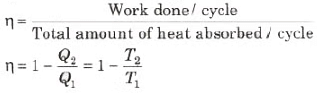Thermodynamics | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
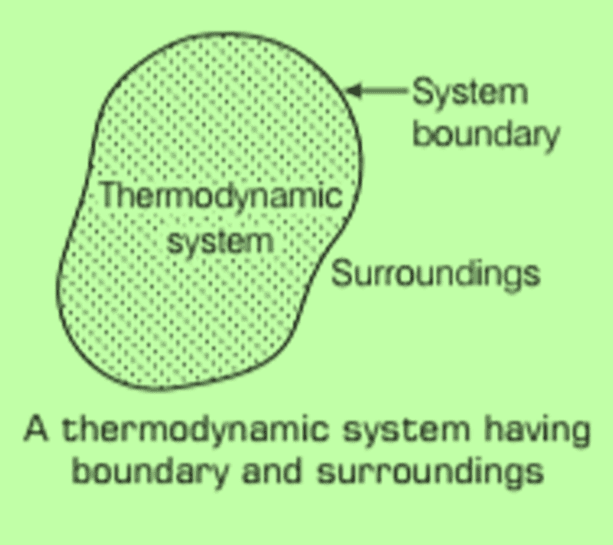
Thermodynamic System, Surroundings And Boundary
- A thermodynamic system consists of a large number of particles (like atoms or molecules), allowing it to have specific properties such as pressure, volume, and temperature. This system can exist in various forms, such as solid, liquid, gas, or a mixture of these states.
- The surroundings include everything outside the system that can affect it directly, like the environment. The space outside the system is known as its surroundings.
- The system is separated from its surroundings by a boundary. This boundary is a real or imaginary surface that encloses the space occupied by the system. It can allow or prevent the exchange of energy and work between the system and its surroundings, depending on its characteristics.

Thermal Equilibrium
Two systems are considered in thermal equilibrium if they are at the same temperature. Imagine two gases, A and B, separated by an adiabatic wall that prevents any heat exchange. If this wall is replaced by a diathermic wall, allowing heat to flow between them, then the pressure, volume, or both of the gases may change spontaneously until equilibrium is reached. In this state, there is no further flow of energy between A and B, indicating that they are at the same temperature and in thermal equilibrium.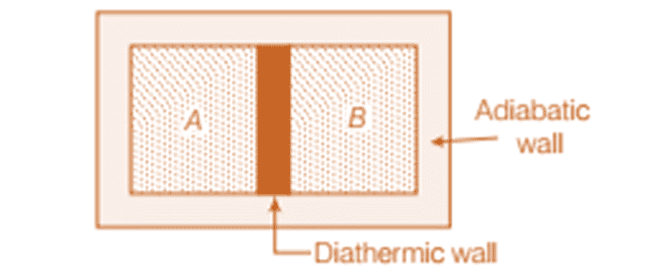
For two systems to be in equilibrium, certain conditions must be met:
- If no unbalanced forces or torques act on the system, it is in mechanical equilibrium.
- If the system undergoes no spontaneous internal changes like chemical reactions or diffusion, it is in chemical equilibrium.
- Thermal equilibrium occurs when there is no net flow of heat between systems in thermal contact.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
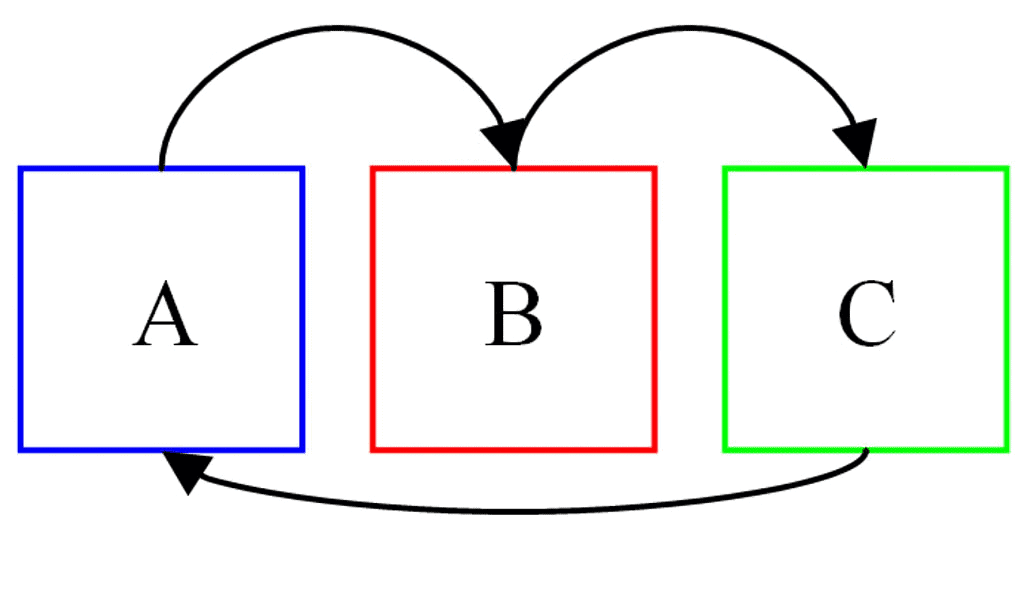
According to this law, two systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system separately are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Thus, if A and B are separately in equilibrium with C, that is
If TA = TC and TB = TC, then
⇒ TA = TB
i.e., the systems A and B are also in thermal equilibrium.
