BGB (Broader Gateway Protocol) Interdomain Routing | Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
BGB (Broader Gateway Protocol) Interdomain Routing
The Internet is organized as autonomous systems, each of which is under the control of a single administrative entity. A corporation’s complex internal network might be a single AS, as may the network of a single Internet service provider. A key design goal of interdomain routing is that policies like the example above, and much more complex ones, should be supported by the interdomain routing system.To make the problem harder, I need to be able to implement such a policy without any help from other ASs, and in the face of possible misconfiguration or malicious behavior by other ASs.
There have been two major interdomain routing protocols in the recent history of the Internet. The first was the Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP). EGP had a number of limitations, perhaps the most severe of which was that it constrained the topology of the Internet rather significantly. EGP basically forced a treelike topology onto the Internet, or to be more precise, it was designed when the Internet had a treelike topology, such as that illustrated in Figure. EGP did not allow for the topology to become more general. Note that in this simple treelike structure, there is a single backbone, and autonomous systems are connected only as parents and children and not as peers.
The replacement for EGP is the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), which is in its fourth version at the time of this writing (BGP-4). BGP is also known for being rather complex. This section presents the highlights of BGP-4.As a starting position, BGP assumes that the Internet is an arbitrarily interconnected set of ASs. Given this rough sketch of the Internet, if we define local traffic as traffic that originates at or terminates on nodes within an AS, and transit traffic as traffic that passes through an AS, we can classify ASs into three types:
■ Stub AS: an AS that has only a single connection to one other AS; such an AS will only carry local traffic. The small corporation is an example of a stub AS.
■ Multihomed AS: an AS that has connections to more than one other AS but that refuses to carry transit traffic;
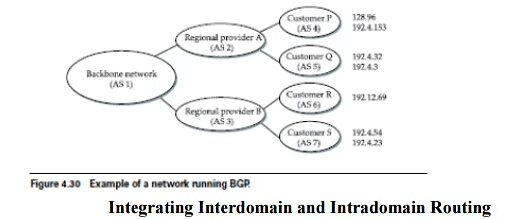
■ Transit AS: an AS that has connections to more than one other AS and that is designed to carry both transit and local traffic, such as the backbone providers. The first is simply a matter of scale. An Internet backbone router must be able to forward any packet second challenge in inter domain routing arises from the autonomous nature of the domains. Note that each domain may run its own interior routing protocols, and use any scheme they choose to assign metrics to paths. This means that it is impossible to calculate meaningful path costs for a path that crosses multiple ASs. A cost of 1,000 across one provider might imply a great path, but it might mean an unacceptably bad one from another provider. As a result, interdomain routing advertises only reach ability. The concept of reach ability is basically a statement that “you can reach this network through this AS.” This means that for interdomain routing to pick an optimal path is essentially impossible.
The third challenge involves the issue of trust. Provider A might be unwilling to believe certain advertisements from provider B for fear that provider B will advertise erroneous routing information.
For example, trusting provider B when he advertises a great route to anywhere in the Internet can be a disastrous choice if provider B turns out to have made a mistake configuring his routers or to have insufficient capacity to carry the traffic. the task of forwarding packets between ASs. BGP does not belong to either of the two main classes of routing protocols (distance-vector and link-state protocols) prefix.
Integrating Interdomain and Intradomain Routing
The final level of complexity comes in backbone networks, which learn so much routing information from BGP that it becomes too costly to inject it into the intradomain protocol. For example, if a border router wants to inject 10,000 prefixes that it learned about from another AS, it will have to send very big link-state packets to the other routers in that AS, and their shortest-path calculations are going to become very complex.
For this reason, the routers in a backbone network use a variant of BGP called interior BGP (iBGP) to effectively redistribute the information that is learned by the BGP speakers at the edges of the AS to all the other routers in the AS. (The other variant of BGP, discussed above, runs between ASs and is called exterior BGP or eBGP.) Ibgp enables any router in the AS to learn the best border router to use when sending a packet to any address.At the same time, each router in the AS keeps track of how to get to each border router using a conventional intradomain protocol with no injected information. By combining these two sets of information, each router in the AS is able to determine the appropriate next hop for all prefixes.
|
21 videos|113 docs|66 tests
|
FAQs on BGB (Broader Gateway Protocol) Interdomain Routing - Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is BGB (Broader Gateway Protocol) and how does it relate to interdomain routing? |  |
| 2. What are the benefits of using BGB for interdomain routing? |  |
| 3. How does BGB handle routing updates and maintain routing tables? |  |
| 4. What are some of the challenges in BGB interdomain routing? |  |
| 5. Are there any alternatives to BGB for interdomain routing? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|

















