Lymph and Circulatory System | Biology for JAMB PDF Download
What is lymph?
Lymph is a clear, colorless fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system. It is derived from interstitial fluid that has entered the lymphatic vessels
- When blood travels through tiny vessels in tissues, some water and small, water-soluble substances leak out into the spaces between cells, forming what's called interstitial fluid or tissue fluid.
- This fluid, which has the same mineral content as blood plasma, serves as a medium for exchanging nutrients, gases, and other substances between blood and cells. The lymphatic system, made up of a network of vessels, collects this fluid and returns it to the main veins.
- The fluid in the lymphatic system is called lymph. Lymph is clear and contains special white blood cells called lymphocytes, which play a key role in the body's immune responses. It also carries nutrients, hormones, and fats absorbed from the intestines through structures called lacteals in the intestinal villi.
What is Circulatory System?
An expanded pipeline system is present in the human body. It is called the closed circulatory system.
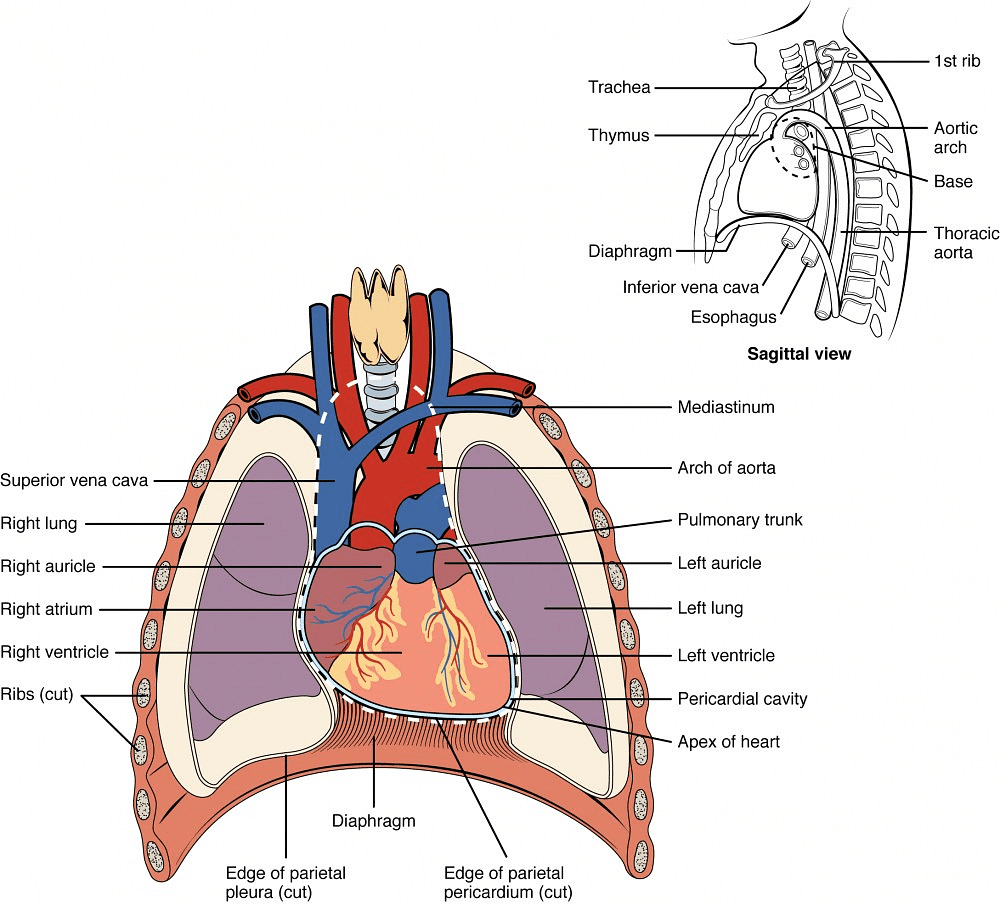
A continuous chemical exchange of materials between the animal body and environment among different tissues of the body is done through this system. In this way, digested nutrients from the digestive system, oxygen from respiratory organs, hormones from endocrine glands are distributed to all the cells of the body. Also, the transport of CO2 from body