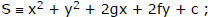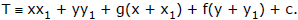Circle: Theorems and Equation | Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Definition |

|
| Basic Theorems and Results of Circles |

|
| Theorem 4 |

|
| Cyclic Quadrilaterals |

|
| Tangents to a Circle |

|
| Standard equations of the circle |

|
Definition
A circle is characterized as the locus of a point undergoing planar motion, whereby its distance from a fixed point, termed the center, remains invariant. The constant distance is precisely identified as the radius of the circle.
Basic Theorems and Results of Circles
- Concentric circles: Circles having same centre.
- Congruent circles: Iff their radii are equal.
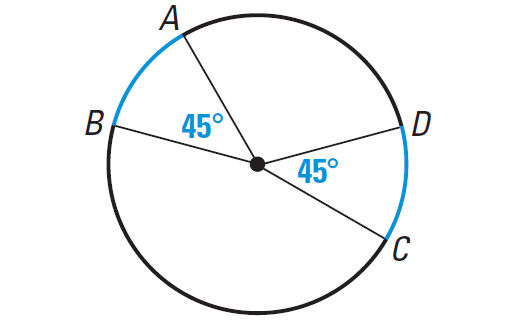
- Congruent arcs: Iff they have same degree measure at the centre.
Theorem 1
- If two arcs of a circle (or of congruent circles) are congruent, the corresponding chords are equal.
Converse : If two chords of a circle are equal then their corresponding arcs are congruent. - Equal chords of a circle (or of congruent circles) subtend equal angles at the centre.
Converse : If the angle subtended by two chords of a circle (or of congruent circle) at the centre are equal, the chords are equal.
Theorem 2
- The perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord.
Converse : The line joining the mid point of a chord to the centre of a circle is perpendicular to the chord. - Perpendicular bisectors of two chords of a circle intersect at tis centre.
Theorem 3
- There is one and only one circle passing through three non collinear points.
- If two circles intersects in two points, then the line joining the centres is perpendicular bisector of common chords.
Theorem 4
- Equal chords of a circle (or of congruent circles) are equidistant from the centre.
Converse: Chords of a circle (or of congruent circles) which are equidistant from the centre are equal. - If two equal chords are drawn from a point on the circle, then the centre of circle will lie on angle bisector of these two chords.
- Of any two chords of a circle larger will be near to centre.
Theorem 5
- The degree measure of an arc or angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point of alternate segment.
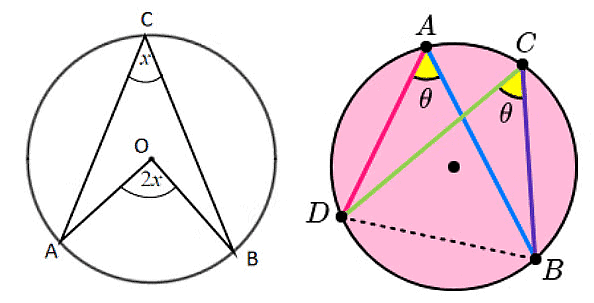
- Angle in the same segment of a circle are equal.
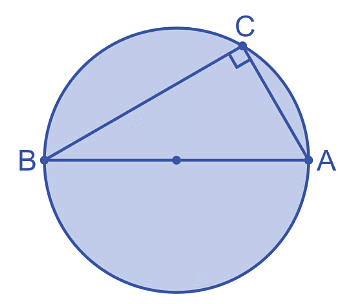
- The angle in a semi circle is right angle.
Converse: The arc of a circle subtending a right angle in alternate segment is semi circle.
Theorem 6
An angle subtended by a minor arc in the alternate segment is acute and any angle subtended by a major arc in the alternate segment is obtuse.
Theorem 7
If a line segment joining two points subtends equal angles at two other points lying on the same side of the line segment, the four points are concyclic, i.e. lie on the same circle.
Cyclic Quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral is called a cyclic quadrilateral if its all vertices lie on a circle.
Theorem 1
The sum of either pair of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180º.
OR
The opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary.
Converse : If the sum of any pair of opposite angle of a quadrilateral is 180º, then the quadrilateral is cyclic.
Theorem 2
If a side of a cyclic quadrilateral is produced, then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle.