 Zeroth Law
Zeroth Law
Heat, Internal Energy, and Work
- Understanding the functioning of a heat engine and the microscopic movements within a glass of water unveils the realm of internal energy.
- Thermodynamics, the study of heat and work effects on state changes, is governed by fundamental rules known as thermodynamic laws.
- Energy generated or absorbed during chemical processes transforms following thermodynamic principles.
- Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another, forming the basis of energy transformation utilized across various sectors.
- Thermodynamics delves into the transfer of energy between different forms, exploring the intricate relationship between heat, temperature, energy, and work involved.
Internal Energy of an Ideal Gas
In an ideal gas, there are no attractive forces between molecules, meaning intermolecular forces are absent, and the gas lacks intermolecular potential energy (Up = 0).
Therefore, the internal energy of an ideal gas is solely the sum of the kinetic energies from various types of random molecular motion, such as translational, rotational, and vibrational movements. This internal energy of an ideal gas is directly related to its temperature.
Internal Energy of a Real Gas
In a real gas, the intermolecular forces are significant because the gas molecules exert mutual attraction on each other. This attraction means that energy is required to alter the distances between molecules.
Therefore, the internal energy of a real gas consists of both the internal kinetic energy and the internal potential energy of the gas molecules. It is influenced by the temperature and volume of the gas.
Key points regarding internal energy in a real gas:
Macroscopic State Variable: Internal energy is a state property, depending on the gas’s pressure, volume, temperature, mass, and composition, as shown when the container is at rest in Fig. (a).
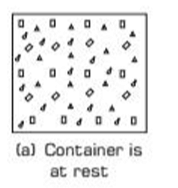
Path Independence: Internal energy depends on the system’s state, not the process or path used to reach that state.
Variable State Properties: Changes in internal energy lead to variations in the macroscopic state variables of the gas.
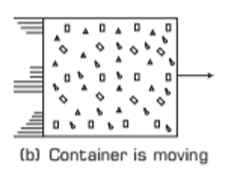
Exclusion of Kinetic Energy of Motion: In thermodynamics, the overall kinetic energy of the system's movement (e.g., if the gas container moves, as in Fig. (b)) does not contribute to the internal energy. Only the molecular motions within the gas matter for internal energy.
[Question: 1229827]
Sample Problems
Problem 1. When a piece of ice is placed on your hand, why do you feel a cold sensation?
Ans: Feeling a cold sensation when ice is placed on your hand occurs because the temperature of the ice is lower than that of your hand. Heat transfers from the warmer body (hand) to the colder body (ice).
Problem 2. Is it possible to determine the absolute value of internal energy? Why or why not?
Ans: The absolute value of internal energy cannot be precisely determined since it comprises various forms of energy, some of which are not directly measurable.
Problem 3. What factors influence the internal energy of a system?
Ans: Temperature and volume play crucial roles in altering the internal energy of a system. As the system's temperature rises, molecules gain speed, leading to increased kinetic energy.
Heat
It is the energy that exchanged between a system and its environment because of the temperature difference between them.
SI unit of heat is joule. The amount of heat Q given to a body to raise its temperature from Ti to Tf depends on mass, nature of substance and change in its temperature.
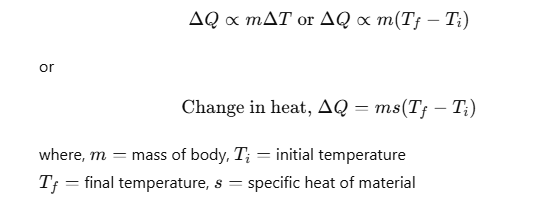
Work
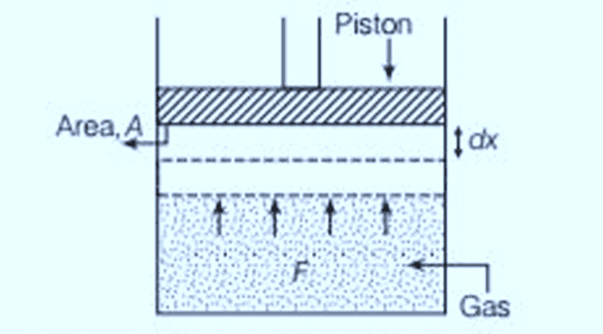
When we discuss "work" in thermodynamics, it refers to the work done by or on a system. For example, if a gas is in a cylinder with a movable piston and pressure p acts on the piston with area A, then the force F exerted by the gas on the piston is F= p A. If the piston moves an infinitesimally small distance dx, then the work dW done by the gas can be expressed as:
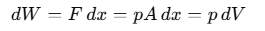
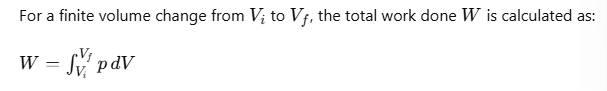
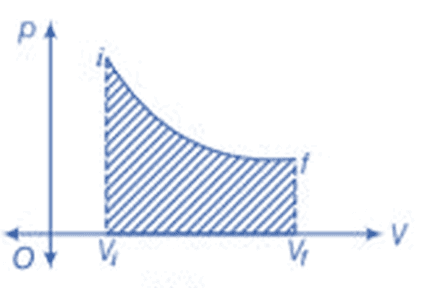 p - V diagram
p - V diagram
Work is path-dependent, meaning that it varies based on the process path taken. In cyclic processes, the work done corresponds to the area enclosed by the p - V curve, which is positive if clockwise and negative if counterclockwise.
