Lymphatic System | Biology for JAMB PDF Download
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
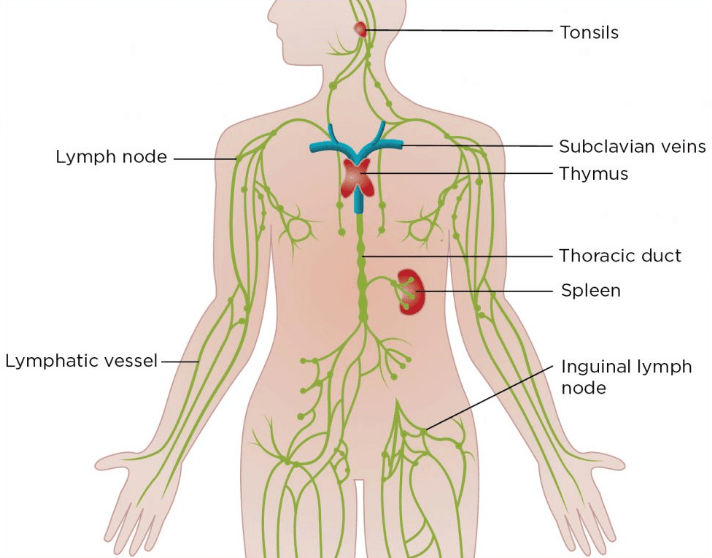 The major components of the lymphatic system
The major components of the lymphatic system



Lymphatic Circulatory System : Here a different kind of circulating fluid (lymph) transfers CO2 and waste products from the interstitial spaces to the veins through lymph vessels. This fluid is derived from filteration of blood in the capillaries. If is devoid of RBC's. The lymph vessels originated from lymph capillaries and end either in the vein or a main big lymph vessel called thoracic duct. This fluid is propelled from the interstitial space to the veins ultimately due to pressure differences.
The Lymph :
From arteriolar regions of capillaries, about 90 percent fluid is returned back into their venous regions. To drain back the remaining ten percent of the filtered out fluid, vertebrates possess an additional independent system of pipelines, called lymphatic system. This system begins in tissue fluid with lymphatic capillaries which are always terminally closed. These capillaries occur extensively in between the blood capillaries in various body parts except in skin epidermis, hair follicles, cornea of eyes, most cartilages, brain, spinal cord, spleen and bone marrow. The cavity of lymph capillaries is wider and irregular. Their wall is thinner than that of blood capillaries, but its pores are so much larger as to allow entrance of even bacteria, cell debris and proteins and other larger colloid particles. The fluid that flows into these capillaries from the interstitium is called lymph.
Arteries divide into blood capillaries inside the tissue. These capillaries combine to form a vein at the other end.
These veins carry impure blood from tissue. Blood pressure is more at the side of arteriole side of blood capillaries. It is approximately 40 mm Hg. Colloidal osmotic pressure of blood is 28 mm Hg. Thus net filteration pressure of blood in this region remains only 12mm Hg column. In this region blood is filtered filtrate is called tissue fluid. There are present plasma WBCs, O2 and nutrients in tissue fluid.
The systemic venous pressure is as low as 15 mm Hg, while colloid osmotic pressure here remains 28 mm Hg.
Hence due to a negative pressure (-13 mm Hg) the lymph is poured from lymphatics into the veins.
W.B.Cs. and plasma are found in lymph but R.B.Cs. and platelets are absent from lymph.
Lymph forms second circulatory system in the body. Lymphatic system is also known as helping circulatory system.
Clotting capacity is present in lymph but its clotting takes more time as compared to blood.
Differences between lymph and blood:-
Blood | Lymph |
1. It forms circulatory system. | 1. It forms lymphatic system. |
2. R.B.Cs. present | 2. R.B.Cs. absent |
3. Neutrophils more | 3. Lymphocytes in largest amount |
4. Soluble proteins in large amount but insoluble proteins in small amount. | 4. Soluble proteins in small amount but in |
5. O2 & nutrients in large amount but CO2 very less. | 5. O2 & nutrients in small amount but CO2 in large amount. |
6, It is of red colour. | 6. It is of alourlffis, just like water. |
7. More WBC | 7. Lesser WBC |
Lymph Vessels:-
Lymph capillaries combine together to form lymph vessels in rabbit/man
Lymph vessels are like veins in structure. Their wall is comparatively thin. One way semilunar valves are present in these vessels which open towards heart; valves are more in number than veins
Lymph vessels combine to from two bigger vessels, these are left thoracic lymph duct and right thoracic lymph duct.
Right thoracic lymph duct is some what smaller lymph vessels of head, neck, right part of thorax and right hand open into it. It (right duct) opens into right sub-clavian vein.
Left thoracic lymph duct (Largest lymph vessel of body) is made up of lymph vessels of head, neck left part of thorax, left anterior limb and both the hind limbs, alimentary canal, some parts of thorax and abdomen.
This duct is connected by a big bag like structure called cisterna chyli just behind the diaphragm in abdominal cavity. It opens in left sub-clavian vein at its anterior side.
Lymphatic capillaries of intestinal villi are called lacteals. Their lymph is milky in colour due to the absorbed fat from the intestine. It is called chyle. This chyle drains into cisterna chyli.
Lymphoid organs and lymph nodes:- lymphoid organs made up of lymph tissue are present in lymphatic system, which are related to lymph capillaries and lymph vessels. Lymph nodes ,spleen, thymus, patches of payer, tonsil etc. are such type of organs.
(a) Lymph nodes:- At places many lymphatics may intersect with each other forming a knob or node like structure called the lymph node. The vessels entering the lymph node carrying lymph from the interstitial space are called afferent lymphatics. The lymphatic leaving the lymph node and draining the lymph in vein or thoracic duct is called efferent lymphatic.
The lymph node thus act as a filter apparatus which filter the lymph coming from the interstitial space and remove cellular debris etc. from it.
Their other functions are as follows
1. These form lymphocytes and pour into lymph.
2. Filter and clean the lymph.
3. Synthesize the antibodies.
4. Destroy bacteria and other harmful substance by feeding upon (phagocytize)
Lymph nodes are present in all parts of body, but their number is comparatively more in armpits of hands legs, groins, neck and abdomen. Their number is much more in neck region
Spleen
Spleen is known to be the largest lymph node of body. It is the blood bank of the body.
Spleen is also called " Graveyard of RBC".
Spleen originates from embryonic mesoderm.
Spleen is red- coloured lymph node, it is found attached by mesentery to the lateral side of stomach. It is the largest solid mass of reticulo-endothelial tissue in the body.
It is covered by a capsule formed of elastic fibrous connective tissue and smooth muscles. It is called splenic capsule.
Narrow fold like septa extend inwards from the capsule, dividing the spleen tissue into several incomplete lobules. These septa are known as trabeculae.
A special type of connective tissue is filled in the spleen which is called reticulo-endothelial tissue or splenic pulp
Splenic pulp has 2 parts
(1) White pulp:- It is scattered in the form of patches (in the splenic pulp) of long and irregular size lymphatic endothelium. The meshes of this network are studded with numerous splenic cells, lymphocytes. The splenic cells are mostly aggregated around arterioles forming nodules which appear whitish and hence recognized as white pulp.

