Menstrual Cycle: Introduction, Duration & Phases | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Menarche
The beginning of menstruation or first menstruation is called menarche. The beginning menstruation varies. It usually occurs between 12 and 15 years.
Menstrual Cycle
Duration – 28 Days (Range - 22 to 32 days)
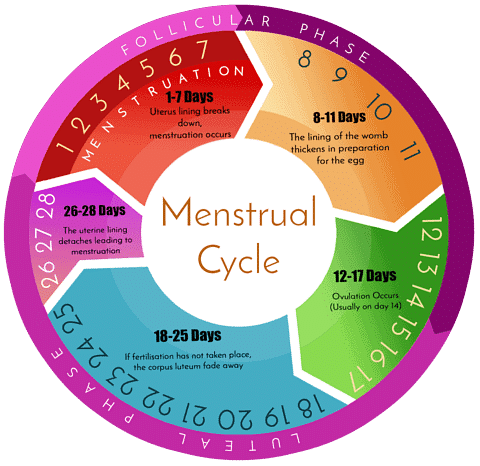
This is exhibited by the primate group of animals. In this cycle, the female body prepares itself for a possible pregnancy. If the pregnancy does not occur then the body aborts all preparation done and restarts the preparation for pregnancy again in a monthly cyclic manner.
 Flow Chart of Menstrual CycleThe menstrual cycle has three main phases:
Flow Chart of Menstrual CycleThe menstrual cycle has three main phases:
- Bleeding phase or menstruation phase.
- Proliferative/preovulatory/follicular phase or oestrogenic phase.
- Secretary/post-ovulatory/luteal phase or progesterone phase.
 Schematic Diagram of Menstrual Cycle
Schematic Diagram of Menstrual Cycle
1. Bleeding Phase
The cycle starts with the bleeding phase in its first four to five days. During this bleeding, the part of the layer of the endometrium gets shed off. The total loss of blood per day is about 20 ml, so an average of 40 to 80 ml blood/cycle is lost. This blood can not clot.
2. Preovulatory/Proliferative Phase
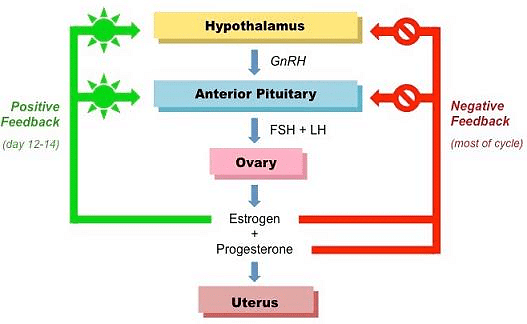
- After the first four of five days this phase begins. During this phase, due to the release of some GnRH, the Pituitary secretes some FSH to stimulate the ovarian follicle. The ovarian follicle now begins to develop.
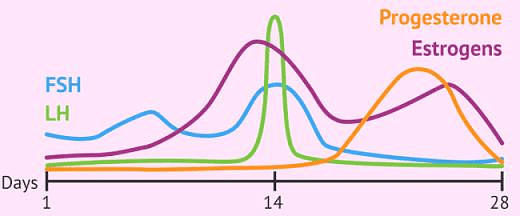
 Level of Hormones during Menstruation
Level of Hormones during Menstruation - Developing follicle now starts secreting an increasing amount of estrogen. The rising level of estrogen causes the endometrium to proliferate and thicken.
- It also causes an increase in the vascularity and granularity of the endometrium. The rising level of estrogen also activates the hypothalamus.
- Due to this, the hypothalamus releases more GnRH. This GnRH induces the pituitary to release more of FSH. The rising FSH levels now cause :
(i) Further growth and development ovarian follicle to form Graafian follicle
(ii) Even further release of estrogen from the theca interna of this developing follicle. - As the estrogen level goes on rising, by the end of 10 days the extreme levels of estrogen (which have by then caused maturation of Graafian follicle and growth of endometrium) now give positive feedback of high concentration of estrogen causing a rise in LH secretion but due to release of inhibin by graffian follicle, FHS falls secretome falls, therefore, the LH secretion from the pituitary goes on rising.