Theorem 3
The quadrilateral formed by angle bisectors of a cyclic quadrilateral is also cyclic.
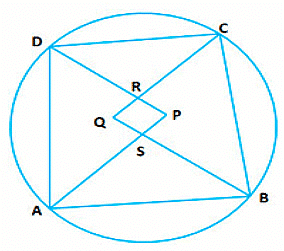
Theorem 4
If two sides of cyclic quadrilateral are parallel then the remaining two sides are equal and the diagonals are also equal.
OR
A cyclic trapezium is isosceles and its diagonals are equal.
Converse : If two non-parallel sides of a trapezium are equal then it is cyclic.
OR
An isosceles trapezium is always cyclic.
Theorem 5
The bisectors of the angles formed by producing the opposite sides of a cyclic quadrilateral (provided they are not parallel), intersect at right angle.
Tangents to a Circle
Theorem 1
A tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
Converse: A line drawn through the end point of a radius and perpendicular to it is a tangent to the circle.
Theorem 2
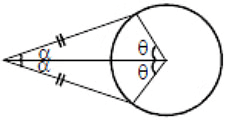
If two tangents are drawn to a circle from an external point, then:
- They are equal.
- The subtend equal angles at the centre.
- They are equally inclined to the segment, joining the centre to that point.
Theorem 3
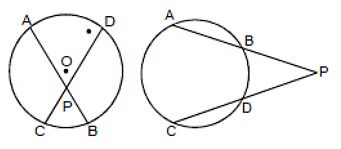
If two chords of a circle intersect inside or outside the circle when produced, the rectangle formed by the segments of one chord is equal in area to the rectangle formed by the two segments of the other chord
PA × PB = PC × PD
Theorem 4
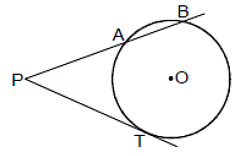
If PAB is a secant to a circle intersecting the circle at A and B and PT is tangent segment, the PA × PB = PT2
OR
Area of the rectangle formed by the two segments of a chord is equal to the area of the square of side equal to the length of the tangent from the point on the circle.
Theorem 5
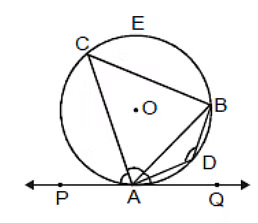
If a chord is drawn through the point of contact of tangent to a circle, then the angles which this chord makes with the given tangent are equal respectively to the angles formed in the corresponding alternate segments.
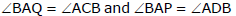
Converse
If a line is drawn through an end point of a chord of a circle so that the angle formed with the chord is equal to the angle subtended by the chord in the alternate segment, then the line is a tangent to the circle.
Standard equations of the circle
Central Form
If (h, k) is the centre and r is the radius of the circle then its equation is (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2
Special Cases
(i) If centre is origin (0, 0) and radius is `r' then equation of circle is x2 + y2 = r2 and this is called the standard form.
(ii) If radius of circle is zero then equation of circle is (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = 0.
Such circle is called zero circle or point circle.
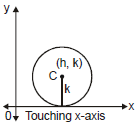
(iii) When circle touches x-axis then equation of the circle is
(x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = k2.
or x2 + y2 - 2hx - 2ky + h2 = 0
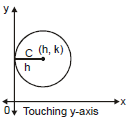
(iv) When circle touches y-axis then equation of the circle is
(x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = h2
or x2 + y2 - 2hx - 2ky + k2 = 0
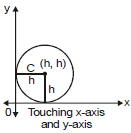
(v) When circle touches both the axes (x-axis and y-axis) then equation of the circle is
(x - h)2 + (y - h)2 = h2
or x2 + y2 - 2hx - 2hy + h2 = 0
(vi) When circle passes through the origin and centre of the circle is (h, k) then radius = r and intercept cut on x-axis OP = 2h, and intercept cut on y-axis is OQ = 2k and equation of circle is
(x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = h2 + k2 or x2 + y2 - 2hx - 2hy = 0
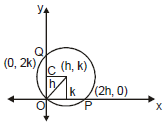
Note : Circle may exist in any quadrant hence for general cases use ± sign before h and k.
General equation of circle
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0. where g, f, c are constants and centre is (-g, -f)
i.e. and radius r =
Notes :
(i) If (g2 + f2 - c) > 0, then r is real and positive and the circle is a real circle.
