Solid State & Classification of Solid Crystals | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Solid State (Crystallography) |

|
| Classification of Solids |

|
| Solids & Pseudo Solids |

|
| Classification of Solid Crystals on the basis of nature of bonds |

|
| Some Solved Questions for You |

|
Solid State (Crystallography)
Out of three states of matter, liquids and gases are fluids and possess fluidity on account of their molecular motion.
- On the other hand, solid-state has fixed positions of constituent ions (in ionic solids) or fixed positions of atoms (in molecular solids) and these atoms or ions can only oscillate about their position.
 Solid-state of matter possesses fixed mass, volume, shape, and rigidity
Solid-state of matter possesses fixed mass, volume, shape, and rigidity
- The chapter includes the studies on the geometry (the external form and internal structure) of crystals and crystalline substances, i.e., solids, their development, growth as well as related properties.
- Solids are characterized by their high density, low compressibility, definite shape, considerable mechanical strength, and rigidity.
- These properties are due to the existence of very strong intermolecular/ interatomic/ interionic forces of attraction amongst the molecules, atoms, or ions of the solids. These strong forces do not allow motion and confer rigidity and long-range orders in solids.
Classification of Solids
Solids are divided into two classes, namely crystalline and amorphous solids.
- A solid is said to be crystalline if the constituents atoms or ions are arranged in a very regular and long-range order fashion in a three-dimensional.
- On the other hand, in amorphous solids, the arrangement of building constituents is not regular (short-range order).
Difference between Crystalline and Amorphous Solids:

