Introduction: Pollution & Pollutants | Chemistry for JAMB PDF Download
POLLUTION
"Any undesirable change in physical, chemical or biological characteristic of air, water and land which is harmful to the man directly or indirectly through the animals, plants industrial unit or raw materials is called pollution."
Pollutants
"Any material or product of man or nature which leads to pollution is called pollutants."
 Fig: Some common types of pollutants
Fig: Some common types of pollutants
Types of Pollutants:
Usually Pollutants are Divided into Following Categories:
1. Non-degradable pollutants: Many of such pollutants are usually not degraded or degraded partially in environment. Such as aluminium pecks, Mercury compounds of phenols, Glass, D.D.T., Benzene, BHC pesticides, etc.
They are collected in the environment and cause pollution. These pollutants are harmful even in low concentration and harm increases with their increasing concentration. No treatment is found in the nature for their recycling. There are only two methods by which we can stop the pollution caused by pollutant.
(i) Such type of substance should be banned by law.
(ii) Use their alternative substance.
 Fig: Non-degradable waste
Fig: Non-degradable waste
2. Biodegradable pollutants: The domestic sewage papers, woods, garbage, live stock wastes, etc. are easily degraded completely by micro-organisms, it becomes useful. But if these materials enter the environment in such large quantities, that they cannot be degraded completely then addition of these materials cause pollution in environment.
a. Primary pollutants- These persist in the form in which they are added to the environment. Eg., DDT, CO etc.
b. Secondary pollutants- These are formed by chemical reaction among primary pollutants. eg., Photochemical smog, London smog, PAN, O3.
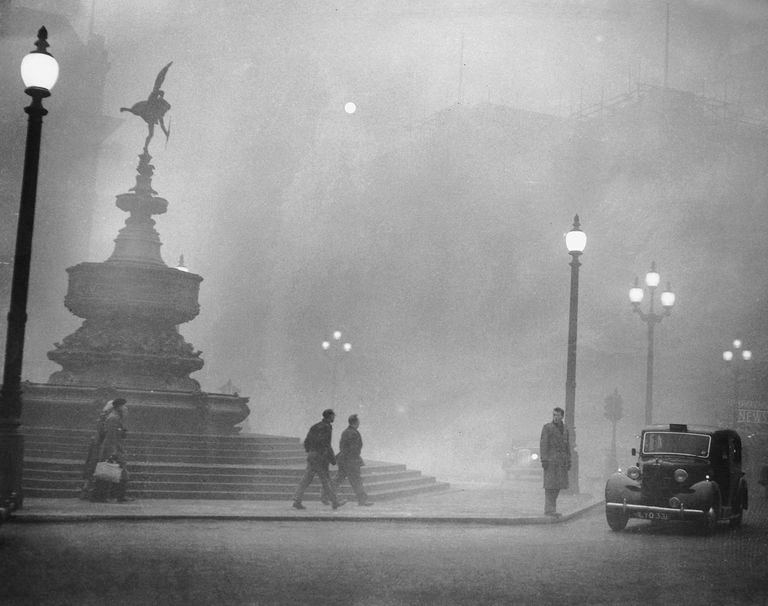 Fig: London smog
Fig: London smog
Synergism- Formation of secondary pollutants is known as synergism. Secondary pollutants are more toxic than primary pollutants.
1. Quantitative pollutants- These are the substances which occur in nature but become pollutant when their concentration reaches beyond a threshold value in the environment.
eg., CO2, Nitrogen oxide.
2. Qualitative pollutants- These are the substance which do not occur in the environment but are passed in through human activity. eg., Fungicides, Herbicides, DDT etc.
Other types of pollution:
1. Natural pollution- Caused by natural sources like, CH4 from paddy fields and cattle, marsh, forest fire.
 Fig: Forest fires2. Anthropogenic pollution- Caused by human activities.
Fig: Forest fires2. Anthropogenic pollution- Caused by human activities.
Main sources of pollution:
(i) Point source pollution- Where the effluent discharge occurs at a specific site.
eg., factory outlet and Municipal sewage.
(ii) Line source pollution- It is passed along a narrow belt, Roads, eg., Rods, Railway tracks.
(iii) Diffuse source pollution- It is over a large area.
eg., sprayed fertilizer or pesticides through run off.
(iv) Area source pollution- Industrial estate and mining area.

|
214 videos|199 docs|162 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction: Pollution & Pollutants - Chemistry for JAMB
| 1. What are the main sources of pollution? |  |
| 2. How does pollution affect human health? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of pollutants? |  |
| 4. How does pollution impact the environment? |  |
| 5. What measures can be taken to reduce pollution? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JAMB exam
|

|