(ii) If (g2 + f2 - c) = 0, then radius r = 0 and circle is a point circle.
(iii) If (g2 + f2 - c) < 0, then r is imaginary then circle is also an imaginary circle with real centre.
(iv) x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0, has three constants and to get the equation of the circle at least three conditions should be known ⇒ A unique circle passes through three non collinear points.
(v) The general quadratic equation in x and y, ax2 + by2 + 2hxy + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0
represents a circle if :
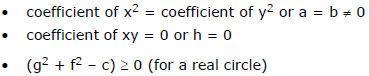
Intercepts cut by the circle on axes
The intercepts cut by the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 on :
(i) x-axis =
(ii) y-axis =
Notes :
(i) If the circle cuts the x-axis at two distinct point then g2 - c > 0
(ii) If circle touches x-axis then g2 = c.
(iii) If circle touches y-axis f2 = c.
(iv) Circle lies completely above or below the x-axis then g2 < c.
(v) Intercept cut by a line on the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 or length of chord of the circle =
where a is the radius and P is the length of perpendicular from the centre to the chord.
Diametrical form of circle
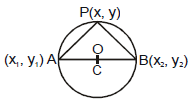
If A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) are the end points of the diameter of the circle and P(x, y) is the point other then A and B on the circle then from geometry we know that 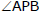 = 90º.
= 90º.
⇒ (Slope of PA) × (Slope of PB) = -1
⇒
⇒ (x - x1) (x - x2) + (y - y1) (y - y2) = 0
Note : This will be the circle of least radius passing through (x1, y1) and (x2 , y2)
The parametric forms of the circle
(i) The parametric equation of the circle x2 + y2 = r2 are x = r cosθ, y = r sinθ; 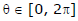
(ii) The parametric equation of the circle (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2 is
x = h + r cosθ, y = k + r sinθ where θ is parameter.
(iii) The parametric equation of the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 are x = - g + cosθ
y = - f + sinθ where θ is parameter.
Note that equation of a straight line joining two point 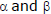 on the circle x2 + y2 = a2 is
on the circle x2 + y2 = a2 is
x cos .
Example 1. Find the centre and the radius of the circles
(A)
(B)
(C) , for some l.
Sol. (A) We rewrite the given equation as
Hence the centre is and the radius is
(B)
Centre of this circle is . Radius
(C)
We rewrite the equation as ...(i)
Since, there is no term of xy in the equation of circle
So, equation (i) reduces to
centre is
& Radius
Example 2. If the lines and
are tangents to a circle, then the radius of the circle is
Sol. The diameter of the circle is perpendicular distance between the parallel lines (tangents) and
and so it is equal to
. Hence radius is
.
Example 3. If y = 2x + m is a diameter to the circle , then find m
Sol. Centre of circle = (-3/2, - 2). This lies on diameter y = 2x + m
Example 4. The equation of a circle which passes through the point (1, - 2) and (4, -3) and whose centre lies on the lies 3x + 4y = 7 is
Sol. Let the circle be ...(i)
Hence, substituting the points, (1, - 2) and (4, -3) in equation (i)
...(ii)
...(iii)
= centre (-g, -f) lies on line . Hence
solving for g, f, c, we get
Hence the equation is
Example 5. A circle has radius equal to 3 units and its centre lies on the line y = x - 1. Find the equation of the circle if it passes through (7, 3).
Sol. Let the centre of the circle be 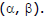 It lies on the line y = x - 1
It lies on the line y = x - 1
. Hence the centre is
.
The equation of the circle is
It passes through (7, 3)
Hence the required equations are and
Position of A Point W.R.T. Circle
- Let the circle is
and the point is (x1, y1) then point (x1, y1) lies out side the circle or on the circle or inside the circle according as
or
- The greatest & the least distance of a point A from a circle with centre C & radius r is AC + r & AC - r respectively.
Example 6. If P(2, 8) is an interior point of a circle x2 + y2 - 2x + 4y - p = 0 which neither touches nor intersects the axes, then set for p is
Sol. For internal point P(2, 8), 4 + 64 - 4 + 32 - p < 0 ⇒ p > 96 and x intercept therefore 1+p<0
and y intercept
Tangent Line of Circle
When a straight line meet a circle on two coincident points then it is called the tangent of the circle.
