length of the electric dipole is 2l. The dipole moment p makes an angle θ with the direction of the electric field. Two forces F and −F, which are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, act on the dipole.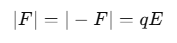
The net force is zero. Since the two forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction and act at different points, they constitute a couple. A net torque τ acts on the dipole about an axis passing through the mid-point of the dipole.

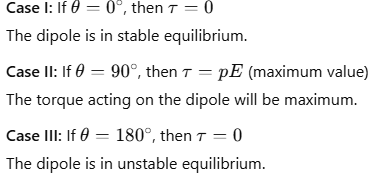
Work Done on a Dipole in a Uniform Electric Field
When an electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field, it experiences a torque that makes it tend to align with the field to reach a stable equilibrium. The small amount of work required to rotate the dipole by a tiny angle dθ against this torque is expressed as: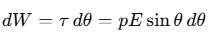
Thus, the total work done in rotating the dipole from an initial angle θ1 to a final angle θ2 is:
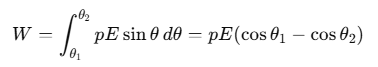
Therefore, the potential energy U of the dipole, when it rotates from θ1 to θ2, is given by: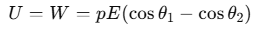
If we assume that the dipole initially starts perpendicular to the electric field direction and is then rotated to an θ with respect to the field direction, the work done in rotating the dipole from θ1=90∘ to θ2=θ becomes:
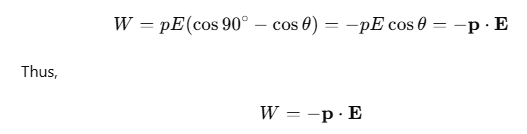
 |
Download the notes
Electric Flux and Electric Dipole
|
Download as PDF |
Continuous Charge Distribution
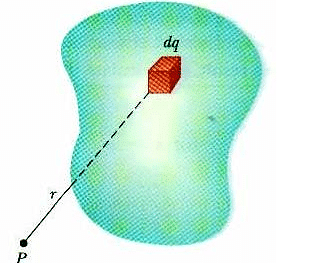
With the help of Coulomb’s Law and Superposition Principle, we can easily find out the electric field due to the system of charges or discrete system of charges. The word discrete means every charge is different and has the existence of its own. Suppose, a system of charges having charges as q1, q2, q3……. up to qn. We can easily find out the net charge by adding charges algebraically and net electric field by using the principle of superposition.
This is because:
- Discrete system of charges is easier to solve
- Discrete system of charges do not involve calculus in calculations

Fig: A system in which charge is distributed over a conductor, is called continuous charge distribution system
But how to calculate electrostatics terms in continuous charge system? For an Example if there is a rod with charge q, uniformly distributed over it and we wish to find the electric field at some distance ‘r’ due it. It would be illogical and irrelevant to simply add electric field using principle of superposition as the charge is uniformly distributed over the rod. So we take a small element of the rod and integrate it with proper limits.
We consider element, based on how density of charge is centered on the material or object. If the charge is uniformly distributed over the surface of the conductor, then it is called Surface Density. If the charge varies linearly along the length of the conductor, then it is called Linear Charge Density. And if the charge changes with volume of the conductor, then it is called Volume Charge Density.
What is Continuous Charge Distribution?
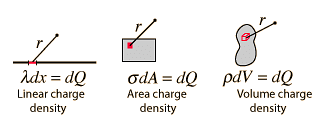
Fig: Types of Charge Distribution
The continuous charge distribution system is a system in which the charge is uniformly distributed over the conductor. In continuous charge system, infinite numbers of charges are closely packed and have minor space between them. Unlikely from the discrete charge system, the continuous charge distribution is uninterrupted and continuous in the conductor. There are three types of the continuous charge distribution system.
- Linear Charge Distribution
- Surface Charge Distribution
- Volume Charge Distribution

