Test: Product Of Inertia For An Area - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Product Of Inertia For An Area
The product of Inertia for an area is required so as to _____________
Determine the product of inertia for the triangle in the given figure.
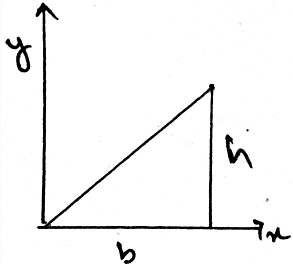
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Moment of Inertia is the integration of the square of the distance of the centroid and the del area along the whole area of the structure and after these calculations we multiply the moment of areas.
There is perpendicular axis theorem for the area, and it is can be used to determine the product of moment of inertia.
What is parallel axis theorem and to whom it is applied so that it can give the product of inertia of an area?
The product of moment of inertia is the sum of _____________ and _________________
The distance in the parallel axis theorem for the use in the determination of the product of moment of inertia is multiplied by:
One of the use of the centre of mass or centroid is as in the determination of the product of moment of inertia is that the net force acts at the ___________ of the loading body.
The product of Inertia for an area is helpful so as to _____________
Determine the del product of inertia for the triangle in the given figure used for the calculations.
If the non-Uniform loading is of the type of parabola then for calculating the product of moment of inertia for areas?
If any external force also is applied on the structure and we are determining the product of moment of inertia then what should we consider?
The body is sometimes acted by two or three force members and we need to find the product of moment of inertia for the same. The difference between the two and the three force members is:
Whenever the distributed loading acts perpendicular to an area its intensity varies __________ for the determination of the product of moment of inertia.
The calculation of the product of moment of the body due to the loadings involve a quantity called ____________
Whenever the distributed loading acts perpendicular to an area its intensity varies __________ for the determination of the product of moment of inertia.

















