Newton's Law of Cooling | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
8. Newton's law of cooling
According to this law, if the temperature T of the body is not very different from that of the surroundings T0, then rate of cooling -  is proportional to the temperature difference between them. To prove it let us assume that
is proportional to the temperature difference between them. To prove it let us assume that
T = T0 + Dt



if the temperature difference is small.
Thus, rate of cooling
 or
or 
as dT = dq or DT = Dq
8.1 Variation of temperature of a body according to Newton's law
Suppose a body has a temperature qi at time t = 0. It is placed in an atmosphere whose temperature is q0. We are interested in finding the temperature of the body at time t, assuming Newton's law of cooling to hold good or by assuming that the temperature difference is small. As per this law,


rate of cooling µ temperature difference
or  or
or 
Here  is a constant
is a constant


From this expression we see that q = qi at t = 0 and q = q0 at t = ¥, i.e., temperature of the body varies exponentially with time from qi to q0 (< qi). The temperature versus time graph is a shown in figure.
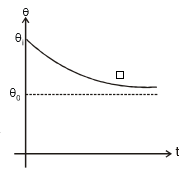
Note : If the body cools by radiation from q1 to q2 in time t, then taking the approximation
 and
and 
The equation  becomes
becomes

This form of the law helps in solving numerical problems related to Newton's law of cooling.
8.2 Limitations of Newton's Law of Cooling :
(a) The difference in temperature between the body and surroundings must be small
(b) The loss of heat from the body should be radiation only.
(c) The temperature of surroundings must remain constant during the cooling of the body.
Ex.20 A body at temperature 40°C is kept in a surrounding of constant temperature 20°C. It is observed that its temperature falls to 35°C in 10 minutes. Find how much more time will it take for the body to attain a temperature of 30°C.
Sol.

for the interval in which temperature falls from 40 to 35°C

for the next interval
(30 - 20) = (35 - 20) e-kt 


Alter: (by approximate method)
for the interval in which temperature falls from 40 to 35°C

from equation 

for the interval in which temperature falls from 35°C to 30°C

from equation (14.4)

⇒ required time,
9. NATURE OF THERMAL RADIATIONS : (WIEN'S DISPLACEMENT LAW)
From the energy distribution curve of black body radiation, the following conclusions can be drawn :
(a) The higher the temperature of a body, the higher is the area under the curve i.e. more amount of energy is emitted by the body at higher temperature.
(b) The energy emitted by the body at different temperatures is not uniform. For both long and short wavelengths, the energy emitted is very small.

(c) For a given temperature, there is a particular wavelength (lm) for which the energy emitted (El) is maximum
(d) With an increase in the temperature of the black body, the maxima of the curves shift towards shorter wavelengths.
From the study of energy distribution of black body radiation discussed as above, it was established experimentally that the wavelength (lm) corresponding to maximum intensity of emission decreases inversely with increase in the temperature of the black body. i.e.
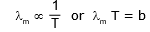
This is called Wien's displacement law.
Here b = 0.282 cm-K, is the Wien's constant.
|
97 videos|378 docs|103 tests
|
FAQs on Newton's Law of Cooling - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is Newton's Law of Cooling? |  |
| 2. How is Newton's Law of Cooling applied in real-life situations? |  |
| 3. What are the assumptions made in Newton's Law of Cooling? |  |
| 4. How can Newton's Law of Cooling be expressed mathematically? |  |
| 5. Can Newton's Law of Cooling be used for objects that are undergoing phase changes? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