➢ Condition of Tangency
The line L = 0 touches the circle S = 0 if P the length of the perpendicular from the centre to that line and radius of the circle r are equal i.e. P = r.
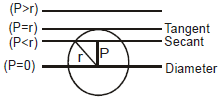
Example 7. Find the range of parameter `a' for which the variable line y = 2x + a lies between the circle x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y + 1 = 0 and x2 + y2 - 16x - 2y + 61 = 0 without intersecting or touching either circle.
Sol. The given circles are and
The line will lie between these circle if centre of the circles lie on opposite sides of the line, i.e.
Line wouldn't touch or intersect the circles if,
or
or
Hence common values of `a' are .
Example 8. The equation of a circle whose centre is (3, -1) and which cuts off a chord of length 6 on the line
2x - 5y + 18 = 0.
Sol.
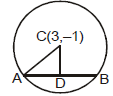
Let AB(= 6) be the chord intercepted by the line 2x - 5y + 18 = 0 from the circle and let CD be the perpendicular drawn from centre (3, - 1) to the chord AB.
i.e.,
Therefore, . Hence required equation is
Example 9. The area of the triangle formed by line joining the origin to the points of intersection(s) of the line and circle x2 + y2 = 10 is
Sol.
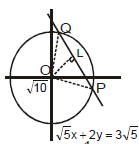
Length of perpendicular from origin to the line is
Radius of the given circle
.
Thus area of
➢ Equation of the tangent (T = 0)
- Tangent at the point (x1, y1) on the circle
is
.
- The tangent at the point (acos t, asin t) on the circle
is
- The point of intersection of the tangents at the points
and
is
- The equation of tangent at the point (x1, y1) on the circle
is
- If line y = mx + c is a straight line touching the circle
, then
and contact points are
or
and equation of tangent is
- The equation of tangent with slope m of the circle
is
Note : To get the equation of tangent at the point (x1, y1) on any curve we replace xx1 in place of x2, yy1 in place of
in place of
in place of y,
in place of xy and c in place of c.
➢ Length of tangent :
The length of tangent draw from point (x1, y1) out side the circle
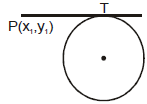
is,
Note : When we use this formula the coefficient of x2 and y2 must be 1.
➢ Equation of Pair to tangents (SS1 = T2)
Let the equation of circle and
is any point outside the circle.
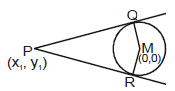
From the point we can draw two real and distinct tangent PQ & PR and combine equation of pair of
tangents is or
Example 10. Let A be the centre of the circle x2 + y2 - 2x - 4y - 20 = 0 and B(1, 7) and D(4, -2) are points on the circle then, if tangents be drawn at B and D, which meet at C, then area of quadrilateral ABCD is
Sol.
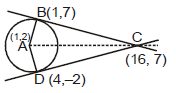
or y = 7 ...(i)
Tangent at is
...(ii)
Solving (i) and (ii), C is (16, 7)
Area ABCD = AB × BC = 5 × 15 = 75 units.
Normal of Circle
Normal at a point of the circle is the straight line which is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact and passes through the centre of circle.
(a) Equation of normal at point (x1, y1) or circle is
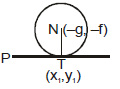
(b) The equation of normal on any point (x1, y1) of circle is
(c) If is the equation of the circle then at any point `t' of this circle (a cos t, a sin t), the equation of normal is x sin t - y cos t = 0.
Example 11. Find the equation of the normal to the circle x2 + y2 - 5x + 2y - 48 = 0 at the point (5, 6).
Sol. Since normal to the circle always passes through the centre so equation of the normal will be the line passing through (5, 6) & i.e. y + 1 =
⇒ 5y + 5 = 14x - 35
⇒ 14x - 5y - 40 = 0
Example 12. If the straight line ax + by = 2; a,  touches the circle x2 + y2 - 2x = 3 and is normal to the circle x2 + y2 - 4y = 6, then the values of a and b are respectively
touches the circle x2 + y2 - 2x = 3 and is normal to the circle x2 + y2 - 4y = 6, then the values of a and b are respectively
Sol. Given x2 + y2 - 2x = 3
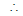 centre is (1, 0) and radius is 2 and x2 + y2 - 4y = 6
centre is (1, 0) and radius is 2 and x2 + y2 - 4y = 6
Given x2 + y2 - 4y = 6
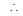 centre is (0, 2) and radius is
centre is (0, 2) and radius is . Since line ax + by = 2 touches the first circle
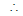
= 2 or (a - 2) =
.............(i)
Also the given line is normal to the second circle. Hence it will pass through the centre of the second circle.
