Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Thermodynamics - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Thermodynamics
If an endothermic reaction is non-spontaneous at freezing point of water and becomes feasible at its boiling point, then
A heat engine abosrbs heat Q1 at temperature T1 and heat Q2 at temperature T2. Work done by the engine is J (Q1 + Q2). This data [2002]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For the reactions, [2002] 2C + O2 → 2CO2 ; ΔH = -393 J
2Zn + O2 → 2ZnO ; ΔH = -412 J
2Zn + O2 → 2ZnO ; ΔH = -412 J
The heat required to raise the temperature of body by 1 K is called [2002]
The internal energy change when a system goes from state A to B is 40 kJ/mole. If the system goes from A to B by a reversible path and returns to state A by an irreversible path what would be the net change in internal energy ? [2003]
If at 298 K the bond energies of C — H, C — C, C = C and H — H bonds are respectively 414, 347, 615 and 435 kJ mol–1, the value of enthalpy change for the reaction H2C = CH2(g) + H2(g) → H3C — CH3(g) at 298 K will be [2003]
In an irreversible process taking place at constant T and P and in which only pressure-volume work is being done, the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) and change in entropy (dS), satisfy the criteria [2003]
The correct relationship between free energy change in a reaction and the corresponding equilibrium constant Kc is [2003]
The enthalpy change for a reaction does not depend upon [2003]
An ideal gas expands in volume from 1×10–3 to 1 × 10–2 m3 at 300 K against a constant pressure of 1×105 Nm–2. The work done is [2004]
The enthalpies of combustion of carbon and carbon monoxide are – 393.5 and – 283 kJ mol–1 respectively. The enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide per mole is
Consider an endothermic reaction X → Y with the activation en er gies Eb and Ef for the backward and forward reactions, respectively. In general [2005]
Consider the reaction : N2 + 3H2 → 2 NH3 carried out at constant temperature and pressure. If ΔH and ΔU are the enthalpy and internal energy changes for the reaction, which of the following expressions is true ? [2005]
If the bond dissociation energies of XY, X 2 and Y2 (all diatomic molecules) are in the ratio of 1 : 1 : 0.5 and ΔHf for the for mation of XY is – 200 kJ mole -1 . The bond dissociation energy of X2 will be [2005]
An ideal gas is allowed to expand both reversibly and irreversibly in an isolated system. If Ti is the initial temperature and Tf is the final temperature, which of the following statements is correct? [2006]
The standard enthalpy of formation (DfHº) at 298 K for methane, CH4(g) is –74.8 kJ mol–1. The additional information required to determine the average energy for C – H bond formation would be [2006]
The enthalpy changes for the following processes are listed below : [2006]
Cl2(g) → 2Cl(g), 242.3 kJ mol–1
I2(g) → 2I(g), 151.0 kJ mol–1
ICl(g) → I(g) + Cl(g), 211.3 kJ mol–1I2(s) → I2(g), 62.76 kJ mol–1
Given that the standard states for iodine and chlorine are I2(s) and Cl2(g), the standard enthalpy of formation for ICl(g) is : [2006]
(ΔH – ΔU) for the formation of carbon monoxide (CO) from its elements at 298 K is [2006] (R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1)
In conversion of lime-stone to lime, CaCO3 (s) → CaO(s)+ CO2(g) the values of ΔH° and ΔS° are + 179.1 kJ mol-1 and 160.2 J/K respectively at 298 K and 1 bar. Assuming that ΔH° and ΔS° do not change with temperature, temperature above which conversion of limestone to lime will be spontaneous is [2007]
Assuming that water vapour is an ideal gas, the internal energy change (ΔU) when 1 mol of water is vapourised at 1 bar pressure and 100°C, (given : molar enthalpy of vapourisation of water at 1 bar and 373 K = 41 kJ mol–1 and R = 8.3 J mol–1 K–1) will be [2007]
Identify the correct statement regarding a spontaneous process: [2007]
Oxidising power of chlorine in aqueous solution can be determined by the parameters indicated below:


(using the data,


 will be [2008]
will be [2008]
Standard entropy of X2, Y2 and X Y3 are 60, 40 and 50 J K–1 mol–1, respectively. For the reaction,
 , to be at equilibrium, the temperature will be [2008]
, to be at equilibrium, the temperature will be [2008]
On the basis of the following thermochemical data :
(Δ f G°H+ (aq)= 0) [2009]
 = 57.32kJ
= 57.32kJ
 = –286.20kJ
= –286.20kJ
The value of enthalpy of formation of OH– ion at 25° C is:
The standard enthalpy of for mation of NH3 is – 46.0 kJ mol–1. If the enthalpy of formation of H2 from its atoms is – 436 kJ mol–1 and that of N2 is – 712 kJ mol–1, the average bond enthalpy of N – H bond in NH3 is [2010]
For a particular reversible reaction at temperature T, ΔH and ΔS were found to be both +ve. If Te is the temperature at equilibrium, the reaction would be spontaneous when [2010]
The entropy change involved in the isothermal reversible expansion of 2 mole of an ideal gas from a volume of 10 dm3 to a volume of 100 dm3 at 27°C is: [2011]
The incorrect expression among the following is : [2012]
A piston filled with 0.04 mol of an ideal gas expands reversibly from 50.0 mL to 375 mL at a constant temperature of 37.0ºC. As it does so, it absorbs 208 J of heat. The values of q and w for the process will be: [JEE M 2013]
(R = 8.314 J/mol K) (ln 7.5 = 2.01)
For complete combustion of ethanol, C2H5OH (l) + 3O2(g)—→ 2CO2 ( g)+ 3H2O (l), the amount of heat produced as measured in bomb calorimeter, is 1364.47 kJ mol–1 at 25ºC. Assuming ideality the enthalpy of combustion, ΔcH, for the reaction will be: (R = 8.314 kJ mol–1) [JEE M 2014]





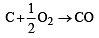 ΔH = -110.5 kJmol–1
ΔH = -110.5 kJmol–1 for an endothermic reaction ΔH = +ve hence for ΔH to be negative
for an endothermic reaction ΔH = +ve hence for ΔH to be negative
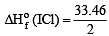 = 16.73 kJ / mol
= 16.73 kJ / mol


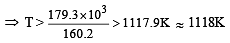

 is given by
is given by
 (–349) (–381) kJmol–1
(–349) (–381) kJmol–1 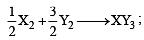 ΔH= –30kJ (given)
ΔH= –30kJ (given)
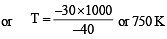
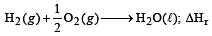 = –286.20 kJ
= –286.20 kJ
 -
- 
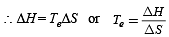

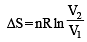 = 2 × 8.314 × 2.303 log
= 2 × 8.314 × 2.303 log 

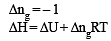
 = – 1366.93 kJ mol–1
= – 1366.93 kJ mol–1