(2) Red Pulp:- It forms the maximum part of spleen. It is reddish due to excess number of RBCs. It is made up of venous sinuses. A tissue is filled in intermediates spaces which form splenic cord, Red pulp of spleen contains erythrocytes (dead and alive) and blood filled sinuses.
Cord of Billroth found in spleen are big blood sinuses.
In the pulp of spleen, there are found some large sized phagocytes which are called macrophage cells. These cells phagocytize the dead and decaying RBCs. bacteria, toxic substances, harmful pigments etc. and purify the blood.
Functions of spleen:-
1. Its macrophages engulf or phagocytize and destroy wornout blood cells, live or dead pathogens,cell debris etc.
2. In the embryonic stage it produces RBCs.
3. Some antibodies are synthesised here.
4. In adult stage spleen works as blood bank. Its sinuses serve as reservoirs of blood when required their blood is squeezed into circulation.
5. Spleen stores iron.
6. The size of spleen increases at the time of malaria because lymphocytes and dead RBC number is increased in it at that time (splenomegaly).
BRIEF REVIEW
SPECIAL FEATURES IN HEART –
Single chambered heart is present in invertebrates and protochordates.
Two chambered heart is present in fishes.
Three chambered heart is present in amphibians.
In reptiles, heart is almost four chambered there are two well developed auricles and two less developed non clear ventricles , but in crocodiles all the birds and all the mammals, the heart is fully developed and four chambered.

Sinus Venosus And Conus Arteriosus- Sinus venosus and conus arteriosus are not found in human but they are present in frog. In human Sinus-venosus is formed in the embryo but later it becomes a part of the wall of the right-auricle. So the impure (deoxygenated) blood collected by the precavals (SVC) and postcaval (IVC) directly comes into the right auricle. The pure blood brought by the pulmonary veins from the lungs directly come into the left auricle.
Due to the separation of ventricles and the absence of Conus-arteriosus in human , the pulmonary arches and the Carotico-systemic arches or aorta,arise respectively from the right and the left-ventricles.
Anatomical landmarks
Coronary artery – Supplies blood to HEART
Vasso - Vassorium – Blood vessels which supply blood to wall of blood vessels
Bicuspid valve – Mitral valve (Between L.A. & L.V.)
Tricuspid valve – (Between R.A. & R.V.)
Haversian valve – [On the end of opening of precavals]
Eustachian valve – On opening of postcavals.
Semilunar valve – At opening of Aorta and ventricles
Thebesian valve – Coronary valve = at opening of coronary sinus
Columnae carnae – Finger like projection from ventricle walls
Papillary muscles – Present at tip of columnae carnae
Chordae tendinae – Arise from papillary muscles and keep the valves in proper position.

