(Part - 2) - Psychological Disorders Class 12 Psychology
Somatic Symptom and Related Disorder
The term "somatic symptom and related disorders" refers to conditions in which clients experience physical symptoms and psychological distress without any clear medical explanation.
The main types of these disorders are described as follows:
- Somatic Symptom Disorder: This disorder is characterized by persistent physical symptoms that do not have a clear medical explanation.
 Individuals with this disorder are excessively worried about their health and preoccupied with their symptoms, leading them to seek medical attention frequently.
Individuals with this disorder are excessively worried about their health and preoccupied with their symptoms, leading them to seek medical attention frequently.
- Illness Anxiety Disorder: People diagnosed with Illness Anxiety Disorder are excessively concerned about the possibility of having or developing a serious medical condition or illness.
- Conversion Disorder: Individuals who have conversion disorder experience a loss or alteration in bodily function or a body part, such as blindness, deafness, or difficulty in walking, without any underlying medical cause.
Dissociative Disorders
Dissociation refers to a state of feeling detached, unreal, or disconnected from one's surroundings or sense of self.
Several types of dissociative disorders are:
- Dissociative disorders are characterized by feelings of estrangement, unreality, or depersonalization. There are several types of dissociative disorders, including Dissociative Amnesia, which involves selective memory loss of a specific incident or period of time due to high stress.

- Dissociative Identity Disorder, also known as multiple personality disorder, is rooted in traumatic childhood experiences and involves a person taking on different personalities that may or may not be aware of each other.
- Depersonalization is characterized by a dream-like state in which a person feels disconnected from themselves and reality.
- Dissociative Fugue involves the formation of a new identity as a result of unexpected travel away from home and work, with an inability to recall the previous identity.
Depressive Disorder
Depression is a commonly known mental disorder characterized by a variety of negative emotions and behavioral changes. It often occurs following a relationship breakdown or when a person fails to achieve an important goal.
Major Depressive Disorder
- Depression is a common mental disorder marked by a variety of negative emotions and behavioral changes. It is often triggered by a breakdown in a relationship or a failure to achieve an important goal.

- Symptoms of depression include disinterest and lack of enthusiasm towards most activities, disrupted sleep patterns, changes in appetite and weight, irritability, and withdrawal from social relationships.
- There are several factors that increase the risk of depression, including age, with women more likely to experience depression in young adulthood and men more likely to experience it in middle age due to midlife crisis.
- Genetics is also a significant factor that determines a person's susceptibility to depression.
- Additionally, other factors such as significant life events or a lack of desired social support can also contribute to depression.
Bipolar And Related Disorders
Bipolar and related disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by extreme mood swings. There are three main types of bipolar disorders:
- Bipolar I Disorder: This is the most severe form of bipolar disorder. It involves manic episodes that last at least 7 days or require hospitalization. Depressive episodes usually last for at least 2 weeks.
- Bipolar II Disorder: This involves less severe manic episodes, known as hypomania, that last for at least 4 days. Depressive episodes last for at least 2 weeks.
- Cyclothymic Disorder: This involves milder mood swings that last for at least 2 years. Hypomania and depressive symptoms are present, but not as severe as in bipolar I and II disorders.
Suicide Prevention Measures:
- Limiting access to the means of suicide
- Reporting of suicide by media in a responsible way
- Implementing alcohol-related policies
- Early identification, treatment, and care of people at risk
- Training health workers in assessing and managing for suicide
- Care for people who have attempted suicide and providing community support
Identifying Students in Distress:
- Any unexpected or striking change affecting the adolescent's performance, attendance, or behavior should be taken seriously, such as:
- Lack of interest in common activities
- Declining grades
- Decreasing effort
- Misbehavior in the classroom
- Mysterious or repeated absence
- Smoking or drinking, or drug misuse
Strengthening Students' Self-esteem:
- Having a positive self-esteem is important in the face of distress and helps in coping adequately. To foster positive self-esteem in children, the following approaches can be useful:
- Accentuating positive life experiences to develop a positive identity. This increases confidence in self.
- Providing opportunities for the development of physical, social, and vocational skills.
- Establishing trustful communication.
- Setting goals for the students that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and to be completed within a relevant time frame.
Schizophrenia Disorders
Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It is a chronic condition that requires lifelong treatment. 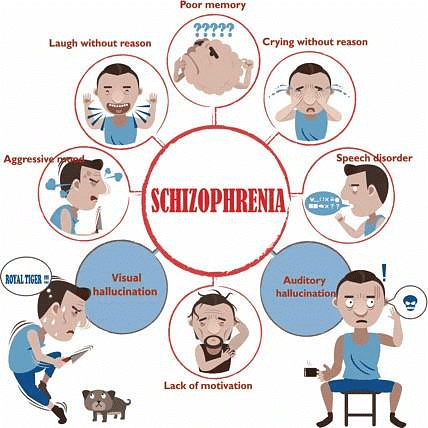
Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders: Schizophrenia refers to a cluster of psychotic conditions that lead to a decline in personal, social, and occupational functioning due to disrupted thought processes, unusual perceptions, emotional states, and motor issues. It is a severe disorder with significant social and psychological burdens on patients, their families, and society.