| Crystalline solids | Amorphous solids |
| 1. They have definite and regular geometry due to the definite and orderly arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in three-dimensional space. | 1. They do not have any pattern of arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules and, thus do not have any definite geometrical shape. |
| 2. They have sharp melting points and change abruptly into liquids. | 2. Amorphous solids do not have sharp melting points and do not change abruptly into liquids. |
| 3. Crystalline solids are anisotropic. Some of their physical properties are different in different directions. | 3. Amorphous solids are isotopic. Their physical properties are the same in all direction. |
| 4. These are considered true solids. | 4. These are considered pseudo solids or supercooled liquids. |
| 5. Crystalline solids are rigid and their shape is not distorted by mild distorting forces. | 5. Amorphous solids are not very rigid. These can be distorted by bending or compressing forces. |
| 6. Crystals are bound by plane faces. The angle between any two faces is called an interfacial angle. For a given crystalline solid, it is a definite angle and remains always constant no matter how the faces develop. When a crystalline solid is hammered, it breaks up into smaller crystals of the same geometrical shape. | 6. Amorphous solids do not have well-defined planes. When an amorphous solid is broken, the surfaces of the broken pieces are generally not flat and intersect at random angles. (Amorphous solids do not have any symmetry) |
| 7. Example: NaCl, KCl, Sugar, Quartz, etc. | 7. Example: Plastic, Glass, Rubber, etc. |
Solids & Pseudo Solids
Solids are also classified as true solids and pseudo solids.
- A pseudo solid is more easily distorted by bending and compressing forces. It may even tend to flow slowly under its own mass and lose shape.
- The rigidity and shape of pseudo solids are only apparent. These do not melt sharply and are gradually softened over a wide range of temperatures and eventually lapse into a liquid state.
- Pitch and glass are referred to as pseudo solids. On account of the above characteristics, the term pseudo solids have now been replaced by supercooled liquids.
- Thus, pitch and glass are now called supercooled liquids.
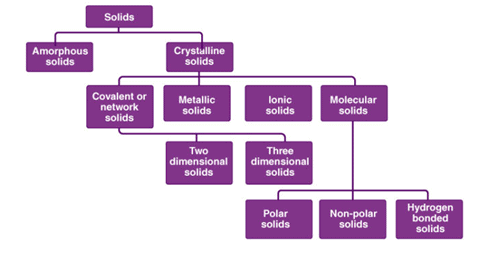
Classification of Solid Crystals on the basis of nature of bonds
The attractive forces which hold together atoms or molecules of a substance in form of groups are called bonds.
- The forces that hold crystals particles together are generally of five types and thus crystals can be classified into five types according to be types of bonds that hold the constituent particles of the crystals because of these forces.
(a) Ionic Crystals:
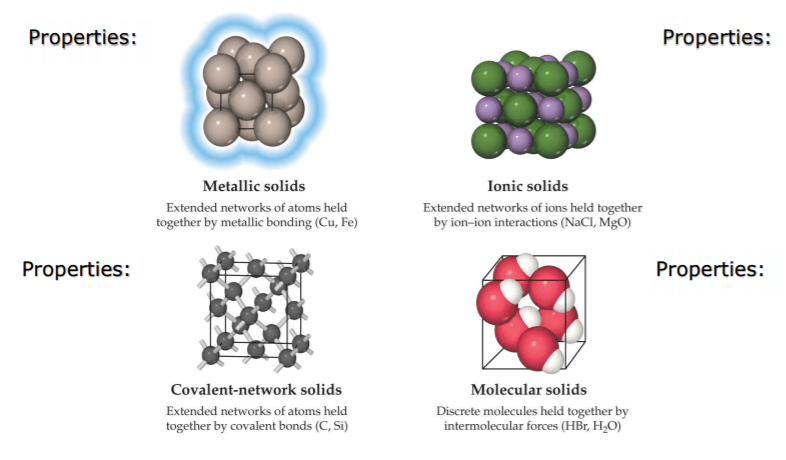
Ionic solids are built from the mutual attractions of cations and anions. The lattices in ionic crystals consist of alternately positive and negative ions in equivalent amounts arranged in order so that the potential energy of the ions in the lattice is minimum. The forces which bind the constituent ions are electrostatic in nature and are strong forces. Such crystals are normally found in ionic compounds, e.g., NaCl, MgCl2, KCl, etc.
(b) Molecular Crystals:
Molecular solids are assemblies of discrete molecules held in place by intermolecular forces. In molecular crystals, the repeating unit is chemically identifiable atoms or molecules which do not carry a net charge. Molecular solids are further divided into three categories.
- Non-polar Molecular Solids: Molecular bonds are formed for those elements or compounds whose electronic configuration is such that there is little transfer of electrons between their atoms, e.g., noble gases. These bonds are arised from the Vander Waals’ forces of attractions which exist between atoms of molecules. In these solids, the atoms or molecules (H2, Cl2, O2, etc.) are held by weak dispersion forces of London forces. These forces being relatively weaker than forces involved in ion and covalent bonding and hence cohesive forces or bonding energy of molecular crystals are small.
- Polar Molecular Solids: The molecules like HCl, SO2, are formed by polar covalent bonds. The molecules in such solids are held together by relatively stronger dipole-dipole attraction. Most of these types of solids are gases or liquids at room temperature.
- Hydrogen Bonding Crystals: The molecules having H-atom attached on N, O or f give rise to hydrogen bonding crystals. The existence of H-bonding in the crystal lattice is beyond doubt, e.g., in ice crystal, each oxygen atom is surrounded by four hydrogen atoms at the corner of the tetrahedral structure. Hydrogen bonded crystals have the same features as covalent crystals.
(c) Covalent Crystals:
- Covalent solids or network solids consist of atoms covalently bonded to their neighbors throughout the extent of solid.
- In covalent crystals, atoms at their lattice point are held together by shared pairs of electrons between them.
- The covalent bonding extends throughout the crystals in a spatial direction and has no small molecules in the conventional sense.
- The continuous, directional, and rigid bonding in the lattice makes the whole crystal a single large molecule.
- Pure covalent solids are good insulators because all the valence electrons are tightly held in the covalent bonding. However, in presence of certain impurities, they become reasonably good conductors and are known as semiconductors.
- Since covalent bonds are relatively weaker than ionic bonds and therefore covalent solids have relatively lower m.pt.
- However, covalent solids with giant molecular structures possess very high m.pt. e.g., carbon; the two crystalline polymorphous of carbon are diamond and graphite.
(d) Metallic Crystal:
In metallic crystals, the lattice consists of an assembly of positive ions immersed in a sea of mobile electrons. The binding force is due to:
- The attraction between positive ions or ion cores (consisting of a nucleus and non-valence electrons) of the metal and electron cloud of valence electrons,
- The mutual repulsion of free electrons,
- The mutual repulsion of ion cores.
- The electrons cloud of valence electrons can migrate throughout the crystal lattice and gives rise to high electrical conductance, metallic luster, and thermal conductivity, etc.
Some Solved Questions for You
Q.1. The molecules in polar molecular solid are held together by __________
a) dipole-dipole interaction
b) london forces
c) ionic bond
d) metallic bond
Answer: a
Explanation: The force responsible for holding together the molecules of polar molecular solids is a dipole-dipole force of attraction. Polar molecular solids are non-conductors of electricity.
Q.2. Which of the following tend to be volatile liquids or soft solids at room temperature and pressure?
a) Non polar molecular solids
b) Metallic solids
c) Polar molecular solids
d) Hydrogen bonded molecular solids
Answer: d
Explanation: In hydrogen bonded molecular solid, the intermolecular forces are strong hydrogen bonds. Hence, it tends to be volatile liquids or soft solids at room temperature and pressure.
Q.3. Which type of solids are formed by a three-dimensional arrangement of cations and anions bound by strong electrostatic force?
a) Polar molecular solids
b) Ionic solids
c) Covalent solids
d) Metallic solids
Answer: b
Explanation: Ionic solids are made up of three-dimensional arrangement of cations and anions bound by strong electrostatic force.
Q.4. Which of the following is non-conductor of electricity at solid state but can conduct electricity in the molten state or when dissolved in water?
a) Non polar molecular solids
b) Metallic solids
c) Ionic solids
d) Hydrogen bonded molecular solids
Answer: c
Explanation: Ionic Solids, when dissolved in water, tend to separate cations and the anions which allows the solution to conduct electricity. Also, they have high melting and boiling points.
Q.5. Which of the following is an orderly collection of positive ions surrounded and held together by a sea of electrons?
a) Gas
b) Non-metal
c) Metal
d) Metalloids
Answer: c
Explanation: Metal is said to be an orderly collection of positive ions surrounded and held together by a sea of delocalized electrons. These delocalized electrons are mobile and are responsible for the conduction of electricity.
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Solid State & Classification of Solid Crystals - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What is solid state crystallography? |  |
| 2. How are solids classified in the field of crystallography? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of crystals based on the nature of bonds? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of crystals belonging to different classifications? |  |
| 5. How is solid state crystallography relevant in various scientific fields? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|


