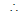 a(0) + b(B) = 2 or 2b = 2 or b = 1
a(0) + b(B) = 2 or 2b = 2 or b = 1
Putting this value in equation (i) we get a - 2 = or (a - 2)2 = 4(a2 + 1)
or a2 + 4 - 4a = 4a2 + 4 or 3a2 + 4a = 0 or a(3a + 4) = 0 or = 0, -4/3
 values of a and b are respectively according to the given choices.
values of a and b are respectively according to the given choices.
Power of the point
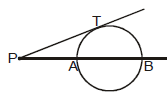
Square of the length of the tangent from the point P is defined as
power of the point `p' w.r. to given circle ⇒ PT2 = S1
Note: Power of a point remains constant w.r. to a circle PA.PB = PT2
Chord of contact
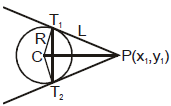
A line joining the two points of contacts of two tangents drawn from a point out side the circle, is called chord of contact of that point.
If two tangents PT1 & PT2 are drawn from the point P(x1, y1) to the circle 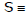 x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0, then the equation of the chord of contact T1T2 is : xx1 + yy1 + g (x + x1) + f (y + y1) + c = 0
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0, then the equation of the chord of contact T1T2 is : xx1 + yy1 + g (x + x1) + f (y + y1) + c = 0
(i.e. T = 0 same as equation of tangent).
Remember
(a) Length of chord of contact T1 T2 =
.
(b) Area of the triangle formed by the pair of the tangents & its chord of contact =
Where R is the radius of the circle & L is the length of the tangent from (x1, y1) on S = 0.
(c) Angle between the pair of tangents from P(x1, y1) = tan-1
(d) Equation of the circle circumscribing the triangle PT1T2 or quadrilateral CT1PT2 is :
(x - x1) (x + g) + (y - y1) (y + f) = 0.
(e) The joint equation of a pair of tangents drawn from the point A (x1, y1) to the circle
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 is : SS1 = T2.
Where
'
Example 13. The chord of contact of tangents drawn from a point on the circle x2 + y2 = a2 to the circle x2 + y2 = b2 touches the circle x2 + y2 = c2. Show that a, b, c are in G.P.
Sol.
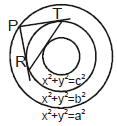
Let P(a cosθ, a sinθ) be a point on the circle x2 + y2 = a2.
The equation of chord of contact of tangents drawn from
P(a cosθ, asinθ) to the circle x2 + y2 = b2 is axcosθ + aysinθ = b2 .....(i)
This touches the circle x2 + y2 = c2 .....(ii)
 Length of perpendicular from (0, 0) to (i) = radius of (ii)
Length of perpendicular from (0, 0) to (i) = radius of (ii)
= c or b2 = ac ⇒ a, b, c are in G.P.
Equation of the chord with a given middle point (t = s1)
The equation of the chord of the circle  + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 in terms of its mid point M(x1, y1) is
+ y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 in terms of its mid point M(x1, y1) is
y - y1 = - (x - x1). This on simplification can be put in the form
xx1 + yy1 + g (x + x1) + f (y + y1) + c = x12 + y12 + 2gx1 + 2fy1 + c which is designated by T = S1.
Note: The shortest chord of a circle passing through a point `M' inside the circle, is one chord whose middle point is M.
Example 14. Let a circle be given by 2x(x - a) + y(2y - b) = 0 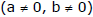 Find the condition on a and b if two chords, each bisected by the x-axis, can be drawn to the circle from (a, b/2).
Find the condition on a and b if two chords, each bisected by the x-axis, can be drawn to the circle from (a, b/2).
