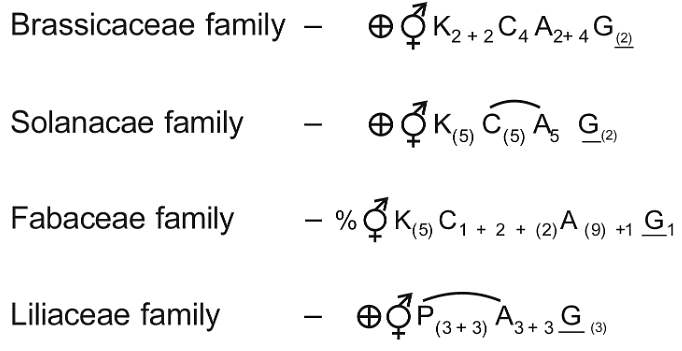31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Morphology of Flowering - 1 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Morphology of Flowering - 1
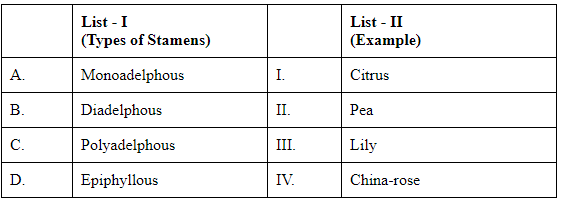
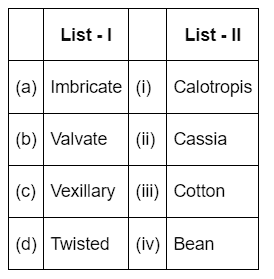
Q3: Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)

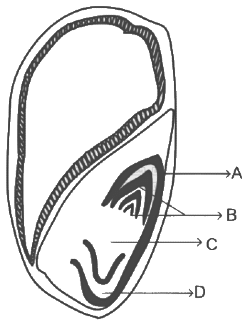
Identify the part of the seed from the given figure which is destined to form root when the seed germinates. (NEET 2024)

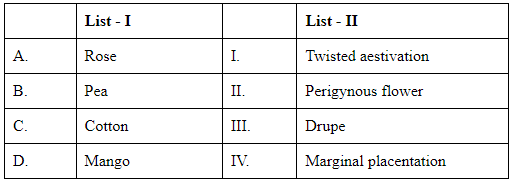
Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)

Which of the following is an example of actinomorphic flower? (NEET 2024)
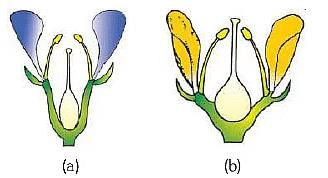
Identify the type of flowers based on the position of calyx, corolla, and androecium with respect to the ovary from the given figures (a) and (b) ( NEET 2024)
Family Fabaceae differs from Solanaceae and Liliaceae with respect to the stamens. Pick out the characteristics specific to family Fabaceae but not found in Solanaceae or Liliaceae. (NEET 2023)
Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion A and the other as Reason R:
Assertion A: A flower is defined as a modified shoot wherein the shoot apical meristem changes to floral meristem.
Reason R: Internode of the shoot gets condensed to produce different floral appendages laterally at successive nodes instead of leaves.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below: (NEET 2023)
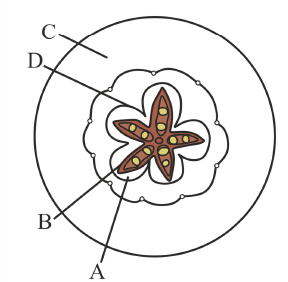
Which part of the fruit, labelled in the given figure make it a false fruit: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Q7: The flowers are Zygomorphic in: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(A) Mustard
(B) Gulmohar
(C) Cassia
(D) Datura
(E) Chilly
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Q5: Which one of the following plants shows vexillary aestivation and diadelphous stamens? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
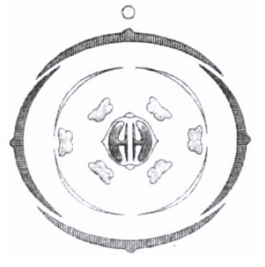
Q4:The Floral Diagram represents which one of the following families? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Match List - I with List - II: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Match Column-I with Column-II (NEET 2021)
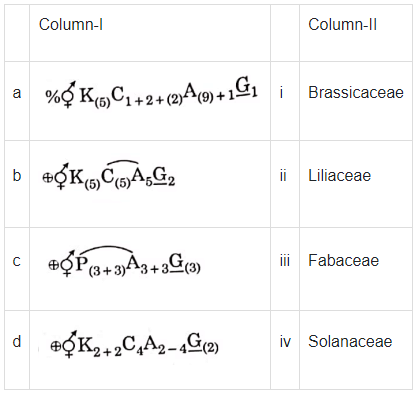
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Diadelphous is found in [2021]
Ray florets have (NEET 2020)
Placentation in which ovules develop on the inner wall of the ovary or in peripheral part, is [2019]
Coconut fruit is a [2017]
The standard petal of a papilionaceous corolla is also called [2016]
Tricarpellary syncarpous gynoecium is found in flowers of [2016]
Proximal end of the filament of stamen is attached to the [2016]
Cotyledon of maize grain is called [2016]
Perigynous flowers are found in :- [2015 RS]
Among china rose, mustard, brinjal, potato, guava, cucumber, onion and tulip, how many plants have superior ovary? [2015 RS]
Axile placentation is present in [2015 RS]
What type of placentation is seen in sweet pea? [2006]