Link State (OSPF) | Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Link State(OSPF)
Link-state routing is the second major class of intra domain routing protocol. The starting assumptions for link-state routing are rather similar to those for distance-vector routing. Each node is assumed to be capable of finding out the state of the link to its neighbors (up or down) and the cost of each link.
Reliable Flooding
Reliable flooding is the process of making sure that all the nodes participating in the routing protocol get a copy of the link-state information from all the other nodes. As the term “flooding”suggests, the basic idea is for a node to send its link-state information out on its entire directly connected links, with each node that receives this information forwarding it out on all of its links. This process continues until the information has reached all the nodes in the network.
- The ID of the node that created the LSP;
- A list of directly connected neighbors of that node, with the cost of the link to
- each one;
- A sequence number;
- A time to live for this packet.
One of the most widely used link-state routing protocols is OSPF. The first word, “Open,” refers to the fact that it is an open, nonproprietary standard, created under the auspices of the IETF. The “SPF” part comes from an alternative name for link-state routing.

- Authentication of routing messages
- Additional hierarchy
- Load balancing
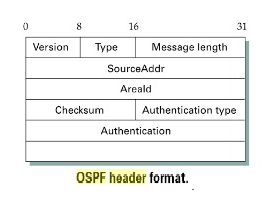
OSPF Header Format
There are several different types of OSPF messages, but all begin with the same header The Version field is currently set to 2, and the Type field may take the values 1 through 5. The SourceAddr identifies the sender of the message, and the AreaId is a 32-bit identifier of the area in which the node is located. The entire packet, except the authentication data, is protected by a 16-bit checksum using the same algorithm as the IP header (see Section 2.4). The Authentication type is 0 if no authentication is used; otherwise it may be 1, implying a simple password is used, or 2, which indicates that a cryptographic authentication checksum, of the sort described in Section 8.3, is used. In the latter cases the Authentication field carries the password or cryptographic checksum.Of the five OSPF message types, type 1 is the “hello” message, which a router sends to its peers to notify them that it is still alive and connected as described above.
The remaining types are used to request, send, and acknowledge the receipt of link-state messages. The basic building block of link-state messages in OSPF is known as the linkstate advertisement (LSA). One message may contain many LSAs. The LS sequence number is used exactly as described above, to detect old or duplicate LSAs.
|
21 videos|113 docs|66 tests
|
FAQs on Link State (OSPF) - Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is Link State in OSPF? |  |
| 2. How does OSPF use Link State information? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using Link State routing in OSPF? |  |
| 4. How does OSPF ensure the reliability of Link State information? |  |
| 5. Can OSPF operate without Link State information? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|

















