Inductance | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
What is Inductance?
- Inductance is like a resistance to changes in electric current in a wire. We measure it in Henrys, where 1 Henry means it takes 1 volt to make a change in current of 1 Ampere per second.
- When electricity moves through a wire, it makes a magnetic field. If the current changes, this field changes too, which creates a kind of electric push-back. This push-back is what we call inductance. We use a component called an inductor to add inductance to a circuit.
 An Inductor
An Inductor
- Inductance is classified into two types as:
- Self Inductance
- Mutual Inductance
Self induction
- Self induction is induction of emf in a coil due to its own current change. Total flux N
 passing through a coil due to its own current is proportional to the current and is given as N
passing through a coil due to its own current is proportional to the current and is given as N  = L i where L is called coefficient of self induction or inductance.
= L i where L is called coefficient of self induction or inductance. - The inductance L is purely a geometrical property i.e., we can tell the inductance value even if a coil is not connected in a circuit. Inductance depends on the shape and size of the loop and the number of turns it has.
If current in the coil changes by ΔI in a time interval Δt, the average emf induced in the coil is given as
ε =  =
= 
The instantaneous emf is given as
ε = - = -
= - 
S.I unit of inductance is wb/amp or Henry (H)
L - self inductance is +ve Quantity.
L depends on :
(1) Geometry of loop
(2) Medium in which it is kept.
L does not depend upon current. L is a scalar Quantity.
Self Inductance of solenoid
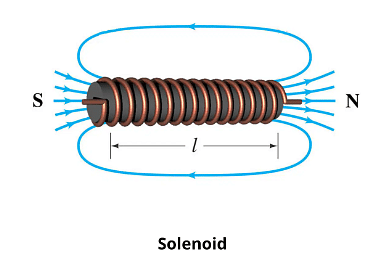 Let the volume of the solenoid be V, the number of turns per unit length be n. Let a current I be flowing in the solenoid. Magnetic field in the solenoid is given as B = μ0 nl. The magnetic flux through one turn of solenoid f = μ0 n l A.
Let the volume of the solenoid be V, the number of turns per unit length be n. Let a current I be flowing in the solenoid. Magnetic field in the solenoid is given as B = μ0 nl. The magnetic flux through one turn of solenoid f = μ0 n l A.
The total magnetic flux through the solenoid = N 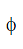
= N μ0 n l A
= μ0 n2 l A l
Therefore, L = μ0 n2 l A = μ0 n2 V
Ф= μ0 n i pr2 (n l)
L = Ф/i = μ0 n2 πr2 l
Inductance per unit volume = μ0 n2
Ex. The current in a coil of self-inductance L = 2H is increasing according to the law i = 2 sin t2. Find the amount of energy spent during the period when the current changes from 0 to 2 ampere.
Sol. Let the current be 2 amp at t = τ
Then 2 = 2 sin τ2 ⇒ τ = 
When the instantaneous current is i, the self induced emf is L 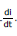 . If the amount of charge that is displaced in time dt is dθ, then the elementary work done
. If the amount of charge that is displaced in time dt is dθ, then the elementary work done
= 
W =  =
= 
W =  =
= 
Let θ = 2t2
Differentiating dθ = 4t dt
Therefore, W = 
= L (- cosθ) = - L cos 2t2
W = 
= 2 L = 2 × 2 = 4 joule
Inductor
It is represented by

electrical equivalence of loop
 ⇒
⇒ 

If current i through the inductor is increasing the induced emf will oppose the increase in current and hence will be opposite to the current. If current i through the inductor is decreasing the induced emf will oppose the decrease in current and hence will be in the direction of the current.

Over all result

VA - L  = VB
= VB
Note
 If there is a resistance in the inductor (resistance of the coil of inductor) then :
If there is a resistance in the inductor (resistance of the coil of inductor) then :


Ex. A B is a part of circuit. Find the potential difference vA - vB if

(i) current i = 2A and is constant
(ii) current i = 2A and is increasing at the rate of 1 amp/sec.
(iii) current i = 2A and is decreasing at the rate 1 amp/sec.
Sol. 
 =
= 
writing KVL from A to B
VA - 1 - 5 - 2 i = VB
- 5 - 2 i = VB
(i) Put i = 2,  = 0
= 0
VA - 5 - 4 = VB Therefore, VA - VB = 9 volt
(ii) Put i = 2,  = 1 ;
= 1 ;
VA - 1 - 5 - 4 = VB or VA - VB = 10 V0
(iii) Put i = 2,  = - 1
= - 1
VA + 1 - 5 - 2 × 2 = VB
VA = 8 volt
Ex. Find current i, i1 and i2 in the following circuit.

Sol. at t = 0
i = i2 =  and i1 = 0
and i1 = 0
at t = ∞

⇒ i1 = i2 =  =
= 
Energy stored in an inductor
If current in an inductor at an instant is i and is increasing at the rate di/dt, the induced emf will oppose the current. Its behaviour is shown in the figure.

