Excretion in Animals & Human Excretory System | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
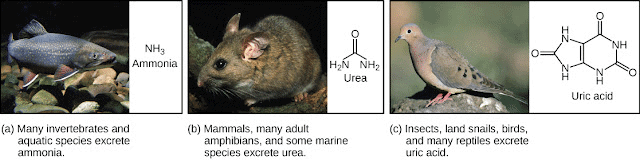
Animals accumulate ammonia, urea, uric acid, carbon dioxide, water, and ions like Na+, K+, Cl−, phosphate, and sulfate through metabolic activities or excess ingestion.These substances need to be removed either totally or partially.
Types of Nitrogenous Wastes

Modes of Excretion
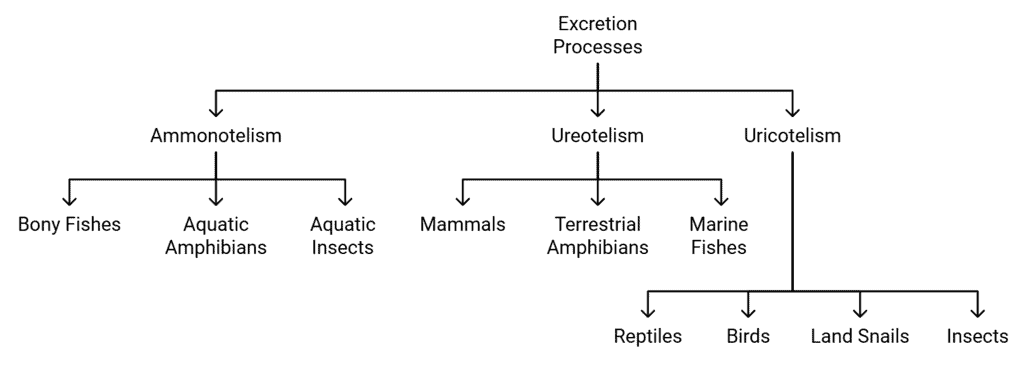 Modes of Excretion and Examples
Modes of Excretion and Examples
(i) Ammonotelism
- Process of excreting ammonia.
- Common in bony fishes, aquatic amphibians, and aquatic insects.
- Ammonia is excreted by diffusion across body surfaces or through gills as ammonium ions.
- Kidneys do not play a significant role in ammonia removal.
(ii) Ureotelism
- Process of excreting urea.
- Common in mammals, terrestrial amphibians, and marine fishes.
- Ammonia is converted into urea in the liver and excreted by the kidneys.
- Some urea may be retained in the kidneys to maintain osmolarity.
(iii) Uricotelism
- Process of excreting uric acid.
- Common in reptiles, birds, land snails, and insects.
- Uric acid is excreted in the form of pellets or paste with minimal water loss.
Excretory Structures in Animals
Invertebrates
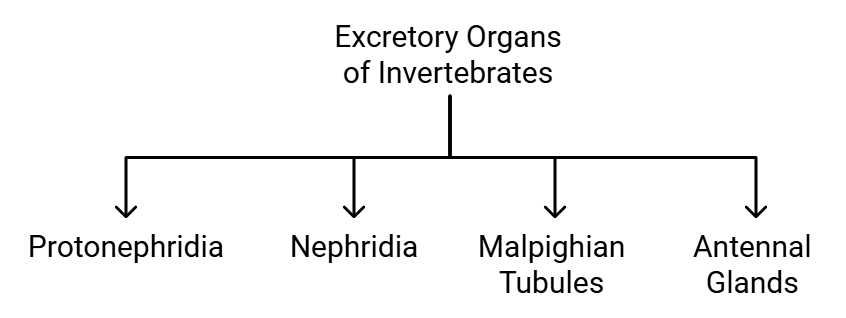
- Protonephridia or Flame Cells: Found in Platyhelminthes (flatworms like Planaria), rotifers, some annelids, and the cephalochordate Amphioxus. These structures are primarily involved in ionic and fluid volume regulation (osmoregulation).
- Nephridia: Tubular excretory structures found in earthworms and other annelids. Nephridia help remove nitrogenous wastes and maintain fluid and ionic balance.