Sol. The given circle is 2x(x - a) + y(2y - b) = 0 or x2 + y2 - ax - by/2 = 0
Let AB be the chord which is bisected by x-axis at a point M. Let its co-ordinates be M(h, 0).
and 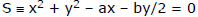
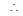 Equation of chord AB is T = S1
Equation of chord AB is T = S1
hx + 0 - (x + h) -
(y + 0) = h2 + 0 - ah - 0
Since its passes through (a, b/2) we have
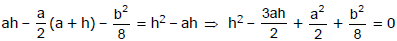
Now there are two chords bisected by the x-axis, so there must be two distinct real roots of h.
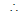 B2 - 4AC > 0
B2 - 4AC > 0
⇒ - 4.1.
> 0
⇒ a2 > 2b2.
Director Circle
The locus of point of intersection of two perpendicular tangents to a circle is called director circle. Let P(h, k) is the point of intersection of two tangents drawn on the circle x2 + y2 = a2. Then the equation of the pair of tangents is SS1 = T2.
i.e. (x2 + y2 - a2) (h2 + k2 - a2) = (hx + ky - a2)2
As lines are perpendicular to each then, coefficient of x2 + coefficient of y2 = 0.
⇒ [(h2 + k2 - a2) - h2] + [(h2 + k2 - a2) - k2] = 0
⇒ h2 + k2 = 2a2
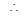 locus of (h, k) is x2 + y2 = 2a2 which is the equation of the director circle.
locus of (h, k) is x2 + y2 = 2a2 which is the equation of the director circle.
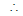 director circle is a concentric circle whose radius is
director circle is a concentric circle whose radius is times the radius of the circle.
Note : The director circle of x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 is x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + 2c - g2 - f2 = 0
Example 15. Let P be any moving point on the circle x2 + y2 - 2x = 1, from this point chord of contact is drawn w.r.t the circle x2 + y2 - 2x = 0. Find the locus of the circumcentre of the triangle CAB, C being centre of the circle.
Sol. The two circles are (x - 1)2 + y2 = 1 ........(i)
(x - 1)2 + y2 = 2 ........(ii)
So the second circle is the director circle of the first. So 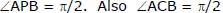
Now circumcentre of the right angled triangle CAB would lie on the mid point of AB
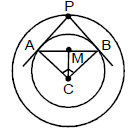
So let the point be 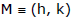
Now, CM = CB sin 45º =
So, (h - 1)2 + k2 =
So, locus of M is (x - 1)2 + y2 = .
Pole and Polar
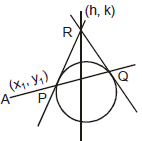
Let any straight line through the given point A(x1 , y1) intersect the given circle S = 0 in two points P' and Q and if the tangent of the circle at P and Q meet at the point R then locus of point R is called polar of the point A and point A is called the pole, with respect to the given circle.
➢ The equation of the polar of point (x1 , y1) w.r.t. circle x2 + y2 = a2.
Let PQR is a chord which passes through the point P(x1, y1) which intersects the circle at point Q and R and the tangents are drawn at points Q and R meet at point S(h, k) then equation of QR the chord of contact is
x1h + y1k = a2
 locus of point S(h, k) is xx1 + yy1 = a2 which is the equation of the polar.
locus of point S(h, k) is xx1 + yy1 = a2 which is the equation of the polar.
Notes :
(i) The equation of the polar is the T = 0, so the polar of point (x1, y1) w.r.t. circle
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 is xx1 + yy1 + g(x + x1) + f(y + y1) + c = 0.
(ii) If point is outside the circle then equation of polar and chord of contact is same. So the chord of contact is polar.
(iii) If point is inside the circle then chord of contact does not exist but polar exists.
(iv) If point lies on the circle then polar, chord of contact and tangent on that point are same.
(v) If the polar of P w.r.t. a circle passes through the point Q, then the polar of point Q will pass through P and hence P and Q are conjugate points of each other w.r.t. the given circle.
(vi) If pole of a line w.r.t. a circle lies on second line. Then pole of second line lies on first line and hence both lines are conjugate lines of each other w.r.t. the given circle.
➢ Pole of a given line with respect to a circle.
To find the pole of a line we assume the coordinates of the pole then from these coordinates we find the polar. This polar and given line represent the same line. Then by comparing the coefficients of similar terms we can get the coordinates of the pole. The pole of lx + my + n = 0.
w.r.t. circle x2 + y2 = a2 will be .