Additionally, there are four ways to change the internal energy of a system:
- When work is done on the system (ΔW =−ve).
- When the system does work (ΔW =+ve).
- When heat is added to the system (ΔQ =+ve).
- When heat is removed from the system (ΔQ =−ve).
Example 1. Work done = 280 J, Force (F) = 51 N. Calculate the distance moved by the piston (s).
Ans. Formula: Work (W) = Force (F) x Distance (s)
Distance moved, s = 280 / F
s = 280 / (51 x 10)
s = 0.54 meters
Example 2. An electric heater supplies heat at 50 W and work done is 25 J/s. Find the rate of increase in internal energy.
Ans. Given: Heat supplied (Q) = 50 W, Work done (W) = 25 J/s
Internal Energy Change: Q = ΔU + W
ΔU = Q - W = 50 - 25 = 25 J/s
The internal energy increases at a rate of 25 J/s.
Heat and Work - Two Different modes of Energy Transfer
To understand the concept, consider the following experiment:
Place a gas-filled cylinder over a burner. Heat energy flows from the burner to the gas, which increases the internal energy of the gas.
When the piston in the cylinder is pushed upward, the gas does work as it expands, causing a decrease in its internal energy.
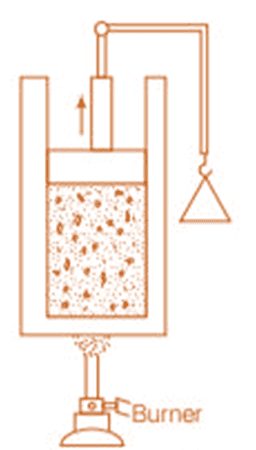 Experimental Arrangement
Experimental Arrangement
These changes can also occur in reverse. For example, if the gas is in contact with something colder, heat will flow out, reducing its temperature and internal energy. If the piston is pushed downward, work is done on the gas, increasing its internal energy.
Heat and work are two different ways to transfer energy and change the internal energy of a system. Heat refers to energy in transit, not a state variable. The system's state is described by internal energy.
In summary, heat and work are not state variables; they are energy transfer methods that change the system's internal energy.
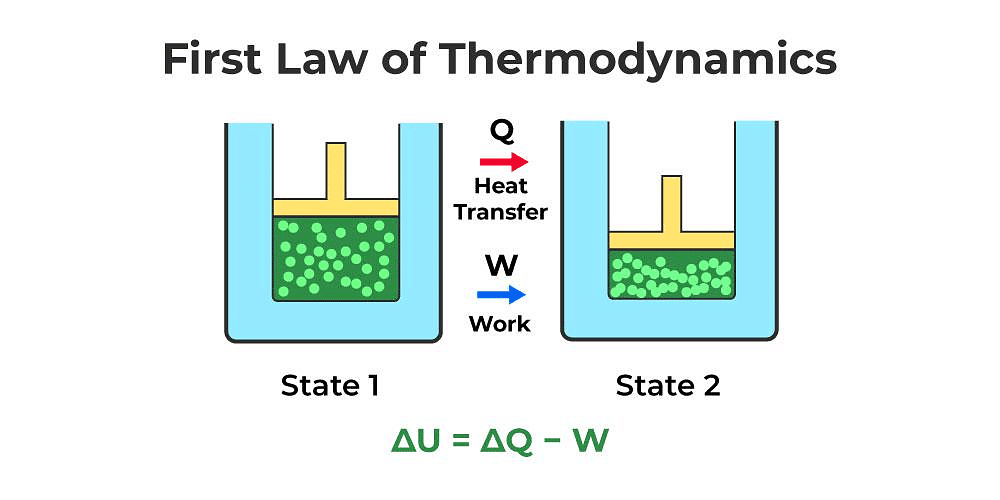
First Law of Thermodynamics
- Heat given to a thermodynamic system (ΔQ) is partially utilized in doing work (ΔW) against the surrounding and the remaining part increases the internal energy (ΔU) of the system.
ΔQ = ΔU + ΔW - First law of thermodynamics is a restatement of the principle conservation of energy.
- In an isothermal process, change in internal energy is zero (ΔU = 0), ΔQ = ΔW
- In an adiabatic process, no exchange of heat takes place, i.e., Δθ = O, ΔU = – ΔW
- In an adiabatic process, if gas expands, its internal energy and hence, temperature decreases and vice-versa.
- In an isochoric process, work done is zero, i.e., ΔW = 0, ΔQ = ΔU
Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics is important because it helps determine how much work can be done by transferring a certain amount of heat energy in a thermodynamic process. However, it has some limitations:
- It doesn't specify the direction in which heat will transfer.
- It doesn’t provide any details about the conditions necessary for heat to be transformed into work.
- It doesn't explain why all the heat energy cannot continuously be converted into mechanical work.
Heat Capacity
If an amount of heat ΔQ is needed to change its temperature by ΔT, then heat capacity can be defined as:
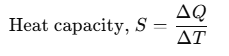
Heat capacity is numerically equal to the heat energy required to change the temperature of a body by unity. Its unit is J/K. Different amounts of heat may be needed for a unit rise in temperature at different temperatures.
Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of heat required to change the temperature of unit mass of a substance by unity is known as specific heat capacity of heat substance.