- Malpighian Tubules: Excretory structures in most insects, including cockroaches. Malpighian tubules aid in the removal of nitrogenous wastes and osmoregulation.
- Antennal Glands or Green Glands: Perform excretory functions in crustaceans like prawns. These glands help in the elimination of waste products and regulation of body fluids.
Vertebrates
- Kidneys: Complex tubular organs responsible for filtering blood, removing waste products, and regulating water and electrolyte balance. Kidneys play a significant role in the excretion of urea and other nitrogenous wastes.
Human Excretory System
The Human excretory system is responsible for removing waste products from the body. It consists of several organs, including the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Excretion plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis (Hemostasis is the body's process of maintaining a stable and balanced internal environment).
Parts of Human Excretory System
Two kidneys & their blood supplies.(a) A pair of ureters
(b) urinary bladder
(c) Urethra
What are kidneys?
Kidneys are vital organs in the human body responsible for filtering waste products and excess fluids from the blood to produce urine. They also help regulate blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and red blood cell production. 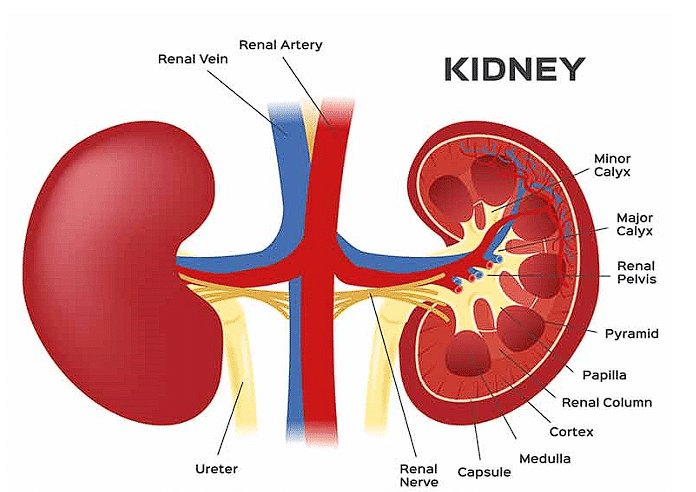 Pair of Kidneys
Pair of Kidneys
Location of Kidneys
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs in our bodies having reddish brown color. and they are located between the last thoracic and third lumbar vertebrae, near the back wall of the abdomen.
- In an adult human each kidney measures 10-12 cm in length, 5-7 cm in width & 2-3 cm in thickness.
- On an average weight of Kidneys is 120- 170 grams.
- In humans right kidney is at slightly lower level than left kidney.
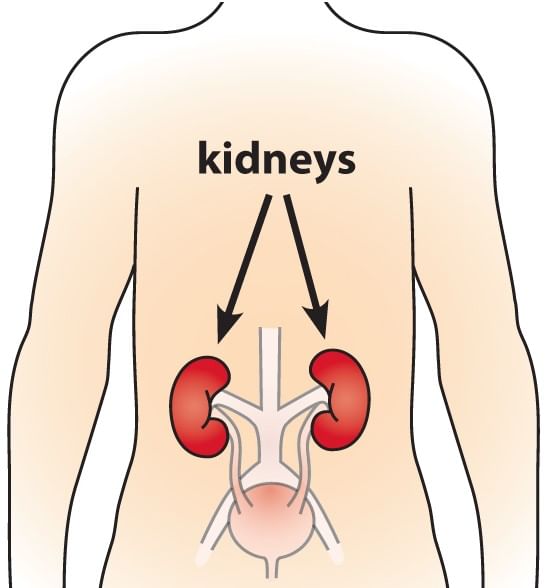 Location Of Kidneys
Location Of Kidneys
Structure of Kidney
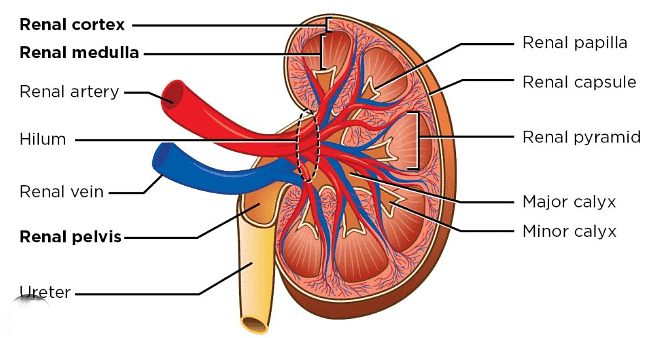 External Structure Of Kidney
External Structure Of Kidney
- The kidneys have a strong outer layer called the capsule.