- Symptoms of Schizophrenia:
- Positive Symptoms: These involve excessive thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. They include delusions, disorganized thinking and speech, heightened perception and hallucinations, and inappropriate affect. Delusions in schizophrenia commonly revolve around persecution, reference, grandeur, and control.
- Formal Thought Disorders: These can lead to illogical thinking and communication difficulties, such as loosening of associations, neologisms, and perseveration.
- Hallucinations: Auditory hallucinations are prevalent, but hallucinations can also affect other senses like touch, taste, smell, and vision.
- Inappropriate Affect: People with schizophrenia may display emotions that are not suitable for a given situation.
- Negative Symptoms: These include poverty of speech, blunted affect, loss of volition, and social withdrawal.
- People with schizophrenia may struggle with logical thinking and exhibit peculiar speech patterns, making communication challenging.
- Formal thought disorders can lead to difficulties such as rapidly shifting between topics (loosening of associations, derailment), creating new words or phrases (neologisms), and repeating thoughts persistently (perseveration).
- Hallucinations are common in schizophrenia, with auditory hallucinations being predominant, where patients hear voices and sounds.
- Other types of hallucinations include tactile, somatic, visual, gustatory, and olfactory hallucinations, involving sensations and perceptions in the absence of stimuli.
- People with schizophrenia may display inappropriate affect, showing emotions that are not suitable for the situation.
- Negative symptoms in schizophrenia include poverty of speech, blunted affect, loss of volition, and social withdrawal.
- Alogia or poverty of speech is a common feature, with reduced speech content observed in many individuals.
- Patients may exhibit blunted affect, flat affect, and avolition, leading to emotional deficits and lack of motivation.
- Psychomotor symptoms in schizophrenia can manifest as reduced spontaneous movements, odd gestures, and extreme forms like catatonia.
- Catatonic stupor involves prolonged periods of silence and immobility.
- Catatonic rigidity refers to maintaining a rigid posture for extended periods.
- Catatonic posturing includes assuming awkward positions for long durations.
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of disorders that manifest early in life and are associated with developmental problems in various areas such as communication, socialization, cognition, and motor function.
 These disorders are usually identified during childhood and can persist into adulthood. Some of the major neurodevelopmental disorders are:
These disorders are usually identified during childhood and can persist into adulthood. Some of the major neurodevelopmental disorders are:
1. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): ASD is a condition characterized by impaired social interaction, communication, and restricted interests or repetitive behavior patterns. Children with ASD may have difficulty in understanding social cues, maintaining eye contact, and expressing emotions.
2. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): ADHD is a condition characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Children with ADHD may have difficulty in paying attention, following instructions, sitting still, and waiting for their turn.
3. Specific Learning Disorder: Specific learning disorder is a condition characterized by difficulty in acquiring and using academic skills like reading, writing, and arithmetic. Children with this disorder may have difficulty in understanding written and spoken language, recognizing letters and numbers, and memorizing information.
4. Intellectual Disability: Intellectual disability is a condition characterized by below-average intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior. Children with this disorder may have difficulty in learning new skills, solving problems, and adapting to new situations.
5. Disruptive, Impulse-Control and Conduct Disorders encompass various conditions, such as Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) and Conduct Disorder, among others.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD):
- Children with ODD exhibit behaviors like stubbornness, irritability, defiance, and hostility in amounts that are not appropriate for their age.
- Individuals with ODD often fail to perceive themselves as angry or defiant, rationalizing their behavior as responses to external circumstances or demands.
- This perception intertwines the disorder's symptoms with challenging social interactions.
Conduct Disorder and Antisocial Behavior:
- Conduct Disorder and antisocial behavior encompass actions and attitudes that contravene family expectations, societal norms, and the rights of others.
- Typical behaviors associated with Conduct Disorder include aggressive actions that endanger individuals or animals, destructive behavior towards property, deceptive practices, and severe breaches of rules.
- Children may exhibit various forms of aggression like verbal (e.g., name-calling, swearing), physical (e.g., hitting, fighting), hostile (e.g., intending harm), and proactive (e.g., dominating without provocation).
- Communication Disorders: Communication disorders are a group of disorders characterized by difficulty in communication. Children with these disorders may have difficulty in understanding spoken language, expressing themselves, and using appropriate social communication skills.
- Motor Disorders: Motor disorders are a group of disorders characterized by problems with movement and coordination. Children with these disorders may have difficulty in performing fine and gross motor skills, such as writing, catching a ball, or walking.