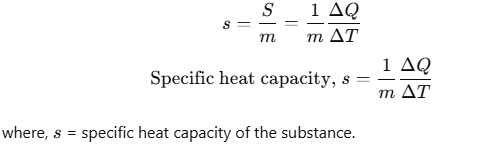
It depends on the nature of substance and its temperature. Its unit J/kg-K. Heat capacity per kg is known as specific heat capacity.
Molar Specific Heat Capacity
Heat capacity per mole is known as molar specific heat capacity.
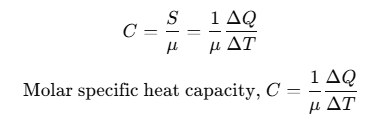
where, μ = number of moles.
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram mole of a substance through a unit is called molar specific heat capacity of the substance.
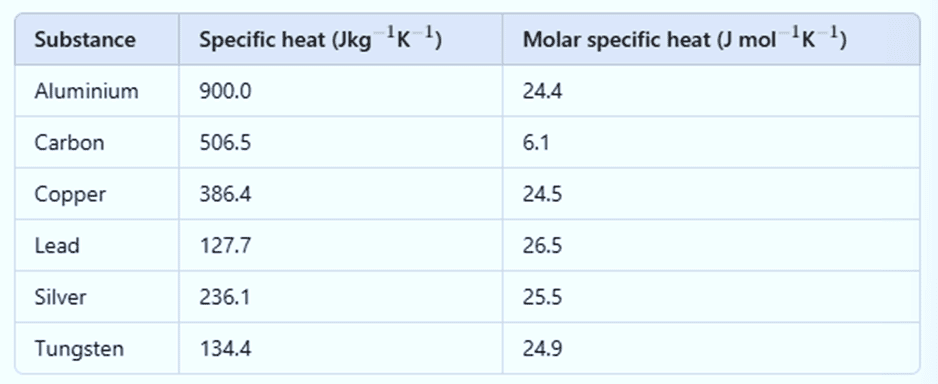
C depends on the nature of the substance, its temperature and the conditions under which heat is supplied. Its unit is J/mol-K.
Using the law of equipartition of energy, we can predict molar specific heat capacities of solids. In a solid consisting of N-atoms, the energy corresponding to vibration in each dimension about the mean position is given by 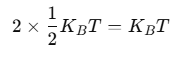
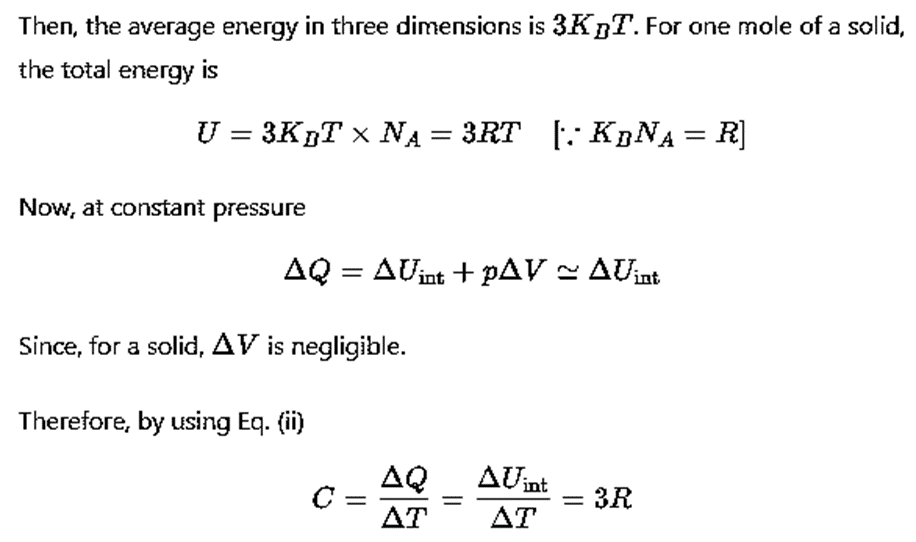
Specific Heat Capacity of Water
In old times, calorie was used as a unit of heat. It was initially defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C. Later, it was observed that the specific heat of water varies slightly with temperature, as shown in the figure below.
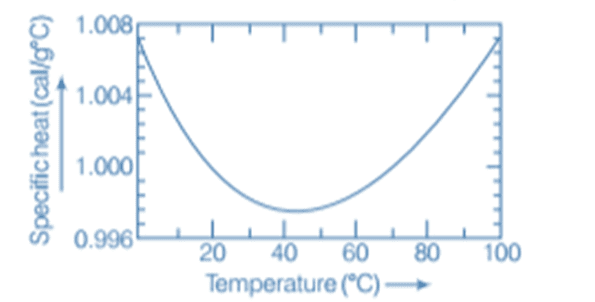 Variation of specific heat capacity of water with temperature
Variation of specific heat capacity of water with temperature
Specifically, one calorie is defined to be the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water from 14.5°C to 15.5°C.
Since heat is a form of energy, the joule (J) is preferred as the unit of heat in the SI system. The specific heat capacity of water in SI units is 4186 J/kg-K or 4.186 J/g-K.
Mechanical Equivalent of Heat
The mechanical equivalent of heat is defined as the amount of work needed to produce 1 calorie of heat. It acts as a conversion factor:
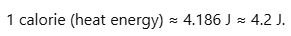
Specific Heat Capacities of Gases
For gases, specific heat capacity depends on the process or condition of heat exchange between the gas and its surroundings. There are two main specific heat capacities for a gas:
Molar heat capacity at constant volume (Cₚ):
- Defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one mole of gas by 1°C (or 1 K) at constant volume.