Family of Circles
- The equation of the family of circles passing through the points of intersection of two circles
S1 = 0 and S2 = 0 is ; S1 + KS2 = 0 (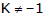 ).
). - The equation of the family of circles passing through the point of intersection of a circle S = 0 and line L = 0 is given by S + KL = 0.
- The equation of a family of circles passing through two given points (x1 , y1) and (x2 , y2) can be written in the form (x - x1) (x - x2) + (y - y1) (y - y2) + K
= 0 where K is a parameter.
- The equation of a family of circles touching a fixed line y - y1 = m (x - x1) at the fixed point (x1, y1) is (x - x1)2 + (y - y1)2 + K [y - y1 - m (x - x1)] = 0, where K is a parameter.
- Family of circles cicumscribing a triangle whose sides are given by L1 = 0; L2 = 0 and L3 = 0 is given by ; L1L2 + λ L2L3 +µ L3L1 = 0 provided coefficient of xy = 0 and coefficient of x2 = coefficient of y2.
- Equation of circle circumscribing a quadrilateral whose side in order are represented by the line L1=0, L2 = 0, L3 = 0 and L4 = 0 are L1L3 + λL2L4 = 0 provided coefficient of x2 = coefficient of y2 and coefficient of xy = 0.
Example 16. The equation of the circle through the points of intersection of x2 + y2 - 1 = 0, x2 + y2 - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0 and touching the line x + 2y = 0, is
Sol. Family of circle is
or
Centre is and radius =
Since it touches the line x + 2y = 0, hence, Radius = Perpendicular distance from centre to the line.
i.e.,
cannot be possible in case of circle. So λ = 1. Thus, we get the equation of circle.
Direct and Transverse Common Tangents
Let two circles having centre C1 and C2 and radii, r1 and r2 and C1C2 is the distance between their centres then
(a) Both circles will touch
(i) Externally : If c1c2 = r1 + r2 i.e. the distance between their centres is equal to sum of their radii and point P divides C1C2 in the ratio r1 : r2 (internally). In this case there will be three common tangents.
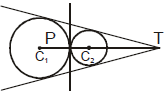
(ii) Internally : If C1C2 = |r1 - r2| i.e. the distance between their centres is equal to difference between their radii and point P divides C1C2 in the ratio r1 : r2 externally and in this case there will be only one common tangent.
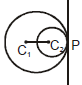
(b) The circles will intersect : when |r1 - r2| < C1C2 < r1 + r2 in this case there will be two common tangents.
(c) The circles will not intersect :
(i) One circle will lie inside the other circle if C1C2 < |r1 - r2| In this case there will be no common tangent.
(ii) When circle are apart from each other the C1C2 > r1 + r2 and in this case there will be four common tangents. Lines PQ and RS are called transverse or indirect or internal common tangents and these lines meet line C1C2 on T1 and T1 divides the line C1C2 in the ratio r1 : r2 internally and lines AB & CD are called direct or external common tangents.
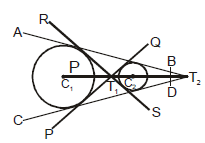
These lines meet C1C2 produced on T2. Thus T2 divides C1C2 externally in the ratio r1: r2.
Note: Length of direct common tangent =
Length of transverse common tangent =
Example 17. Prove that the circles x2 + y2 + 2ax + c2 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 2by + c2 = 0 touch each other, if .
Sol. Given circles are ...(i) and
...(ii)
Let C1 and C2 be the centre of circle (i) and (ii), respectively and r1 and r2 be their radii, then
,
,
Here we find the two circles touch each other internally or externally.
For touch, |C1C2| = |r1 ± r2| or
On squaring
or
Again squaring, or
or
The Angle of Intersection of Two Circles
Definition: The angle between the tangents of two circles at the point of intersection of the two circles is called angle of intersection of two circles. If two circles are
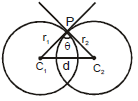
and θ is the angle between them
then or
Here a1 and a2 are the radii of the circles and d is the distance between their centres.
If the angle of intersection of the two circles is a right angle then such circles are called "Orthogonal circles" and conditions for the circles to be orthogonal is
Radical Axis of the Two Circles (S1 - S2 = 0)
➢ Definition : The locus of a point, which moves in such a way that the length of tangents drawn from it to the circles are equal and is called the radical axis.