cells to respiratory organs, NH3, urea etc. excretory substances to excretory organs are the function of the circulatory system. The whole circulatory system is formed by the mesoderm of the embryo. Except the inner lining of blood vessels and heart which are of endodermal origin.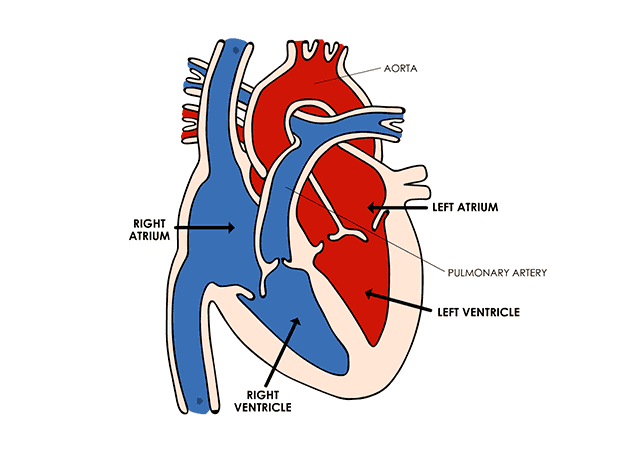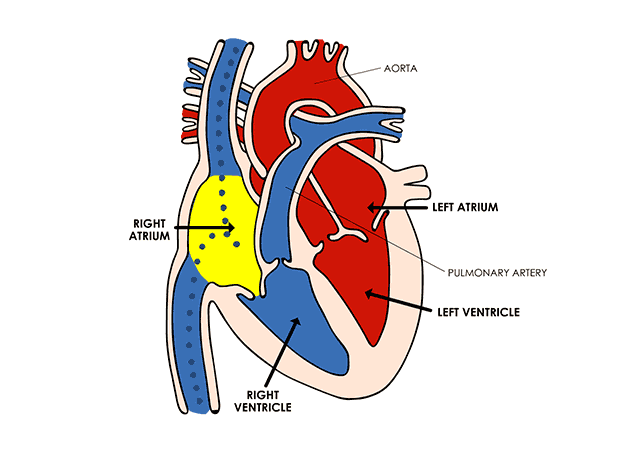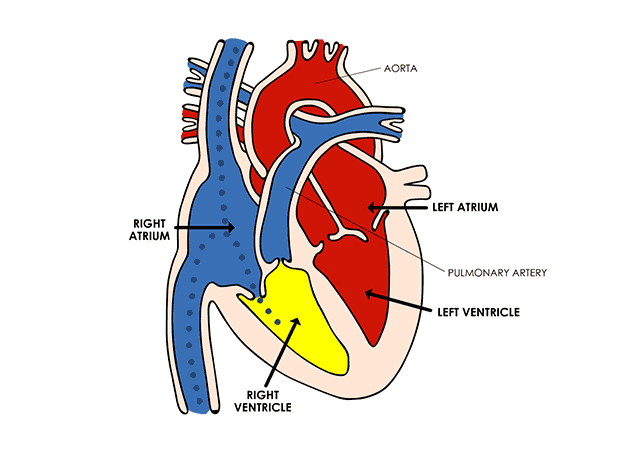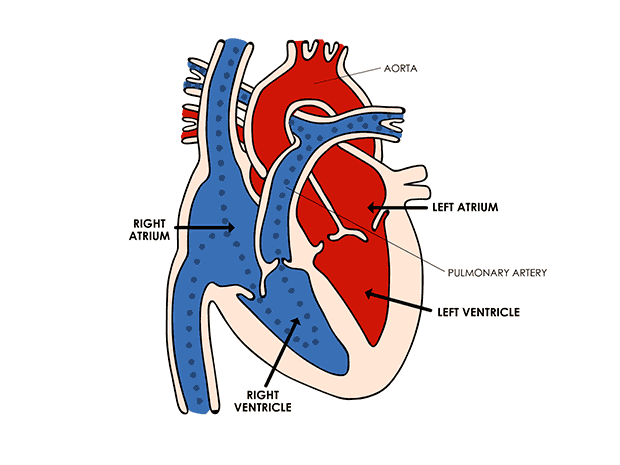 Human Heart
Human Heart
Types of Circulatory System on basis of Complexity and Evolution
Open type | Closed type |
1) Blood is filled in the coelomic channel and sinus coelom is called haemocoel. Fluid is called hemolymph. | 1) Blood circulates in closed vessels. |
2) Tissues are in direct contact with circulating fluid. eg. Arthropodes, non cephalopod molluscs. | 2) Tissues are not in direct contact with circulating fluid. e.g. Annelids, Cephalopod molluscs, Chordates. |
Types of Circulatory System on the basis of Circulating Fluid
In human beings (on the basis of circulating fluid) two types of circulatory system are observed.
- Blood circulatory system: It consists of Blood, Blood vessels, Heart.
- Lymphatic system: It consists of lymph, lymph capillaries, lymph vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid tissues/organs.
The study of blood vascular system or circulatory system is called Angiology.
William Harvey is known as the father of angiology. He called the heart the "Pumping station of the body".
Path of Blood in Double Circuit (Man)
It was first discovered by "William Harvey".