- Represented as Cᵥ.
Molar heat capacity at constant pressure (Cᵥ):
- Defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one mole of gas by 1°C (or 1 K) at constant pressure.
- Represented as Cₚ.
Note: For a gas, Cₚ > Cᵥ. At constant pressure, more heat is required to increase the temperature by 1°C (or 1 K) than at constant volume.
Relation between Cp and Cv (Mayer's Formula)
We can establish the relation between specific heat capacity at constant volume (Cv) and specific heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp) of a gas. For an ideal gas, the relation between Cp and Cv is:
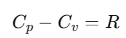
This relation is known as Mayer's Formula.
To establish the relation, we begin with the first law of thermodynamics for 1 mole of the gas:
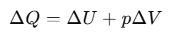
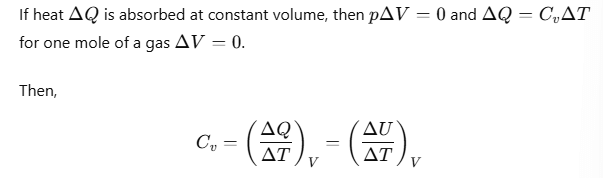
where the subscript V is dropped in the last step, since U of an ideal gas depends only on temperature, not on volume.
Now, heat ΔQ is absorbed at constant pressure, then
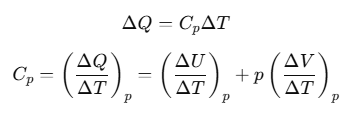
The subscript p can be dropped from the first term since U of an ideal gas depends only on T, not on pressure.
Now, by using Eq. (ii), we have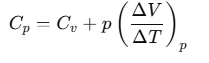
For one mole of an ideal gas, we can write pV=RT.
If the pressure is kept constant
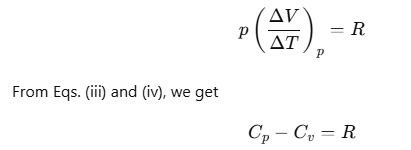
Here, Cp and Cv are molar specific heat capacities of an ideal gas at constant pressure and volume, respectively and R is the universal gas constant.
The ratio of Cp and Cv is notified by γ:
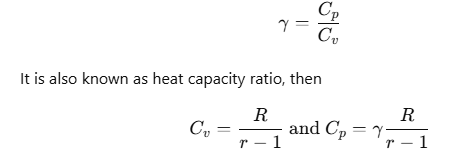
Thermodynamic State Variables and Equation of State
A thermodynamic system in equilibrium is described by specific values of state variables like pressure, volume, temperature, and mass.
Equilibrium State
A system does not start in equilibrium, but over time, it reaches mechanical and thermal equilibrium. For example, gases involved in an explosive chemical reaction, like petrol vapor and air ignited by a spark, initially aren’t in equilibrium. However, over time, the gas reaches a uniform state of temperature and pressure and attains equilibrium with its surroundings.
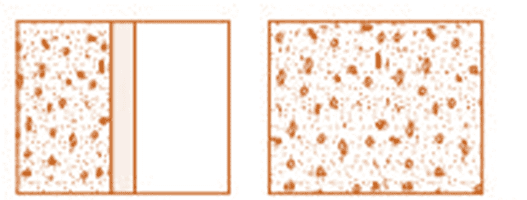 (a) Partition in the box is suddenly removed leading to free expansion of the gas
(a) Partition in the box is suddenly removed leading to free expansion of the gas
 (b) A mixture of gases undergoing an explosive chemical reactionEquation of State
(b) A mixture of gases undergoing an explosive chemical reactionEquation of State
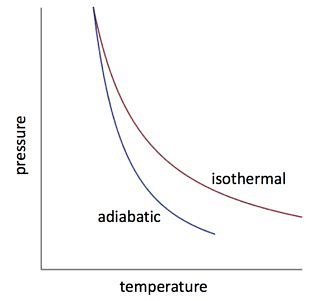
State variables are interconnected, and the relationship between them is called the equation of state. For example, an ideal gas follows the equation pV=μRT, where only two variables (like p and V or T and V) need to be fixed to define the system. A pressure-volume curve at constant temperature is called an isotherm.
Extensive and Intensive State Variables
State variables are either extensive or intensive.
Extensive Variables depend on system size, such as internal energy, volume, and total mass. Dividing a system in half also halves these values.
Intensive Variables are independent of system size, such as pressure, temperature, and density.
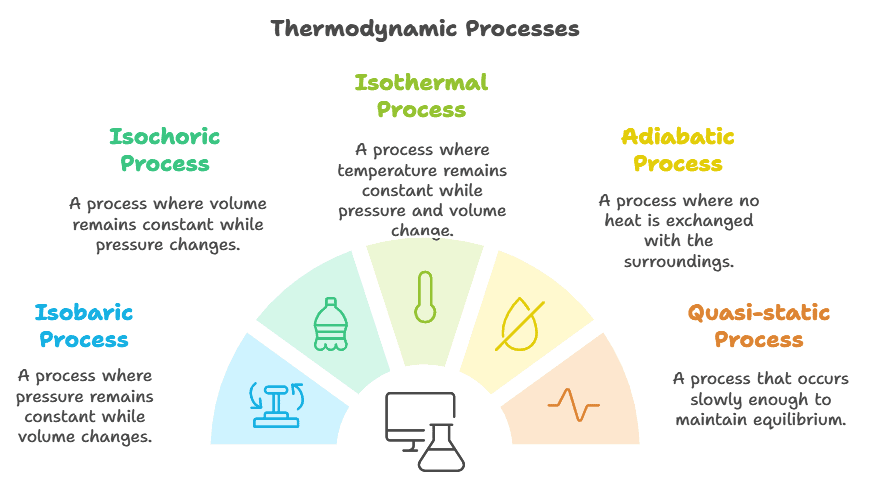
Types of Thermodynamic Processes
- Isobaric process
- Isochoric process
- Isothermal process
- Adiabatic process
- Quasi-static process
Isobaric Process
”Iso” means the same, and ”baric” means pressure.