- They have a hollow area called the hilum where things like the ureter, blood vessels, and nerves go inside.
- Above the hilum, there is a funnel-shaped space called the renal pelvis with small projections called calyces.
Internal Structure of Kidney
(i) An Outer Cortex
- The outer cortex of the kidney is like a shell or outer layer. It surrounds the inner parts of the kidney and helps to protect and support its functions.
- It contains many tiny filtering units called nephrons, which play a vital role in filtering and cleaning the blood.
- The outer cortex is important for the overall functioning of the kidney and maintaining the body's balance of fluids and waste products.
(ii) An Inner Medulla
- The inner medulla of the kidney is divided into cone-shaped structures known as medullary pyramids. These pyramids extend into the calyces and are also referred to as renal columns.
- The cortex extends in between the medullary pyramids as renal columns called Columns of Bertini.
- Nephrons are the structural and functional units of kidneys.
- Nephrons eliminate wastes from the body, regulate blood volume and pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites and regulate blood pH.
(a) Structure and Parts of Nephron
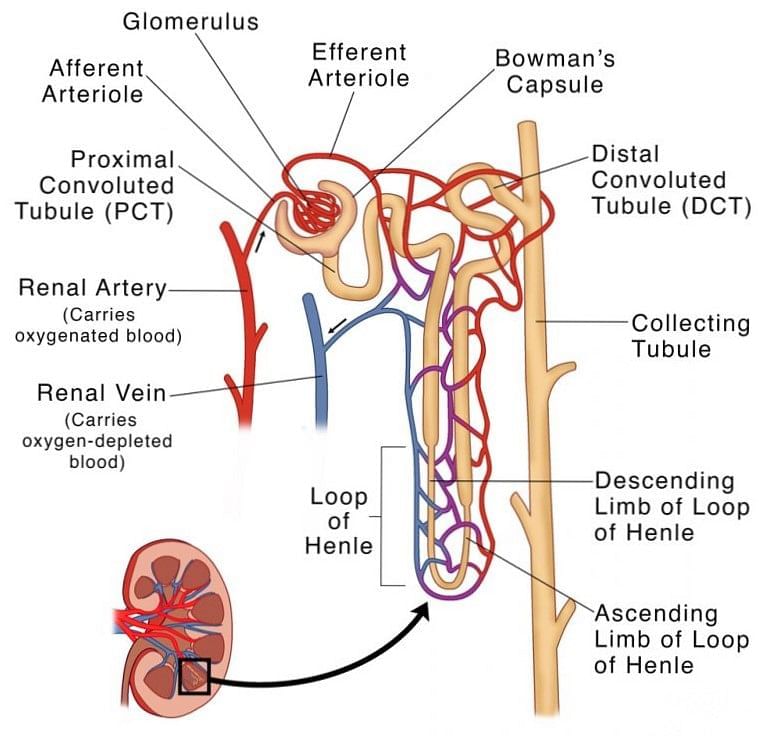 Structure of Nephron
Structure of Nephron
The Nephron is the functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering and processing blood to form urine. It consists of Two main parts:
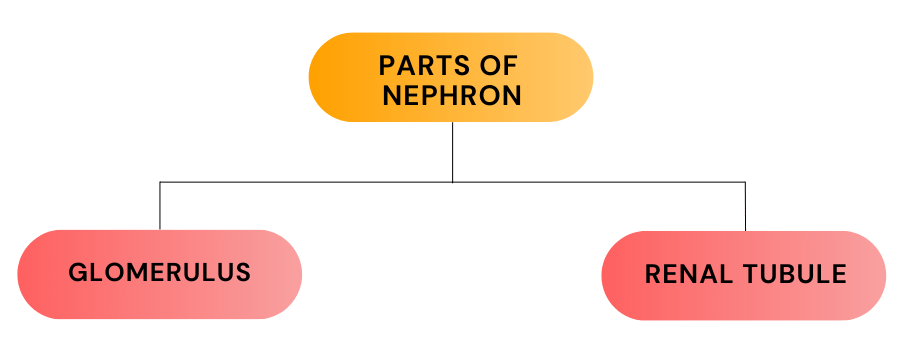
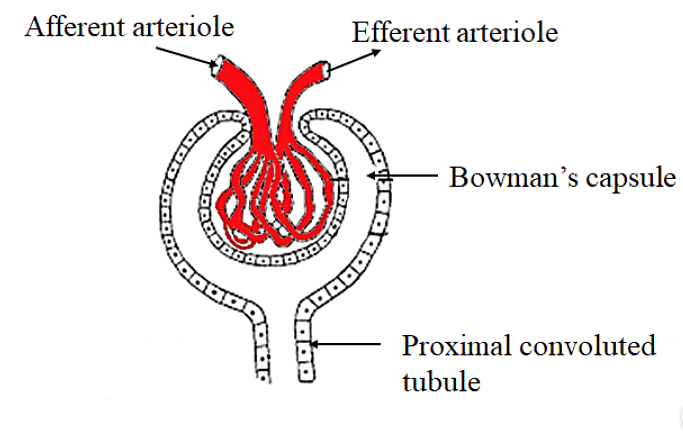
(i) Glomerulus