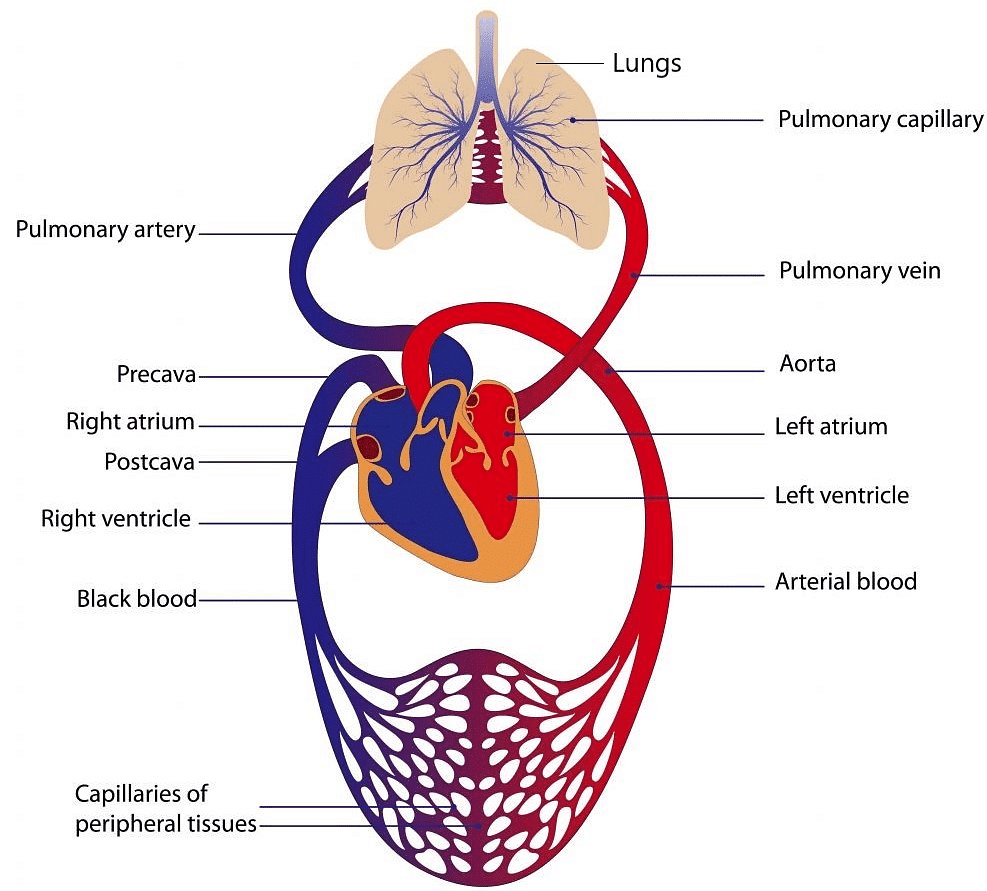 Path of Blood in Double Circuit
Path of Blood in Double Circuit
Circulation of Blood
1. Single Circuit
Example: Fishes

2. Double Circuit
Example: Man, Rabbit

3. Transitional Type Circuit
Two circuits are not completely separate
Example: FROG
Blood mixes in ventricles Evolutionary sequence is present in vertebrates.
- Fishes have a tubular "Venous-Heart" In their heart, deoxygenated blood enters from one side and from the other side enters inside the gills for purification. This is called the "Single Heart Circuit".
- In amphibians (like Frog) and Reptiles, the auricles are divided into right and left. The right auricle gets impure and the left auricle gets pure blood from the body. But only 1 ventricle is present or is incompletely divided so after coming here the pure and impure blood mix up.
- In some reptiles (Crocodile, Gavialis and Alligator) and in all birds and mammals the heart is divided into 2 auricles and 2 ventricles so while circulating inside the heart the pure and impure blood remain separated. The right portion of the heart collects impure blood from the body and sends it to the lungs for purification, while the left portion takes pure blood from the lungs and distributes it to the whole body.
The right portion of the heart is called the "Pulmonary-Heart" and the left portion is termed as the "Systemic-heart". This is termed as "Double Circulation of Heart".because the blood has to pass through the heart twice before being delivered to systemic organs. Types of heart on the basis of type of blood which it receives:
- Venous/Brachial (fishes)
- Arterial (prawn)
- Arteriovenous (lung fishes, tetrapods)
|
224 videos|175 docs|151 tests
|
FAQs on Lymph and Circulatory System - Biology for JAMB
| 1. What is the lymphatic system and its function? |  |
| 2. How does lymph flow through the body? |  |
| 3. What are the main components of the circulatory system? |  |
| 4. How does the circulatory system work in coordination with the lymphatic system? |  |
| 5. What are some common disorders or diseases related to the lymphatic and circulatory systems? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JAMB exam
|

|