Fig: Types of charge distribution system
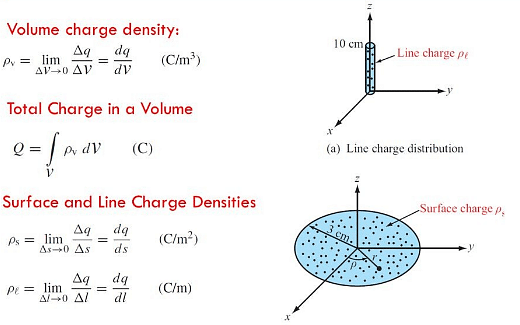
Linear Charge Density
When the charge is non-uniformly distributed over the length of a conductor, it is called linear charge distribution.
It is also called linear charge density and is denoted by the symbol λ (Lambda).
Mathematically linear charge density is λ = dq/dl
The unit of linear charge density is C/m. If we consider a conductor of length ‘L’ with surface charge density λ and take an element dl on it, then small charge on it will be
dq = λl
So, the electric field on small charge element dq will be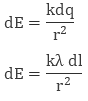
To calculate the net electric field we will integrate both sides with proper limit, that is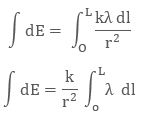
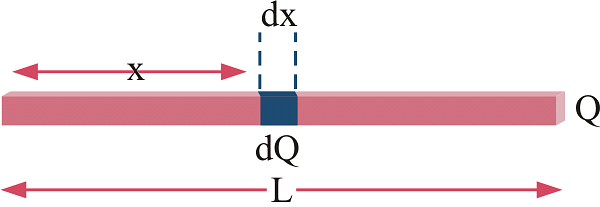
Fig: We take small element x and integrate it in case of linear charge density
Surface Charge Density
When the charge is uniformly distributed over the surface of the conductor, it is called Surface Charge Density or Surface Charge Distribution.
It is denoted by the symbol σ (sigma) symbol and is the unit is C/m2.
It is also defined as charge/ per unit area. Mathematically surface charge density is σ = dq/ds
where dq is the small charge element over the small surface ds. So, the small charge on the conductor will be dq = σds
The electric field due to small charge at some distance ‘r’ can be evaluated as 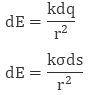
Integrating both sides with proper limits we get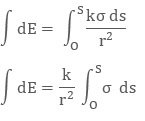
Volume Charge Density
When the charge is distributed over a volume of the conductor, it is called Volume Charge Distribution.
It is denoted by symbol ρ (rho). In other words charge per unit volume is called Volume Charge Density and its unit is C/m3. Mathematically, volume charge density is ρ = dq/dv
where dq is small charge element located in small volume dv. To find total charge we will integrate dq with proper limits. The electric field due to dq will be
dq = ρ dv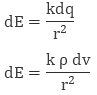
Integrating both sides with proper limits we get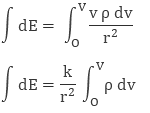
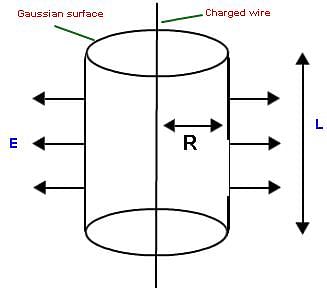
Fig: Electric field in different geometries using charge distribution system
Question for Electric Flux and Electric DipoleTry yourself:What is the term used to describe a system in which the charge is uniformly distributed over a conductor?View Solution
|
98 videos|334 docs|102 tests
|
FAQs on Electric Flux and Electric Dipole - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is electric flux and how is it calculated? |  |
| 2. What is an electric dipole and its significance in electromagnetism? |  |
| 3. How does a dipole behave in a uniform external electric field? |  |
| 4. What is a continuous charge distribution and how does it affect electric flux? |  |
| 5. How does electric flux relate to Gauss's Law? |  |