The Glomerulus, composed of a cluster of tiny capillaries, acts as a filter to remove waste products and excess water from the blood.
The glomerulus consists of three main parts
Afferent Arteriole: This small artery carries blood into the glomerulus under high pressure. It brings blood from the main renal artery into the glomerulus for the process of filtration.
Glomerular Capillaries: These small blood vessels form a network of loops within the glomerulus. They are highly specialized for the purpose of filtration. As blood flows through these capillaries, waste products and excess fluids are filtered out and collected for further processing.
Efferent Arteriole: This small artery carries the filtered blood away from the glomerulus. It transports the purified blood to the next stage of the renal circulation
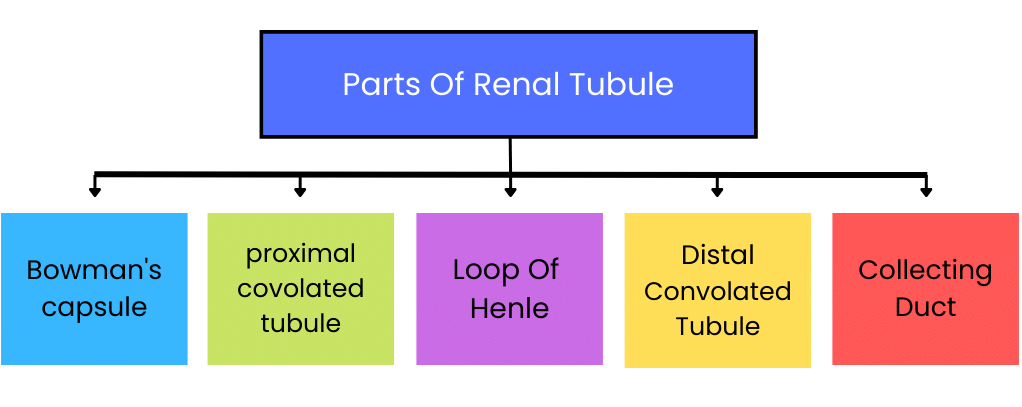
(ii) Renal Tubule
The Renal tubule is a long and twisted tube, plays a crucial role in the kidney's filtration process. It reabsorbs important substances like water, glucose, and salts back into the bloodstream while allowing waste products to continue their journey for elimination as urine.
 Functions of Each Part
Functions of Each Part
(a) Bowman's Capsule: This cup-like structure surrounds the glomerulus and collects the filtrate produced during glomerular filtration.
(b) Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT): This highly coiled region reabsorbs valuable substances from the filtrate, such as glucose, water, and electrolytes, back into the bloodstream. It also secretes waste products for elimination.
