Components of a Computer System - Computer Architecture, Computer Science and IT Engineering - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Components of a Computer System
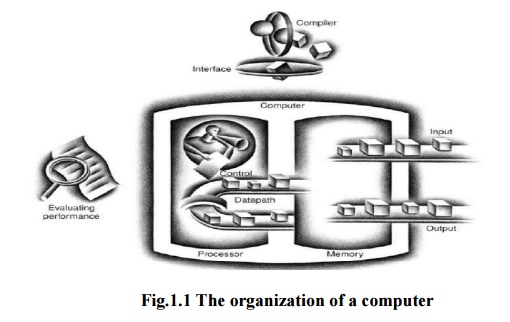
The five classic components of a computer are input, output, memory, datapath, and control. Datapath and control are combined and called as the processor.
COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM
The five classic components of a computer are input, output, memory, datapath, and control. Datapath and control are combined and called as the processor. The figure 1.1 shows the standard organization of a computer. This organization is independent of hardware technology.
The organization of a computer, showing the five classic components.
1. Input writes data to memory
2. Output reads data from memory
3. Memory stores data and programs
4. Control sends the signals that determine the operations of the datapath, memory, input, and output.
5. Datapath performs arithmetic and logic operations
Two key components of computers:
1. Input devices, such as the keyboard and mouse,
2. Output devices, such as the screen.
- Input device - A mechanism through which the computer is fed information, such as the keyboard or mouse.
- Output device - A mechanism that conveys the result of a computation to a user or another computer.
As the names suggest, input feeds the computer, and output is the result of computation sent to the user. Some devices, such as networks and disks, provide both input and output to the computer.
Input Device
The most commonly used input device is a keyboard. Whenever the user presses a key the control signal be sent to the processor. The processor respond for that by displaying the corresponding character on the display.
The next commonly used input device is a mouse.The original mouse was electromechanical and used a large ball. When it is rolled across a surface, it would cause an x and y counter to be incremented. The amount of increase in each counter told how far the mouse had been moved.
The electromechanical mouse has been replaced by the optical mouse. The optical mouse is actually a miniature optical processor including an LED to provide lighting, a tiny black-and-white camera, and a simple optical processor. The LED illuminates the surface underneath the mouse; the camera takes 1500 sample pictures a second under the illumination. Successive pictures are sent to a simple optical processor that compares the images and determines whether the mouse has moved and how far.
Output Device
The most fascinating I/O device is probably the graphics display. Most personal mobile devices use liquid crystal displays (LCDs) to get a thin, low-power display. The LCD is not the source of light; instead, it controls the transmission of light. A typical LCD includes rod-shaped molecules in a liquid that form a twisting helix that bends light entering the display, from either a light source behind the display or less often from reflected light.
Today, most LCD displays use an active matrix that has a tiny transistor switch at each pixel to precisely control current and make sharper images. As in a CRT, a red-green-blue mask associated with each pixel determines the intensity of the three color components in the final image; in a color active matrix LCD, there are three transistor switches at each pixel.
The computer hardware supports a refresh buffer, or frame buffer, to store the bit map. The image to be represented on-screen is stored in the frame buffer, and the bit pattern per pixel is read out to the graphics display at the refresh rate.
Pixel - The smallest individual picture element. Screen are composed of hundreds of thousands to millions of pixels, organized in a matrix.
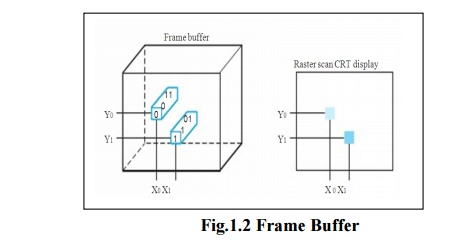
Each coordinate in the frame buffer on the left determines the shade of the corresponding coordinate for the raster scan CRT display on the right. Pixel (X0, Y0) contains the bit pattern 0011, which is a lighter shade of gray on the screen than the bit pattern 1101 in pixel (X1, Y1).
Processor
Central processor unit (CPU) - Also called processor. The active part of the computer, which contains the datapath and control and which adds numbers, tests numbers, signals I/O devices to activate, and so on. The processor gets instructions and data from memory.
- · Datapath - The component of the processor that performs arithmetic operations.
- Control - The component of the processor that commands the datapath, memory, and I/O devices according to the instructions of the program.
Memory
- Memory The storage area in which programs are kept when they are running and that contains the data needed by the running programs.
- Primary memory - Also called main memory. It is a Volatile memory used to hold programs while they are running; typically consists of DRAM in today’s computers.
- Dynamic random access memory (DRAM) Memory built as an integrated circuit, it provides random access to any locationSecondary memory Non- volatile memory used to store programs and data between runs; typically consists of magnetic disks in today’s computers.
- Magnetic disk (also called hard disk) A form of nonvolatile secondary memory composed of rotating platters coated with a magnetic recording material.
- Cache memory A small, fast memory that acts as a buffer for a slower, larger memory. Cache is built using a different memory technology, static random access memory (SRAM). SRAM is faster but less dense, and hence more expensive, than DRAM.
- Volatile memory Storage, such as DRAM, that only retains data only if it is receiving power.
- Nonvolatile memory A form of memory that retains data even in the absence of a power source and that is used to store programs between runs. Magnetic disk is nonvolatile and DRAM is not.
Removable storage technologies:
- Optical disks, including both compact disks (CDs) and digital video disks (DVDs), constitute the most common form of removable storage.
- Magnetic tape provides only slow serial access and has been used to back up disks, in a role now often replaced by duplicate hard drives.
- FLASH-based removable memory cards typically attach by a USB (Universal Serial Bus) connection and are often used to transfer files.
- Floppy drives and Zip drives are a version of magnetic disk technology with removable flexible disks. Floppy disks were the original primary storage for personal computers, but have now largely vanished.
FAQs on Components of a Computer System - Computer Architecture, Computer Science and IT Engineering - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What are the main components of a computer system? |  |
| 2. What is computer architecture? |  |
| 3. What is computer science? |  |
| 4. What is IT engineering? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between computer science engineering (CSE) and IT engineering? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
