Lacteal s → Lymph capillaries of intestinal villi
Lymphatic system present in class Amphibia is of open type.
Lymph heart and lymph sinuses found in frog but are absent in the lymphatic system of mammals.
Payer's patches are present in mucosa of intestine and tonsils are present in mucosa of pharynx.
IMPORTANT POINTS
1. Blood plasma + tissue fluid + lymph combine to form internal environment of the body of vertebrates , which is termed as " The sea within the body" by Baird hastings;
2. First heart transplantation was done by Dr. Christian Bernard (3rd dec. 1967) in the world.
3. In India first heart transplantation was done by Dr. P. Venugopal on 3rd August 1994. This transplant was done on a 42 years old person named Deviram (in AIIMS).
4. [Spleen + liver + kidneys] These three are called filter apparatus of blood.
5. In coronary artery by pass grafting , a segment of patients own saphenous vein or a segment of internal mammary artery is used as a by pass channel.
6. Cardio-pulmonary resuscitation CPR (First aid and management of cardiac arrest) is given in the ratio of 4:1 of compression : ventilation.
7. In acute M.I., Streptokinase (STK) is given intravenously to dissolve the thrombus obstruction which is causing myocardial infarction.
8. The major switch over from foetal to adult type of circulation after parturition occurs due to nitric oxide synthesis, which causes vasodialation of pulmonary artery and veins, thereby allowing much greater quantity of blood to flow through lungs.

10. Lowest rate of heart-beat is of Blue-Whale "Balaenoptera-musculus." (Less than 28 per min.)
11. On an increase of basicity the rate of heart-beat decreases.
12. Solid state lithium cell is used in artificial pacemaker.
13. Heart Failure:- The state of heart when its is not pumping blood effecting enough to meet the needs of the body. Heart failure is not the same as cardiac arrest (when the heart stops beating) or a heart attack (when the heart muscle is suddenly damaged by an inadequate blood supply).
14. Heart-block:- When A.V. Node gets damaged, so contractions do not reach up to ventricles this event is called heart block.
15. Haemostasis:- To prevent bleeding by the blood clotting process is known as haemostasis.
16. Haematemesis:- Presence of blood in vomit i.e. bleeding during vomiting is called haematemesis
17. In frog lymph capillaries open in large irregular lymph sinuses. To drain this lymph in subscapular and femoral veins two pairs lymph hearts are found in frog. So the lymphatic system of frog is of open type.
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OF RABBIT & MAN
RABBIT | MAN |
1. Heart is present towards the base of thoracic cavity and situated on the top of diaphragm. | 1. Heart is situated between the lungs in the thoracic cavity and attached with diaphragm |
2. Heart of rabbit is small triangular in shape of weight upto 30-50 gms. | 2. Heart of man is larger, triangular in shape and weighs upto 300 to 350 gm. |
3. The volume of blood is less than 400 ml . | 3. The volume of blood is 5 to 6 litres and two litre is lymph. |
4. Heart is four chambered. | 4. Heart is also four chambered. |
5. In right auricle two anterior vena cava and one posterior vena cava drain the blood. | 5. In the right auricle one anterior vena and one posterior vena cava drain the blood. |
6. In left auricle two pulmonary veins open through single aperture. | 6. In left auricle four pulmonary veins opens through two different apertures. |
7. The pulse rate of heart is 210 per minute which may increase or decrease at the time of rest and at work. | 7. At the time of birth the heart rate is 120 to 140 per minute and in adult 60-90 per minute. |
8. Caudal artery and caudal vein is long and well developed. | 8. Caudal artery and caudal vein are absent. |
9. Generally in mammals and rabbit hepatic portal system is present. | 9. Along with hepatic portal system a small Hypophyseal portal system is also present.
|
| 10. Lymphatic system is present. | 10. Lymphatic system is present and well developed but lymphatic heart and lymphatic sinus are absent. |
|
224 videos|175 docs|151 tests
|
FAQs on Lymphatic System - Biology for JAMB
| 1. What is the function of the lymphatic system? |  |
| 2. How does the lymphatic system fight infections? |  |
| 3. Can the lymphatic system get blocked? What are the consequences? |  |
| 4. How can I keep my lymphatic system healthy? |  |
| 5. Are there any specific diseases or conditions associated with the lymphatic system? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JAMB exam
|

|

