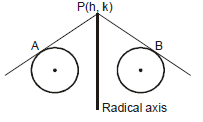
It two circles are -
Let P(h, k) is a point and PA, PB are length of two tangents on the circles from point P. Then from definition : =
or
 locus of (h, k)
locus of (h, k)
⇒ ⇒S1 - S2 = 0
which is the equation of radical axis.
Notes :
(i) To get the equation of the radical axis first of all make the coefficient of x2 and y2 = 1
(ii) If circles touch each other then Radical axis is the common tangent to both the circles.
(iii) When the two circles intersect on real points then common chord is the Radical axis of the two circles.
(iv) The Radical axis of the two circles is perpendicular to the line joining the centre of two circle of two circles but not always pass through mid point of it.
(v) The Radical axis of three circles (Taking two at a time) meet on a point.
(vi) If circles are concentric then the Radical axis does not always exist but if circles are not concentric then Radical axis always exists.
(vii) If two circles are orthogonal to the third circle then Radical axis of both circles passes through the centre of the third circle.
(viii) A system of circle, every pair of which have the same radical axis, is called a coaxial system of circles.
➢ Radical centre
- The radical centre of three circles is the point form which length of tangents on three circles are equal i.e. the point of intersection of radical axis of the circles is the radical centre of the circles. To get the radical axis of three circles S1 = 0, S2 = 0, S3 = 0 we have to solve any two S1 - S2 = 0, S2 - S3 = 0, S3 - S1 = 0
Notes :
(i) The circle with centre as radical centre and radius equal to the length of tangent from radical centre to any of
the circle, will cut the three circles orthogonally.
(ii) If three circles are drawn on three sides of a triangle taking them as diameter then its orthocentre will be its radical centre.
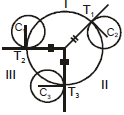
(iii) Locus of the centre of a variable circle orthogonal to two fixed circles is the radical axis between the two fixed circles.
(iv) If two circles are orthogonal, then the polar of a point `P' on first circle w.r.t. the second circle passes through the point Q which is the other end of the diameter through P. Hence locus of a point which moves such that its polars w.r.t. the circles, S1 = 0, S2 = 0 & S3 = 0 are concurrent is a circle which is orthogonal to all the three circles.
Example 18. A and B are two fixed points and P moves such that PA = nPB where  Show that locus of P is a circle and for different values of n all the circles have a common radical axis.
Show that locus of P is a circle and for different values of n all the circles have a common radical axis.
Sol. Let and
so PA = nPB
Hence locus of P is , which is a circle of different values of n.
Let n1 and n2 are two different values of n so their radical axis is x = 0 i.e. y-axis. Hence for different values of n the circle have a common radical axis.
Example 19. Find the equation of the circle through the points of intersection of the circles x2 + y2 - 4x - 6y - 12 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 6x + 4y - 12 = 0 and cutting the circle x2 + y2 - 2x - 4 = 0 orthogonally.
Sol. The equation of the circle through the intersection of the given circles is
...(i)
where is the equation of radical axis for the circle
and
Equation (i) can be rearranged as
It cuts the circle orthogonally.
Hence
Hence the required circle is
i.e.,
Example 20. Find the radical centre of circle ,
and
. Also find the equation of the circle cutting them orthogonally.
Sol. Given circles are
Equation of two radical axes are or
and or
Solving them the radical centre is (3, 2) also, if r is the length of the tangent drawn from the radical centre (3, 2) to any one of the given circles, S1, we have
Hence (3, 2) is the centre and is the radius of the circle intersecting them orthogonally.
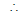 Its equation is
Its equation is
⇒ x2 + y2 - 6x - 4y - 14 = 0
Alternative Method :
Let be the equation of the circle cutting the given circles orthogonally.
or
...(i)
or
...(ii)
and or
...(iii)
Solving (i), (ii) and (iii) we get and
 equation of required circle is
equation of required circle is
|
172 videos|503 docs|154 tests
|
FAQs on Circle: Theorems and Equation - Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the basic theorems and results of circles? |  |
| 2. What is Theorem 4 related to circles? |  |
| 3. How are tangents related to circles? |  |
| 4. What are cyclic quadrilaterals? |  |
| 5. What are the standard equations of a circle? |  |