Bipolar Transistor Configurations | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
Bipolar Transistor Configurations
As the Bipolar Transistor is a three terminal device, there are basically three possible ways to connect it within an electronic circuit with one terminal being common to both the input and output. Each method of connection responds differently to its input signal within a circuit as the static characteristics of the transistor vary with each circuit arrangement.
- Common Base Configuration - has Voltage Gain but no Current Gain.
- Common Emitter Configuration - has both Current and Voltage Gain.
- Common Collector Configuration - has Current Gain but no Voltage Gain
COMMON-BASE CONFIGURATION
Common-base terminology is derived from the fact that the : base is common to both input and output of the configuration. Base is usually the terminal closest to or at ground potential. Majority carriers can cross the reverse-biased junction because the injected majority carriers will appear as minority carriers in the n-type material. All current directions will refer to conventional (hole) flow and the arrows in all electronic symbols have a direction defined by this convention.
Note that the applied biasing (voltage sources) are such so as to establish current in the direction indicated for each branch.

To describe the behavior of common-base amplifiers requires two sets of characteristics:
- Input or driving point characteristics.
- Output or collector characteristics
The output characteristics has 3 basic regions:
- Active region –defined by the biasing arrangements.
- Cutoff region – region where the collector current is 0A.
- Saturation region- region of the characteristics to the left of VCB = 0V.

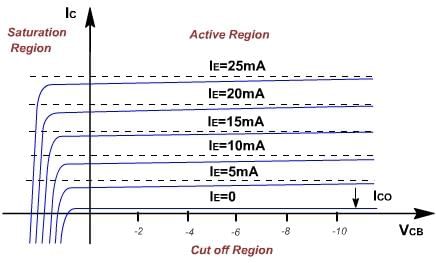

The curves (output characteristics) clearly indicate that a first approximation to the relationship between IE and IC in the active region is given by
IC ≈IE
Once a transistor is in the ‘on’ state, the base-emitter voltage will be assumed to be VBE = 0.7V

In the dc mode, the level of IC and IE due to the majority charge carriers are related by a quantity called alpha, a= αdc
IC = aIE + ICBO
It can then be summarized to IC = aIE (ignore ICBO due to small value)
For ac situations where the point of operation moves on the characteristics curve, an ac alpha defined by αac.
Alpha is a common base current gain factor that shows the efficiency by calculating the percentage of current flow from emitter to collector. The value of a is typical from 0.9 ~ 0.998.
Biasing:Proper biasing CB configuration in active region by approximation IC ≈ IE (IB ≈ 0 uA)

|
137 videos|143 docs|71 tests
|
FAQs on Bipolar Transistor Configurations - Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What are the different bipolar transistor configurations? |  |
| 2. What is the advantage of the common emitter configuration? |  |
| 3. How does the common base configuration differ from the common emitter configuration? |  |
| 4. What is the purpose of the biasing circuit in a bipolar transistor configuration? |  |
| 5. How can the common collector configuration be utilized in practical applications? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|

