- This abrupt rise (on the 11th to 13th day) in LH concentration in blood is called an LH surge. This LH now causes the Graafian follicle to rupture after partial completion of II meiotic division in oocyte and thus the secondary oocyte released. The release of an egg (secondary oocyte) which occurs around 14 days is called ovulation.
3. Postovulatory/Secretory Phase
- After ovulation, the ruptured Graafian follicle transforms into the corpus luteum. The granulosa and theca cells of the ruptured Graafian follicle (which is now called corpus luteum) are found only in mammals and contain yellow lutein or carotene pigment.
- In case of absence of pregnancy, this corpus luteum will get degenerated after 14 days of its formation. The degenerated corpus luteum is called corpus Albicans (white body).
- Stimulated by the rising levels of LH, the corpus luteum secretes the progesterone hormone.
- The progesterone facilitates the preparation of the endometrium for receiving the embryo and its implantation. Progesterone inhibits the contractions of the uterus so that the pregnancy could be maintained.
- Progesterone also inhibits the development of the next new ovarian follicle. If pregnancy occurs then the corpus luteum persists and secretes progesterone.
- Progesterone is important to maintain the pregnancy and it is thus called the pregnancy hormone.
- By the fourth month of pregnancy, the placenta has developed completely.
- This placenta now takes over the job of further progesterone secretion.
- Ovary also secretes some amount of relaxin at the time of parturition.
- If pregnancy does not occur after ovulation, then as the progesterone level rise, its rising levels inhibit the release of GnRH from the hypothalamus. Due to this FSH, LH secretion by the pituitary falls and thereby progesterone secretion by the corpus luteum (which was due to the influence of LH) also now falls.
- As the progesterone level drops, the corpus luteum begins to degenerate and transform in corpus Albicans (which can not secrete progesterone). Due to the lack of progesterone.
1) The overgrown endometrium now begins to break and separate from the inner uterine wall causing bleeding.
2) The uterine contraction (which was till now inhibited due to the presence of progesterone) now starts. - Thus the separated endometrium along with blood is now being passed out via the vaginal route.
- This is again the beginning of the next menstrual or bleeding phase.
- The period between ovulation and the next menstrual bleeding (post-ovulatory period) is always constant (i.e. 14 days).
- However, the ovulation date may vary (causing a change in the pre-ovulatory period).
- After ovulation, the ovum is viable only for two days, while sperms introduced into the vagina can survive for a maximum of four days.
- On the basis of the above data, the safe period method for family planning is calculated.
- Normally it is considered to be day 1 to day 8 and then from day 20 to day 28.
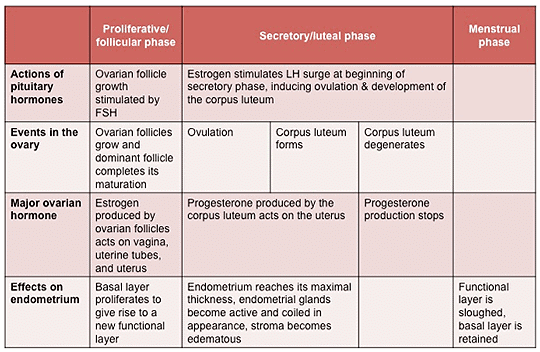
 Phases of Menstrual Cycle
Phases of Menstrual Cycle
Description of Different Phases of Menstrual Cycle
Menopause
It is a medical term that refers to the cessation of menstruation. It is the period in a woman's life when ovulation and menstruation cease. Period. It occurs between the ages of 45 and 55. Some women experience irregular menstrual cycles for months or years before menopause. Others simply discontinue menstruation abruptly.
Symptoms. The uterus and vagina gradually deteriorate (decreased work). During menopause, women may experience temporary depression, hot flashes, and other physiological and psychological issues. The majority of these symptoms can be alleviated by taking hormones prescribed by a doctor. However, due to some negative side effects, hormone replacement therapy is not recommended.
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on Menstrual Cycle: Introduction, Duration & Phases - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is menarche? |  |
| 2. What is the duration of the menstrual cycle? |  |
| 3. What are the phases of the menstrual cycle? |  |
| 4. What are the common symptoms experienced during the menstrual cycle? |  |
| 5. What is menopause? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|