(c) Loop of Henle: The U-shaped portion of the renal tubule consists of a descending limb and an ascending limb. It helps maintain urine concentration by allowing water reabsorption in the descending limb and electrolyte reabsorption in the ascending limb.
(d) Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): Located after the Loop of Henle, this coiled section further reabsorbs water and electrolytes and regulates acid-base balance and the excretion of certain substances.
(e) Collecting Duct: This larger tube receives filtrate from multiple nephrons and carries it towards the renal pelvis, where it becomes urine.
NOTE: The glomerulus, together with Bowman's capsule, is referred to as the Malpighian body or renal corpuscle.
 Malpighian Body
Malpighian Body
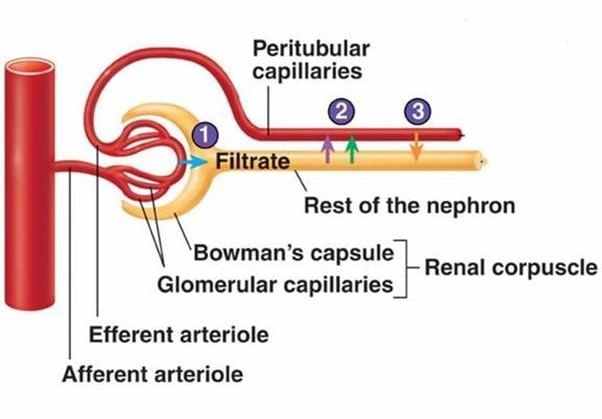
The efferent arteriole that comes out of the glomerulus creates a small network of capillaries surrounding the renal tubule known as the peritubular capillaries. Within this network, there is a tiny vessel that runs alongside the Henle's loop, taking the shape of a 'U', which is called the vasa recta.
(b) Types of Nephrons
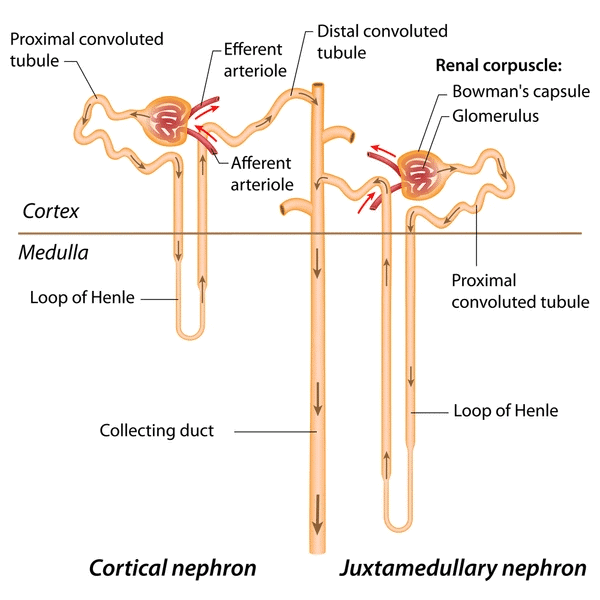
(i) Cortical Nephrons
- Cortical Nephrons are the most common type of nephrons, constituting about 85% of the total nephrons in the kidney.
- They are located in the cortex (outer region) of the kidney. The renal corpuscle (glomerulus and Bowman's capsule) of cortical nephrons is situated in the outer part of the cortex.
- The loop of Henle of cortical nephrons does not extend deeply into the medulla.
(ii) Juxtamedullary Nephrons:
- Juxtamedullary Nephrons are less numerous, accounting for about 15% of the total nephrons in the kidney.
- They have their renal corpuscle situated near the boundary of the cortex and medulla.
- The loop of Henle of juxtamedullary Nephrons extends deeply into the medulla, allowing for the concentration of urine. These nephrons play a crucial role in maintaining the concentration gradient in the kidney.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Excretion in Animals & Human Excretory System - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main functions of the kidneys in the human excretory system? |  |
| 2. Where are the kidneys located in the human body? |  |
| 3. What is the internal structure of a kidney and its significance? |  |
| 4. What is a nephron and what are its parts? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of nephrons found in the kidneys? |  |

