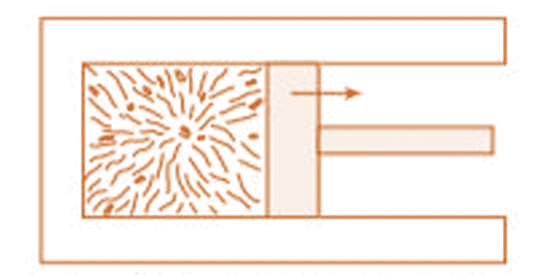
The processes during which the pressure of the system remains constant are called isobaric thermodynamic processes. Suppose there is a fuel in piston and cylinder arrangement. When this fuel burns the pressure of the gases, generated inside the engine. But if the gases are allowed to expand by allowing the piston to move outside, the pressure of the system can be constant.
PV Curve
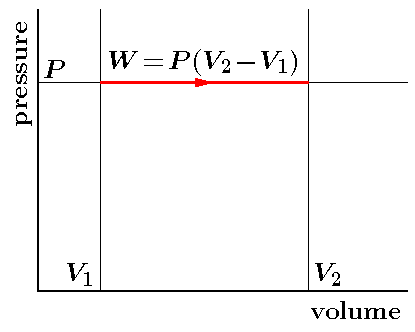
Practically, it is not possible to attain an ideal constant and constant pressure. An isobaric process is one in which the pressure is constant. The quantity of the gas in an isobaric process remains constant and the work done by the system is directly promotional to the change in volume or temperature of the system.
Isochoric Process
The process, during which the volume of the system remains constant, is an isochoric process. Heating of a gas in a closed cylinder is an example of the isochoric process. The change in temperature for a given amount of heat is determined by the specific heat of the gas at a constant volume.
Work done in an isochoric process
W = ∫ PdV
Here, dV = 0
Therefore, W = 0
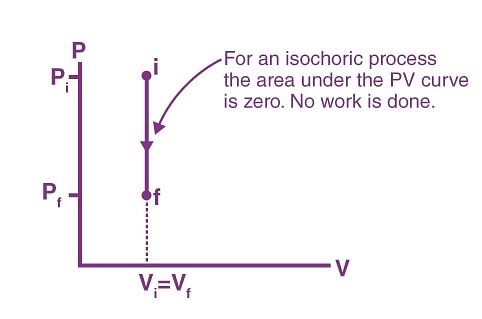
Isothermal Process
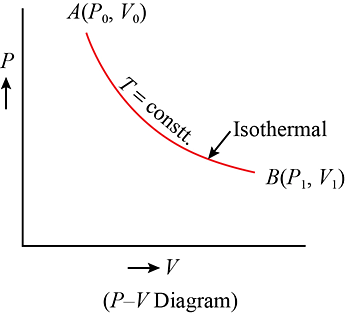
In an isothermal process, there is no change in temperature, that means the temperature remains constant.Like when hot water is kept in a thermos flask, if we remove a certain quantity of water from the flask, but keep its temperature constant then the process is said to be an isothermal process.
Adiabatic Process
The process, during which the heat content of the system remains constant, is an adiabatic process. During this process heat neither enters the system nor leaves the system.
For an adiabatic process,
ΔQ = 0
Then according to the first law of thermodynamics,
ΔU + ΔW = ΔQ = 0
where, Q is the heat supplied to the system and W is the work done by the system and U is the internal energy of the system.
Quasi-Static Process
When a process is which system remains close to an equilibrium state at each time, such process will be termed as the quasi-static process or quasi-equilibrium process. For example, if a person is coming down from roof to ground floor with the help of ladder steps then it is a quasi-static process. But if he jumps from roof to ground floor then it will not be a quasi-static process.
Question For You
Q1. The process in which the internal energy of the system remains constant is:
(a) Adiabatic
(b) Isobaric
(c) Isochoric
(d) Isothermal
Ans: (d)
Solution: Internal energy is a function of temperature only. Therefore, in case of an isothermal process, it will be constant.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics gives a fundamental limitation to the efficiency of a heat engine and the coefficient of performance of a refrigerator. It says that efficiency of a heat engine can never be unity (or 100%). This implies that heat released to the cold reservoir can never be made zero.
Kelvin’s Statement
It is impossible to obtain a continuous supply of work from a body by cooling it to a temperature below the coldest of its surroundings.
Clausius’ Statement
It is impossible to transfer heat from a lower temperature body to a higher temperature body without use of an external agency.
Planck’s Statement
It is impossible to construct a heat engine that will convert heat completely into work. All these statements are equivalent as one can be obtained from the other.