These disorders can have a significant impact on the child's academic, social, and emotional functioning, and early identification and intervention can help in improving the child's outcomes.
Feeding and Eating Disorders
Feeding and Eating Disorders are a group of mental health conditions that affect a person's eating habits, body weight, and physical health. Here are some of the major types of Feeding and Eating Disorders:
- Anorexia Nervosa: This disorder is characterised by an intense fear of gaining weight, distorted body image, and a severely restricted diet that leads to significant weight loss. People with anorexia often have a low body weight and may engage in excessive exercise or other behaviours to lose weight.
- Bulimia Nervosa: This disorder is characterised by episodes of binge eating followed by purging, such as vomiting or using laxatives. People with bulimia often have a normal body weight or may be slightly overweight, and they may be preoccupied with their body shape and weight.
- Binge-Eating Disorder: This disorder involves episodes of binge eating without purging. People with binge-eating disorder may eat large amounts of food in a short period of time and feel a loss of control during these episodes. They may be overweight or obese and may experience guilt, shame, and distress related to their eating habits.
- Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID): This disorder involves a persistent lack of interest in eating or avoidance of certain foods, which can lead to nutritional deficiencies, weight loss, and impaired growth in children. People with ARFID may have sensory sensitivity to certain foods or experience anxiety or fear related to eating.
- Pica: This disorder involves eating non-food items, such as dirt, paint, or hair. Pica is more commonly diagnosed in children and can lead to health problems such as lead poisoning or intestinal blockages.
- Rumination Disorder: This disorder involves regurgitating food after eating and then re-chewing, re-swallowing, or spitting out the food. Rumination disorder is more commonly diagnosed in infants and young children but can also affect adults.
Substance Related and Addictive Disorder
Substance Related and Addictive Disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by compulsive use of substances that lead to significant impairments in personal, social, and occupational functioning. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) lists the following substance-related and addictive disorders:
- Substance use disorders: This includes alcohol use disorder, cannabis use disorder, opioid use disorder, stimulant use disorder, and other substance use disorders.
 It is characterized by compulsive substance use, tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and impaired functioning.
It is characterized by compulsive substance use, tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and impaired functioning. - Gambling disorder: This disorder is characterized by persistent and recurrent gambling behavior that leads to significant distress or impairment.
- Other addictive disorders: This includes internet gaming disorder, which is characterized by excessive gaming behavior that leads to impairment in personal, social, and occupational functioning, and other addictive disorders that are still being researched and defined.

These disorders are serious and can have severe consequences on an individual's life. Treatment for substance-related and addictive disorders often involves a combination of medication, therapy, and support groups.
Alcohol Abuse
- People who misuse alcohol consume large quantities regularly and depend on it to cope with challenging situations. This habit eventually impairs their social interactions and cognitive abilities.
- Their bodies develop a tolerance for alcohol over time, necessitating increased consumption to achieve the desired effects. Additionally, they encounter withdrawal symptoms upon ceasing alcohol intake.
- Alcoholism has devastating effects on numerous families, relationships, and careers. It contributes significantly to road accidents caused by intoxicated drivers.
- Children of individuals battling alcohol use disorder face elevated risks of mental health issues like anxiety, depression, phobias, and substance-related disorders.
- Prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption can severely impact physical health.
Heroin:
- Heroin usage significantly impacts how a person interacts in society and at work. Many individuals who abuse heroin develop a strong reliance on it, organizing their lives around the drug, developing a tolerance, and facing withdrawal symptoms upon cessation.
- The most immediate peril associated with heroin misuse is an overdose, which hampers the brain's respiratory functions, essentially halting breathing and often resulting in fatality.
Cocaine:
- Regular consumption of cocaine can lead to a habit of constant use where the individual remains in an intoxicated state throughout the day, leading to difficulties in social interactions and work performance.
- Cocaine can also impair short-term memory and focus, with a potential for dependency to develop, causing the drug to dominate the individual's life. Increased doses are necessary to achieve the desired effects, and discontinuation can result in feelings of sadness, exhaustion, sleep disturbances, irritability, and anxiety.
- Cocaine presents serious risks, affecting both mental well-being and physical health.
|
25 videos|81 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on (Part - 2) - Psychological Disorders Class 12 Psychology
| 1. What are the most common types of psychological disorders? |  |
| 2. How are psychological disorders diagnosed? |  |
| 3. What are the possible causes of psychological disorders? |  |
| 4. How are psychological disorders treated? |  |
| 5. Can psychological disorders be prevented? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|
 Individuals with this disorder are excessively worried about their health and preoccupied with their symptoms, leading them to seek medical attention frequently.
Individuals with this disorder are excessively worried about their health and preoccupied with their symptoms, leading them to seek medical attention frequently.
 It is characterized by compulsive substance use, tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and impaired functioning.
It is characterized by compulsive substance use, tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and impaired functioning.


















