Endoplasmic Reticulum | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
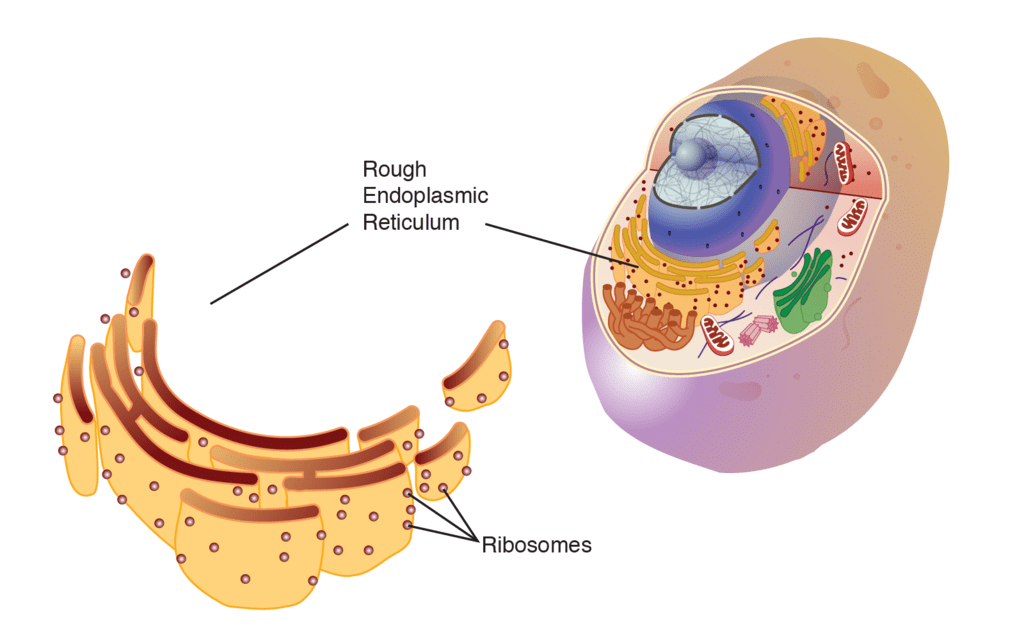
"Garnier" (1897) first observed them and called Ergastoplasm. E. R. name proposed by "Porter" (1961). (Credit for discovery of ER goes toPorter) Components of E.R. :–
(1) Cisternae - These are long flattened and unbranched units arranged in stacks.
(2) Vesicles - These are oval membrane bound structures.
(3) Tubules - These are irregular, often branched tubes bounded by membrane. Tubules may free or associated with cisternae.
- Structure of E.R. is like the golgi body but in E.R. cisternae, vesicles and tubules are isolated in cytoplasm and these do not form complex.
- Golgi body is localised cell organelle while E.R. is widespread in cytoplasm. E.R. is often termed as “System of Membranes”
| Rough E.R. (Granular) | Smooth E.R. (Agranular) |
(1) 80s ribosomes binds by their larger subunit, with the help of two glycoproteins (Ribophorin I and II) on the surface of Rough E.R. | (1) Ribosomes and Ribophorins absent |
| 2) More Stable structure | 2) Less Stable structure |
| 3) Mainly Composed of cisternae and vesicles | (3) Mainly composed of tubules. |
| 4) Abundantly occurs in cells which are actively engaged in protein synthesis e.g. liver, pancreas, Goblet cells. | (4) Abundantly occurs in cells concerned with glycogen and lipid metabolism. e.g. Adipose tissue, Interstitial cells, Muscles,Glycogen storing liver cells, and adrenal cortex. |



MODIFICATIONS OF E.R.
(1) Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (S.R.) :– These smooth E.R. occurs in skeletal and cardiac muscles. S.R. Stores Ca+2 and energy rich compounds required for muscle contraction.
(2) T-tubules :– These are transversely arranged tubules in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. These transmits stimulus for contraction of muscles.
(3) Ergastoplasm :– When the ribosomes are accumulated on the small parallel cisternae of E.R., then called Ergastoplasm. Ergastoplasm of nerve cells is called as Nissl's bodies.
(4) Myeloid Bodies :– Myeloid bodies are the specialised smooth E.R. which found in pigmented epithelial cells of the retina. Myeloid body is light sensitive structure and may be involved in pigment migration.
(5) Microsomes - These are pieces of E.R. with associated ribosomal particles (Claude 1951). These can be obtained by Fragementation and high speed centrifugation of cell. They do not exist as such in the living cell.
ENZYMES OF E.R.
Sucrases, NADH diphosphatase, Gulcose-6-phosphatase, NADH-cytochrome-C-reductase, Mg+2 activated ATPase, Nucleotide diphosphatase, Ascorbic acid synthase are enzymes of E.R.
FUNCTIONS OF E.R.
(1) Mechanical support :– Microfilaments, Microtubules and E.R. forms endoskeleton of cell.
(2) Intracellular exchange :– E.R. forms intracellular conducting system. Transport of materials in cytoplasm from one place to another may occurs through the E.R.
- At some places E.R. is also connected to P.M. So E.R. can secrete the materials outside the cell.
(3) Rough E.R. :– Provides site for the protein synthesis, because rough E.R., has ribosomes on its surface.
(4) Lipid Synthesis :– Lipids (cholesterol & phospholipids) synthesized by the agranular portion of E.R. (Smooth E.R.). The major lipids synthesized by S. E. R. are phospholipids and Cholesterol.
(5) Release of Glucose from Glycogen :– Endoplasmic reticulum seems to play a role in breakdown of glycogen (glycogenolysis).(The polymerisation of glucose to form glycogen probably occur in the cytosol not in the wall of S.E.R.)
(6) Cellular metabolism :– The membranes of the reticulum provides an increased surface for metabolic activities within the cytoplasm.
(7) Formation of nuclear membrane :– Fragmented vesicles of disintegrated nuclear membrane and ER elements arranged around the chromosomes to form a new nuclear membrane during cell division.
(8) Formation of lysosomes, Golgi–body & Micro–bodies. All the organelles are form by E.R. which have membrane except chloroplast and mitochondria (semi autonomous organelles)
(9) Detoxification :– Smooth ER concerned with detoxification of drugs, pollutants and steroids.
- Cytochrome P450 in E.R. act as enzyme which function in detoxification of drugs and other toxins
(10) E.R. provides the precursor of secretory material to golgi body.
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Endoplasmic Reticulum - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum in a cell? |  |
| 2. How is the endoplasmic reticulum structured? |  |
| 3. What are the differences between the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum? |  |
| 4. How does the endoplasmic reticulum play a role in protein synthesis? |  |
| 5. How does the endoplasmic reticulum contribute to lipid metabolism? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