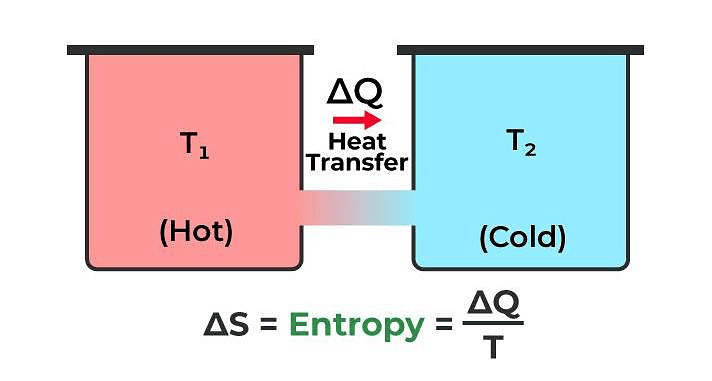
Entropy
Entropy is a physical quantity that remains constant during a reversible adiabatic change.
Change in entropy is given by dS = δQ / T
where, δQ = heat supplied to the system
and T = absolute temperature.
Entropy of a system never decreases, i.e., dS ≥ 0.
Entropy of a system increases in an irreversible process.
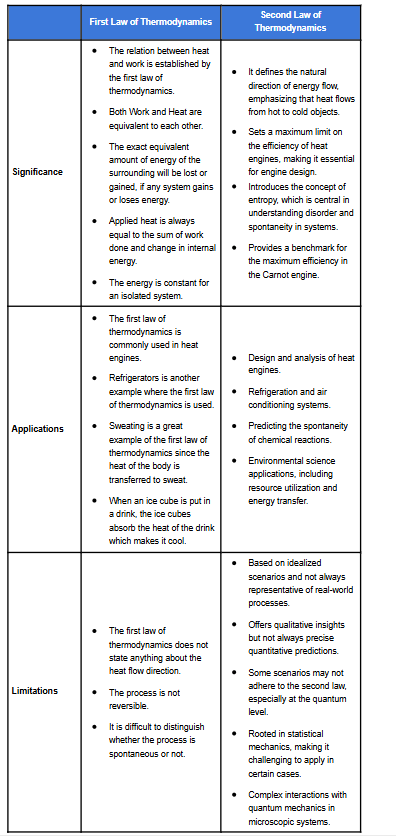
Here is the table for significance, limitations and applications for first and second law of thermodynamics:
Reversible Process
A thermodynamic process is reversible if the process can return back in such a that both the system and the surroundings return to their original states, with no other change anywhere else in the universe. It means both system and surroundings are returned to their initial states at the end of the reverse process.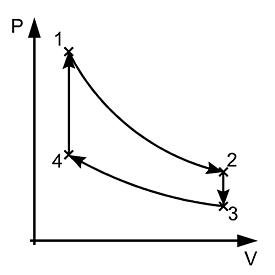
In the figure above, the system has undergone a change from state 1 to state 2. The reversible process can reverse completely and there is no trace left to show that the system had undergone thermodynamic change. During the reversible process, all the changes in state that occur in the system are in thermodynamic equilibrium with each other.
Internally reversible process
The process is internally reversible if no irreversibilities occur within the boundaries of the system. In these processes, a system undergoes through a series of equilibrium states, and when the process reverses, the system passes through exactly the same equilibrium states while returning to its initial state.
Externally reversible process
In externally reversible process no irreversibilities occur outside the system boundaries during the process. Heat transfer between a reservoir and a system is an externally reversible process if the surface of contact between the system and reservoir is at the same temperature.
A process can be reversible only when its satisfying two conditions
- Dissipative force must be absent.
- The process should occur in infinite small time.
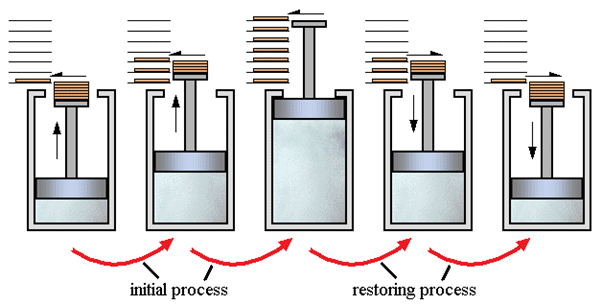
In simple words, the process which can reverse back completely is a reversible process. This means that the final properties of the system can perfectly reverse back to the original properties. The process can be perfectly reversible only if the changes in the process are infinitesimally small. In practical situations it is not possible to trace these extremely small changes in extremely small time, hence the reversible process is also an ideal process. The changes that occur during the reversible process are in equilibrium with each other.
Irreversible Process
Irreversible processes are a result of straying away from the curve, therefore decreasing the amount of overall work done. An irreversible process is a thermodynamic process that departs from equilibrium. In terms of pressure and volume, it occurs when the pressure (or the volume) of a system changes dramatically and instantaneously that the volume (or the pressure) do not have the time to reach equilibrium.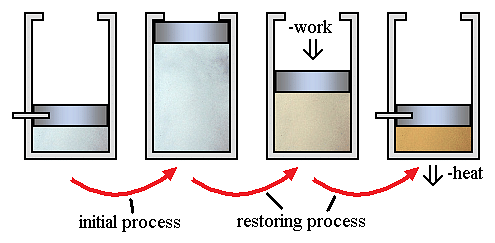
A classic example of an irreversible process is allowing a certain volume of gas to release into a vacuum. By releasing pressure on a sample and allowing it to occupy a large space, the system and surroundings are not in equilibrium during the expansion process.