Power consumed by the inductor = i L 
Energy consumed in dt time = i L  dt
dt
Therefore, total energy consumed as the current increases from 0 to I = 
=  ⇒ U =
⇒ U = 
Note :
 This energy is stored in the magnetic field with energy density
This energy is stored in the magnetic field with energy density

Total energy U = 
Ex. Find out the energy per unit length ratio inside the solid long wire having current density J.
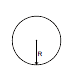
Sol. Take a ring of radius r and thickness dr as an element inside the wire
 =
= 
using B = 

 ⇒
⇒  ⇒
⇒ 
Mutual Inductance
- Consider two coils P and S placed close to each other as shown in the figure. When the current passing through a coil increases or decreases, the magnetic flux linked with the other coil also changes and an induced e.m.f. is developed in it.
- This phenomenon is known as mutual induction. This coil in which current is passed is known as primary and the other in which e.m.f. is developed is called as secondary.
Let the current through the primary coil at any instant be i1. Then the magnetic flux 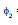 in the secondary at any time will be proportional to i1 i.e.,
in the secondary at any time will be proportional to i1 i.e., 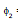 is directly proportional to i1
is directly proportional to i1
Therefore the induced e.m.f. in secondary
when i1 changes is given by
 i.e.,
i.e., 
 =
=  ⇒
⇒ 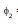 = M i1
= M i1 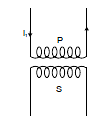
where M is the constant of proportionality and is known as mutual inductance of two coils. It is defined as the e.m.f. induced in the secondary coil by unit rate of change of current in the primary coil. The unit of mutual inductance is henry (H).
Mutual Inductance of a Pair of Solenoids one Surrounding the other coil
Figure shows a coil of N2 turns and radius R2 surrounding a long solenoid of length l1, radius R1 and number of turns N1.
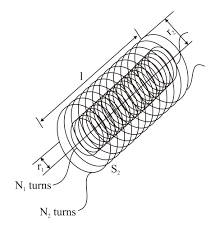
To calculate mutual inductance M between them, let us assume a current i1 through the inner solenoid S1
There is no magnetic field outside the solenoid and the field inside has magnitude,

and is directed parallel to the solenoid's axis. The magnetic flux  through the surrounding coil is, therefore,
through the surrounding coil is, therefore,

Now, 
Notice that M is independent of the radius R2 of the surrounding coil. This is because solenoid's magnetic field is confined to its interior.
Ex.Find the mutual inductance of two concentric coils of radii a1 and a2 (a1 << a2) if the planes of coils are same.
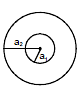
Sol. Let a current i flow in coil of radius a2.
Magnetic field at the centre of coil =
or M i =  or
or 
Ex. Solve the above question, if the planes of coil are perpendicular.
Sol. Let a current i flow in the coil of radius a1. The magnetic field at the centre of this coil will now be parallel to the plane of smaller coil and hence no flux will pass through it, hence M = 0
Ex. Solve the above problem if the planes of coils make θ angle with each other.
Sol. If i current flows in the larger coil, the magnetic field produced at the centre will be perpendicular to the plane of larger coil.
Now the area vector of smaller coil which is perpendicular to the plane of smaller coil will make an angle θ with the magnetic field.
Thus flux =  . πa12 cos θ
. πa12 cos θ
or M = 
Ex. Find the mutual inductance between two rectangular loops, shown in figure.
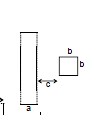
Sol. Let current i flow in the loop having ∞-by long sides. Consider a segment of width dx at a distance x as shown flux through the regent
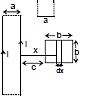
d =
= 
⇒  =
= 
= 
Ex. Figure shows two concentric coplanar coils with radii a and b (a << b). A current i = 2t flows in the smaller loop. Neglecting self inductance of larger loop
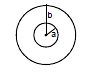
(a) Find the mutual inductance of the two coils
(b) Find the emf induced in the larger coil
(c) If the resistance of the larger loop is R find the current in it as a function of time
Sol. (a) To find mutual inductance, it does not matter in which coil we consider current and in which flux is calculated (Reciprocity theorem) Let current i be flowing in the larger coil. Magnetic field at the centre =  .
.
flux through the smaller coil = 
Therefore, M = 
(ii) |emf induced in larger coil| = 
=  =
= 
(iii) current in the larger coil = 
Ex. If the current in the inner loop changes according to i = 2t2 then, find the current in the capacitor as a function of time.
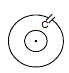
Sol. M = 
|emf induced in larger coil| = 
e =  =
= 
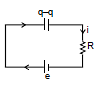
Applying KVL : -
+e -  - iR = 0 ⇒
- iR = 0 ⇒  - -iR = 0
- -iR = 0
differentiate wrt time :  -
-  -
-  on solving it i =
on solving it i = 
Series Combination of Inductors
 =
= 
Therefore, V = V1 + V2

Leθ = L1 + L2 +.................
Parallel Combination of inductor
i = i1 + i2 ⇒ 
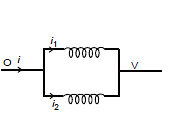


|
105 videos|425 docs|114 tests
|
FAQs on Inductance - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is self-inductance? |  |
| 2. How is self-inductance of a solenoid defined? |  |
| 3. What is the energy stored in an inductor? |  |
| 4. What is mutual inductance? |  |
| 5. How is the mutual inductance of a pair of solenoids, where one surrounds the other coil, calculated? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
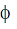 passing through a coil due to its own current is proportional to the current and is given as N
passing through a coil due to its own current is proportional to the current and is given as N 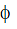 = L i where L is called coefficient of self induction or inductance.
= L i where L is called coefficient of self induction or inductance. 

