Here little work occurs. However, there is a requirement of significant work, with a corresponding amount of energy dissipation as heat flows to the environment. This is in order to reverse the process.
Carnot Heat Engine
A heat energy engine is a device which converts heat energy into mechanical energy.
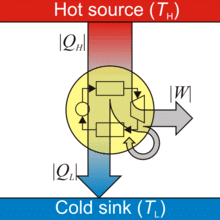 Heat Engine
Heat Engine
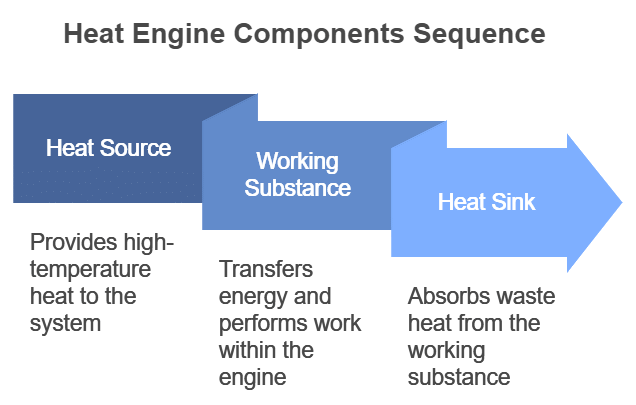
- A heat engine consists of three parts:
(i) Source of heat at higher temperature
(ii) Working substance
(iii) Sink of heat at lower temperature
- Thermal efficiency of a heat engine is given by

where Q1 is heat absorbed from the source,
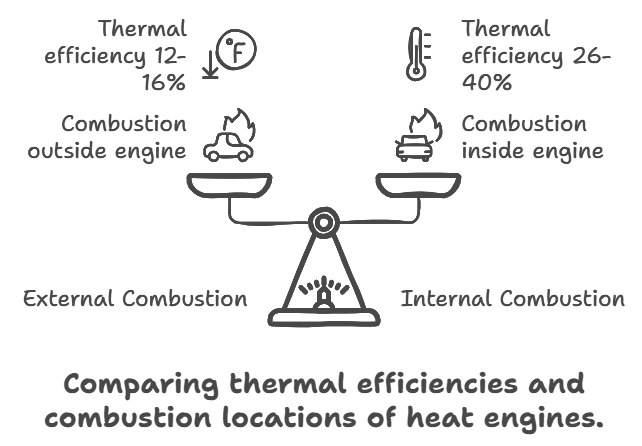
Q2 is heat rejected to the sink and T1 and T2 are temperatures of source and sink. - Heat engine are of two types:
(i)External Combustion Engine: In this engine fuel is burnt a chamber outside the main body of the engine. e.g., steam engine. In practical life thermal efficiency of a steam engine varies from 12% to 16%.
(ii)Internal Combustion Engine: In this engine, fuel is burnt inside the main body of the engine. e.g., petrol and diesel engine. In practical life thermal efficiency of a petrol engine is 26% and a diesel engine is 40%.
Carnot Cycle
Carnot devised an ideal cycle of operation for a heat engine, called Carnot Cycle.


Therefore, efficiency of the cycle is


A Carnot’s cycle contains the following four processes
(i) Isothermal expansion (AB)
(ii) Adiabatic expansion (BO)
(iii) Isothermal compression (CD)
(iv) Adiabatic compression (DA)
The net work done per cycle by the engine is numerically equal to the area of the loop representing the Carnot’s cycle .
After doing the calculations for different processes we can show that
[Efficiency of Carnot engine is maximum (not 1000/0) for given temperatures T1 and T2. But still Carnot engine is not a practical engine because many ideal situations have been assumed while designing this engine which can practically not be obtained.]
Refrigerator or Heat Pump
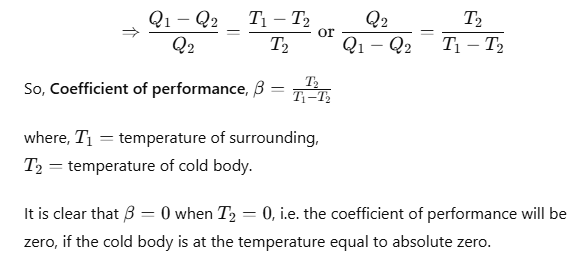
A refrigerator or heat pump is a device used for cooling things. It absorb heat from sink at lower temperature and reject a larger amount of heat to source at higher temperature.
Coefficient of performance of refrigerator is given by
where Q2 is heat absorbed from the sink, Q1 is heat rejected to source and T1 and T2 are temperatures of source and sink.
Relation between efficiency (η) and coefficient of performance (β)
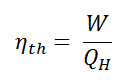
Coefficient of Performance of Carnot Engine
For Carnot refrigerator, 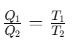
Example 3:


Example 4:
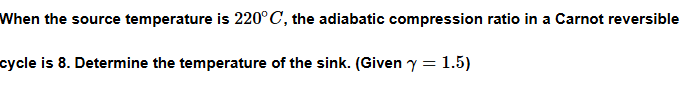
|
97 videos|379 docs|103 tests
|
FAQs on Thermodynamics - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How do heat, internal energy, and work relate to each other in thermodynamics? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of thermodynamic processes? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the First Law of Thermodynamics? |  |
| 5. How does the Second Law of Thermodynamics apply to real-world processes? |  |